💥💥💞💞欢迎来到Matlab仿真科研站博客之家💞💞💥💥
✅博主简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,Matlab项目合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:Matlab仿真科研站博客之家
🏆代码获取方式:
💥扫描文章底部QQ二维码💥
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十;路漫漫其修远兮,吾将上下而求索。

⛄更多Matlab图像处理(仿真科研站版)仿真内容点击👇
Matlab图像处理(仿真科研站版)
⛄一、光流场模型简介
目前对大脑的研究主要借助于 CT、MRI和 PET等医学成像技术通过成像技术得到的图像可以 提供人脑直观的信息为人脑解剖结构的分析、功能 区域的定义、脑疾病的诊断提供有力依据。因此大脑图像的分析和处理具有重要的实用价值和现实 意义。由于配准所求解的位移场与光流场模型所求解的 速度场具有相似性PalosPierre等人将光流场模型引入到了图像配准中。本文在经典光流场算法的基础上将其应用于非刚性医学图像的配准中得到了相对精确的配准结果。
1 光流场模型算法
如果把浮动图像和参考图像分别看作时间间隔为 Δt的视频流中的t时刻与+Δt时刻的图像那么图像的配准可以认为是从浮动图像流动到参考图像的过程即光流场求解的速度场即为配准所要求解的位移 场‚因此可以借助光流场进行图像配准。
1.1 Horn光流场理论

不能同时求出光流的两个速度分量u和vi因此在具 体求解位移场时‚需要在流动场上附加光滑度约束才能得到光流场的合理估计。
1.2 Lucas-Kanade光流算法

2 基于光流场模型的图像非刚体配准
2.1 配准原理和步骤
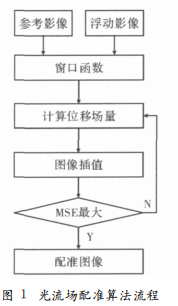
采用光流场模型进行图像配准是一个将浮动图像逐步向参考图像变动来求解对应光流模型速度场然后对浮动图像插值获得配准图像的过程具体步骤如下。

续迭代;否则‚继续下一步。 (5)测度函数已收敛终止迭代I3 就是最终的配准图像。
2.2 配准流程图
⛄二、部分源代码
function varargout = optical_flow(varargin)
% OPTICAL_FLOW M-file for optical_flow.fig
% OPTICAL_FLOW, by itself, creates a new OPTICAL_FLOW or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = OPTICAL_FLOW returns the handle to a new OPTICAL_FLOW or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% OPTICAL_FLOW(‘CALLBACK’,hObject,eventData,handles,…) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in OPTICAL_FLOW.M with the given input arguments.
%
% OPTICAL_FLOW(‘Property’,‘Value’,…) creates a new OPTICAL_FLOW or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before optical_flow_OpeningFunction gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to optical_flow_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE’s Tools menu. Choose “GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)”.
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Copyright 2002-2003 The MathWorks, Inc.
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help optical_flow
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 23-Jul-2012 15:10:21
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct(‘gui_Name’, mfilename, …
‘gui_Singleton’, gui_Singleton, …
‘gui_OpeningFcn’, @optical_flow_OpeningFcn, …
‘gui_OutputFcn’, @optical_flow_OutputFcn, …
‘gui_LayoutFcn’, [] , …
‘gui_Callback’, []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% — Executes just before optical_flow is made visible.
function optical_flow_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to optical_flow (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for optical_flow
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes optical_flow wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% — Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = optical_flow_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% — Executes on button press in pushbutton_start.
function pushbutton_start_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton_start (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
global FilePath1
global FilePath2
global version
if ( isequal(FilePath1,‘No Picture’) || isequal(FilePath2,‘No Picture’) )
errordlg(‘选择图片出错!’,‘MATLAB error’);
return
end
switch version
case { 0, 1, 2 }
optic_flow_brox(FilePath1, FilePath2);
case 3
Horn_WJY(FilePath2, FilePath1);
case 4
Lucas_Kanade(FilePath2, FilePath1);
otherwise
errordlg(‘选择算法出错!’,‘MATLAB error’);
end
% — Executes on button press in pushbutton_pic1.
function pushbutton_pic1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton_pic1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
global FilePath1
[FileName,PathName] = uigetfile({‘.jpg’;'.bmp’},‘Select the picture’);
if ~isequal(FileName,0)
FilePath1 = fullfile(PathName,FileName);
set(handles.edit_lj1,‘String’,FilePath1);
img=imread(FilePath1);
axes(handles.axes_pic1);
imshow(img);
end
guidata(hObject, handles);
% — Executes on button press in pushbutton_pic2.
function pushbutton_pic2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton_pic2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
global FilePath2
[FileName,PathName] = uigetfile({‘.jpg’;'.bmp’},‘Select the picture’);
if ~isequal(FileName,0)
FilePath2 = fullfile(PathName,FileName);
set(handles.edit_lj2,‘String’,FilePath2);
img=imread(FilePath2);
axes(handles.axes_pic2);
imshow(img);
end
guidata(hObject, handles);
function edit_lj1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit_lj1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit_lj1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit_lj1 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit_lj1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit_lj1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
else
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’));
end
function edit_lj2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit_lj2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit_lj2 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit_lj2 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit_lj2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit_lj2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
else
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’));
end
function edit_arithmetic_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit_arithmetic (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit_arithmetic as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit_arithmetic as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit_arithmetic_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit_arithmetic (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
else
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’));
end
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function uipanel_choice_SelectionChangeFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to uipanel_choice (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
global version
if get(handles.radiobutton_horn,‘Value’)
s=1;
end
if get(handles.radiobutton_lk,‘Value’)
s=2;
end
if get(handles.radiobutton_brox,‘Value’)
s=3;
end
if get(handles.radiobutton_bs,‘Value’)
s=4;
end
if get(handles.radiobutton_bss,‘Value’)
s=5;
end
switch s
case 1
version = 3;
set(handles.edit_arithmetic,‘String’,‘Horn-Schunck’);
case 2
version = 4;
set(handles.edit_arithmetic,‘String’,‘Lucas-Kanade’);
case 3
version = 0;
set(handles.edit_arithmetic,‘String’,‘Brox’);
case 4
version = 1;
set(handles.edit_arithmetic,‘String’,‘Brox 改进版本’);
case 5
version = 2;
set(handles.edit_arithmetic,‘String’,‘Brox 改进版本 + Sift’);
end
guidata(hObject, handles);
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function pushbutton_start_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton_start (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function figure1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to figure1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
addpath(‘./Brox’);
addpath(‘./Horn_Schunck’);
addpath(‘./Lucas_Kanade’);
global version
global FilePath1
global FilePath2
version = 3;
FilePath1 = ‘No Picture’;
FilePath2 = ‘No Picture’;
⛄三、运行结果



⛄四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1]侯思祖,陈宇,刘雅婷.基于互信息的紫外成像仪中图像配准研究[J].半导体光电. 2020,41(04)
3 备注
简介此部分摘自互联网,仅供参考,若侵权,联系删除
🍅 仿真咨询
1 各类智能优化算法改进及应用
1.1 PID优化
1.2 VMD优化
1.3 配电网重构
1.4 三维装箱
1.5 微电网优化
1.6 优化布局
1.7 优化参数
1.8 优化成本
1.9 优化充电
1.10 优化调度
1.11 优化电价
1.12 优化发车
1.13 优化分配
1.14 优化覆盖
1.15 优化控制
1.16 优化库存
1.17 优化路由
1.18 优化设计
1.19 优化位置
1.20 优化吸波
1.21 优化选址
1.22 优化运行
1.23 优化指派
1.24 优化组合
1.25 车间调度
1.26 生产调度
1.27 经济调度
1.28 装配线调度
1.29 水库调度
1.30 货位优化
1.31 公交排班优化
1.32 集装箱船配载优化
1.33 水泵组合优化
1.34 医疗资源分配优化
1.35 可视域基站和无人机选址优化
2 机器学习和深度学习分类与预测
2.1 机器学习和深度学习分类
2.1.1 BiLSTM双向长短时记忆神经网络分类
2.1.2 BP神经网络分类
2.1.3 CNN卷积神经网络分类
2.1.4 DBN深度置信网络分类
2.1.5 DELM深度学习极限学习机分类
2.1.6 ELMAN递归神经网络分类
2.1.7 ELM极限学习机分类
2.1.8 GRNN广义回归神经网络分类
2.1.9 GRU门控循环单元分类
2.1.10 KELM混合核极限学习机分类
2.1.11 KNN分类
2.1.12 LSSVM最小二乘法支持向量机分类
2.1.13 LSTM长短时记忆网络分类
2.1.14 MLP全连接神经网络分类
2.1.15 PNN概率神经网络分类
2.1.16 RELM鲁棒极限学习机分类
2.1.17 RF随机森林分类
2.1.18 SCN随机配置网络模型分类
2.1.19 SVM支持向量机分类
2.1.20 XGBOOST分类
2.2 机器学习和深度学习预测
2.2.1 ANFIS自适应模糊神经网络预测
2.2.2 ANN人工神经网络预测
2.2.3 ARMA自回归滑动平均模型预测
2.2.4 BF粒子滤波预测
2.2.5 BiLSTM双向长短时记忆神经网络预测
2.2.6 BLS宽度学习神经网络预测
2.2.7 BP神经网络预测
2.2.8 CNN卷积神经网络预测
2.2.9 DBN深度置信网络预测
2.2.10 DELM深度学习极限学习机预测
2.2.11 DKELM回归预测
2.2.12 ELMAN递归神经网络预测
2.2.13 ELM极限学习机预测
2.2.14 ESN回声状态网络预测
2.2.15 FNN前馈神经网络预测
2.2.16 GMDN预测
2.2.17 GMM高斯混合模型预测
2.2.18 GRNN广义回归神经网络预测
2.2.19 GRU门控循环单元预测
2.2.20 KELM混合核极限学习机预测
2.2.21 LMS最小均方算法预测
2.2.22 LSSVM最小二乘法支持向量机预测
2.2.23 LSTM长短时记忆网络预测
2.2.24 RBF径向基函数神经网络预测
2.2.25 RELM鲁棒极限学习机预测
2.2.26 RF随机森林预测
2.2.27 RNN循环神经网络预测
2.2.28 RVM相关向量机预测
2.2.29 SVM支持向量机预测
2.2.30 TCN时间卷积神经网络预测
2.2.31 XGBoost回归预测
2.2.32 模糊预测
2.2.33 奇异谱分析方法SSA时间序列预测
2.3 机器学习和深度学习实际应用预测
CPI指数预测、PM2.5浓度预测、SOC预测、财务预警预测、产量预测、车位预测、虫情预测、带钢厚度预测、电池健康状态预测、电力负荷预测、房价预测、腐蚀率预测、故障诊断预测、光伏功率预测、轨迹预测、航空发动机寿命预测、汇率预测、混凝土强度预测、加热炉炉温预测、价格预测、交通流预测、居民消费指数预测、空气质量预测、粮食温度预测、气温预测、清水值预测、失业率预测、用电量预测、运输量预测、制造业采购经理指数预测
3 图像处理方面
3.1 图像边缘检测
3.2 图像处理
3.3 图像分割
3.4 图像分类
3.5 图像跟踪
3.6 图像加密解密
3.7 图像检索
3.8 图像配准
3.9 图像拼接
3.10 图像评价
3.11 图像去噪
3.12 图像融合
3.13 图像识别
3.13.1 表盘识别
3.13.2 车道线识别
3.13.3 车辆计数
3.13.4 车辆识别
3.13.5 车牌识别
3.13.6 车位识别
3.13.7 尺寸检测
3.13.8 答题卡识别
3.13.9 电器识别
3.13.10 跌倒检测
3.13.11 动物识别
3.13.12 二维码识别
3.13.13 发票识别
3.13.14 服装识别
3.13.15 汉字识别
3.13.16 红绿灯识别
3.13.17 虹膜识别
3.13.18 火灾检测
3.13.19 疾病分类
3.13.20 交通标志识别
3.13.21 卡号识别
3.13.22 口罩识别
3.13.23 裂缝识别
3.13.24 目标跟踪
3.13.25 疲劳检测
3.13.26 旗帜识别
3.13.27 青草识别
3.13.28 人脸识别
3.13.29 人民币识别
3.13.30 身份证识别
3.13.31 手势识别
3.13.32 数字字母识别
3.13.33 手掌识别
3.13.34 树叶识别
3.13.35 水果识别
3.13.36 条形码识别
3.13.37 温度检测
3.13.38 瑕疵检测
3.13.39 芯片检测
3.13.40 行为识别
3.13.41 验证码识别
3.13.42 药材识别
3.13.43 硬币识别
3.13.44 邮政编码识别
3.13.45 纸牌识别
3.13.46 指纹识别
3.14 图像修复
3.15 图像压缩
3.16 图像隐写
3.17 图像增强
3.18 图像重建
4 路径规划方面
4.1 旅行商问题(TSP)
4.1.1 单旅行商问题(TSP)
4.1.2 多旅行商问题(MTSP)
4.2 车辆路径问题(VRP)
4.2.1 车辆路径问题(VRP)
4.2.2 带容量的车辆路径问题(CVRP)
4.2.3 带容量+时间窗+距离车辆路径问题(DCTWVRP)
4.2.4 带容量+距离车辆路径问题(DCVRP)
4.2.5 带距离的车辆路径问题(DVRP)
4.2.6 带充电站+时间窗车辆路径问题(ETWVRP)
4.2.3 带多种容量的车辆路径问题(MCVRP)
4.2.4 带距离的多车辆路径问题(MDVRP)
4.2.5 同时取送货的车辆路径问题(SDVRP)
4.2.6 带时间窗+容量的车辆路径问题(TWCVRP)
4.2.6 带时间窗的车辆路径问题(TWVRP)
4.3 多式联运运输问题
4.4 机器人路径规划
4.4.1 避障路径规划
4.4.2 迷宫路径规划
4.4.3 栅格地图路径规划
4.5 配送路径规划
4.5.1 冷链配送路径规划
4.5.2 外卖配送路径规划
4.5.3 口罩配送路径规划
4.5.4 药品配送路径规划
4.5.5 含充电站配送路径规划
4.5.6 连锁超市配送路径规划
4.5.7 车辆协同无人机配送路径规划
4.6 无人机路径规划
4.6.1 飞行器仿真
4.6.2 无人机飞行作业
4.6.3 无人机轨迹跟踪
4.6.4 无人机集群仿真
4.6.5 无人机三维路径规划
4.6.6 无人机编队
4.6.7 无人机协同任务
4.6.8 无人机任务分配
5 语音处理
5.1 语音情感识别
5.2 声源定位
5.3 特征提取
5.4 语音编码
5.5 语音处理
5.6 语音分离
5.7 语音分析
5.8 语音合成
5.9 语音加密
5.10 语音去噪
5.11 语音识别
5.12 语音压缩
5.13 语音隐藏
6 元胞自动机方面
6.1 元胞自动机病毒仿真
6.2 元胞自动机城市规划
6.3 元胞自动机交通流
6.4 元胞自动机气体
6.5 元胞自动机人员疏散
6.6 元胞自动机森林火灾
6.7 元胞自动机生命游戏
7 信号处理方面
7.1 故障信号诊断分析
7.1.1 齿轮损伤识别
7.1.2 异步电机转子断条故障诊断
7.1.3 滚动体内外圈故障诊断分析
7.1.4 电机故障诊断分析
7.1.5 轴承故障诊断分析
7.1.6 齿轮箱故障诊断分析
7.1.7 三相逆变器故障诊断分析
7.1.8 柴油机故障诊断
7.2 雷达通信
7.2.1 FMCW仿真
7.2.2 GPS抗干扰
7.2.3 雷达LFM
7.2.4 雷达MIMO
7.2.5 雷达测角
7.2.6 雷达成像
7.2.7 雷达定位
7.2.8 雷达回波
7.2.9 雷达检测
7.2.10 雷达数字信号处理
7.2.11 雷达通信
7.2.12 雷达相控阵
7.2.13 雷达信号分析
7.2.14 雷达预警
7.2.15 雷达脉冲压缩
7.2.16 天线方向图
7.2.17 雷达杂波仿真
7.3 生物电信号
7.3.1 肌电信号EMG
7.3.2 脑电信号EEG
7.3.3 心电信号ECG
7.3.4 心脏仿真
7.4 通信系统
7.4.1 DOA估计
7.4.2 LEACH协议
7.4.3 编码译码
7.4.4 变分模态分解
7.4.5 超宽带仿真
7.4.6 多径衰落仿真
7.4.7 蜂窝网络
7.4.8 管道泄漏
7.4.9 经验模态分解
7.4.10 滤波器设计
7.4.11 模拟信号传输
7.4.12 模拟信号调制
7.4.13 数字基带信号
7.4.14 数字信道
7.4.15 数字信号处理
7.4.16 数字信号传输
7.4.17 数字信号去噪
7.4.18 水声通信
7.4.19 通信仿真
7.4.20 无线传输
7.4.21 误码率仿真
7.4.22 现代通信
7.4.23 信道估计
7.4.24 信号检测
7.4.25 信号融合
7.4.26 信号识别
7.4.27 压缩感知
7.4.28 噪声仿真
7.4.29 噪声干扰
7.5 无人机通信
7.6 无线传感器定位及布局方面
7.6.1 WSN定位
7.6.2 高度预估
7.6.3 滤波跟踪
7.6.4 目标定位
7.6.4.1 Dv-Hop定位
7.6.4.2 RSSI定位
7.6.4.3 智能算法优化定位
7.6.5 组合导航
8 电力系统方面
微电网优化、无功优化、配电网重构、储能配置
9 元胞自动机方面
交通流 人群疏散 病毒扩散 晶体生长
10 雷达方面
卡尔曼滤波跟踪、航迹关联、航迹融合






















 2003
2003











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








