C++初阶——string的使用(下)
一、string类对象的容量操作
对于string的容量操作,我们可以通过顺序表来理解,顺序表是通过动态数组来实现的,在数据结构专栏的第一篇就是顺序表的详细讲解,链接如下:link
我们先来看一下顺序表的结构体:

这里是一个整型数组,通过类型重命名typedef可以将其调整为字符型数组,对字符串进行操作。当然,之前的顺序表是基于C语言实现的,我们这里的string就会使用类(class)来进行模拟实现,下期内容会进行详细讲解。
我们看这里的成员,有一个size,表示目前数组里有几个有效数据;capacity,表示数组目前的容量多大,当size和capacity相等时,就需要使用动态内存开辟进行扩容。
在string类中也是如此:
size:返回字符串有效字符长度capacity返回空间总大小length:返回字符串有效字符长度empty:检测字符串释放为空串,是返回true,否则返回falseclear:清空有效字符reserve:为字符串预留空间resize:将有效字符的个数该成n个,多出的空间用字符c填充
我们来看这样一段代码:

这里不仅对几种容量相关的函数进行了测试,还进一步的探究了扩容的机制,结果如下:

不同环境下扩容的机制不同,这里是VS2022的扩容机制。
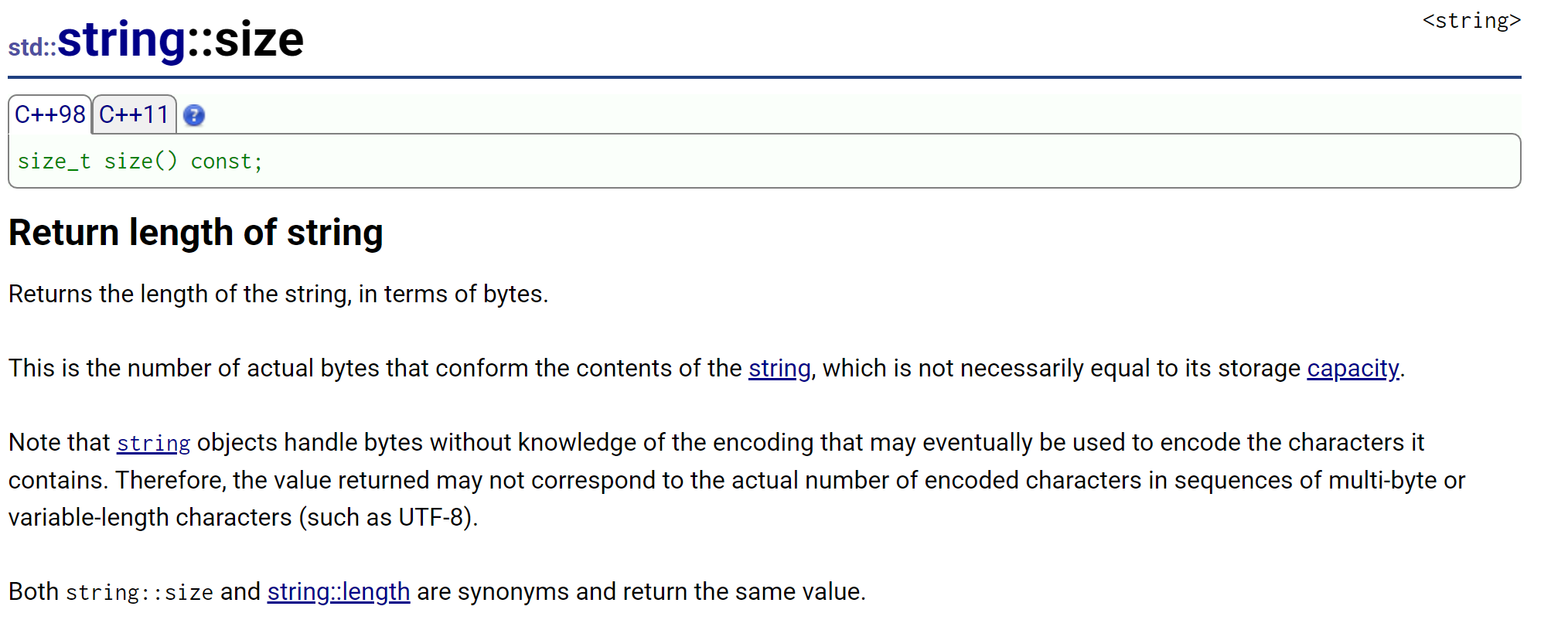
1.size
2.capacity

3.length

size()与length()方法底层实现原理完全相同,引入size()的原因是为了与其他容器的接口保持一致,一般情况下基本都是用size()。
4.max_size

(这个函数没有什么特别大的作用)
5.clear

需要注意的是,clear只是清除了有效数据,并没有把容量(capacity)清零。
6.reserve

使用说明:

reserve(size_t res_arg=0);:为string预留空间,不改变有效元素个数,当reserve的参数小于string的底层空间(就是在实例化的过程中就有的内置空间)总大小时,reserve不会改变容量大小。- 运行结果如图:

7.resize
我们还是以代码为例:

运行结果如图:

resize(size_t n)与resize(size_t n, char c)都是将字符串中有效字符个数改变到n个,不同的是当字符个数增多时:resize(n)用0来填充多出的元素空间,resize(size_t n, char c)用字符c来填充多出的元素空间。注意:resize在改变元素个数时,如果是将元素个数增多,可能会改变底层容量的大小,如果是将元素个数减少,底层空间总大小不变,我们来看一下使用说明:

8.empty
empty比较简单,需要注意的是这里判断依据不是容量 (capacity),而是有效数据的长度(size、length)是否为零,使用说明如下:

二、string的其他常用操作
1.replace

replace顾名思义就是一个替换函数,可以根据自己的需要替换字符串中某些位置的值,其重载的函数多种多样,功能很丰富,使用介绍如图所示:

运行结果如图:

2.find函数

find也是一个非常重要的成员函数,用来寻找所需的字符或者字符串,当然也需要提供查找的范围,如果不提供,默认从第一个位置开始寻找,使用介绍如下:

至于其它的一些find相关的函数,我们也稍作介绍:
find_first_of

find_last_of

refind

三、本期代码资源
//int main()
//{
// string s1("hello world");
//
// cout << s1.size() << endl;
// cout << s1.length() << endl;
// cout << s1.max_size() << endl;
// cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
//
// size_t old = s1.capacity();
// for (size_t i = 0; i < 100; i++)
// {
// s1 += 'x';
// if (old != s1.capacity())
// {
// cout << "扩容:" << s1.capacity() << endl;
// old = s1.capacity();
// }
// }
//
// cout << s1.size() << endl;
// cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
//
// s1.clear();
// cout << s1.size() << endl;
// cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
//
// return 0;
//}
//void TestPushBackReserve()
//{
// string s;
// s.reserve(100);
// size_t sz = s.capacity();
// cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';
// cout << "making s grow:\n";
// for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
// {
// s.push_back('c');
// if (sz != s.capacity())
// {
// sz = s.capacity();
// cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';
// }
// }
// s.clear();
// cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';
// s.reserve(10);
// sz = s.capacity();
// cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';
//}
//
//int main()
//{
// TestPushBackReserve();
// return 0;
//}
//int main()
//{
// string s1("hello world");
//
// //开空间
// s1.reserve(100);
// cout << s1.size() << endl;
// cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
//
// //开空间+填值初始化
// //s1.resize(200);
// s1.resize(200, 'x');
// cout << s1.size() << endl;
// cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
//
// s1.resize(20);
// cout << s1.size() << endl;
// cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
//
// s1.resize(0);
// cout << s1.size() << endl;
// cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
//
// return 0;
//}
//int main()
//{
// try {
// string s1("hello world");
// s1.at(0) = 'x';
// cout << s1 << endl;
// s1.at(15);
// }
// catch (const exception& e)
// {
// cout << e.what() << endl;
// }
//
// return 0;
//}
//int main()
//{
// char str[] = "abcdefg";
// string s1("hello world");
// s1.push_back('!');
// cout << s1 << endl;
// s1.append(str,3);
// cout << s1 << endl;
//
// s1.append("ssssss");
// cout << s1 << endl;
//
// s1.assign("111111111");
// cout << s1 << endl;
//
// s1.insert(0, "hello");
// cout << s1 << endl;
//
// s1.insert(5, "world");
// cout << s1 << endl;
//
// s1.insert(0, 10, 'x');
// cout << s1 << endl;
//
// s1.insert(s1.begin()+10, 10, 'y');
// cout << s1 << endl;
//
// s1.erase(5, 6);
// cout << s1 << endl;
//
// return 0;
//}
//int main()
//{
// //world替换成 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
// string s1("hello world hello bit");
// s1.replace(6, 5, "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx");
// cout << s1 << endl;
//
// s1.replace(6, 23, "yyyyy");
// cout << s1 << endl;
//
// //所有空格替换成20%
// string s2("hello world hello bit");
// string s3;
// for (auto ch : s2)
// {
// if (ch != ' ')
// {
// s3 += ch;
// }
// else
// {
// s3 += "20%";
// }
// }
//
// s2 = s3;
// cout << s2 << endl;
// cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
//
// //c的一些接口函数配合
// string filename = "test.cpp";
// filename += ".zip";
//
// //FILE* fout = fopen(filename.c_str(), "r");
//
// return 0;
//}
//int main()
//{
// string url = "ftp://www.baidu.com/?tn=65081411_1_oem_dg";
// // http://www.baidu.com/?tn=65081411_1_oem_dg
// //string url = "https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/";
// // 协议 域名 资源名
// size_t pos1 = url.find("://");
// string protocol;
// if (pos1 != string::npos)
// {
// protocol = url.substr(0, pos1);
// }
// cout << protocol << endl;
//
// string domain;
// string uri;
//
// size_t pos2 = url.find('/', pos1 + 3);
// if (pos2 != string::npos)
// {
// domain = url.substr(pos1 + 3, pos2 - (pos1 + 3));
// uri = url.substr(pos2 + 1);
// }
// cout << domain << endl;
// cout << uri << endl;
//
// return 0;
//}
//int main()
//{
// std::string str("Please, replace the vowels in this sentence by asterisks.");
// std::size_t found = str.find_first_of("abc");
// while (found != std::string::npos)
// {
// str[found] = '*';
// found = str.find_first_of("abc", found + 1);
// }
//
// std::cout << str << '\n';
//
// return 0;
//}
本期总结+下期预告
本期内容继续介绍了string类的使用,下期内容将要开始进行string的模拟实现!
感谢大家的关注,我们下期再见!

























 237
237

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








