示例:计算[1,]范围内自然数的平方根之和
CPU: i7-7820HQ,8核
1.使用std::package_task和std::future
#include <thread>
#include <future>
#include <numeric>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <chrono>
double accumulate(int min, int max)
{
double sum = 0;
for (int i = min; i <= max; ++i)
{
sum += sqrt(i);
}
return sum;
}
double concurrent_task(int min, int max)
{
//每个线程的执行结果存放在容器中
std::vector<std::future<double>> results;
unsigned concurrent_count = std::thread::hardware_concurrency();
min = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < concurrent_count; i++)
{
std::packaged_task<double(int, int)> task(accumulate); //产生一个未就绪的共享状态
results.push_back(task.get_future());
int range = max / concurrent_count * (i + 1); //任务平均分配到各个线程中
std::thread t(std::move(task), min, range); //通过新线程执行任务
t.detach();
min = range + 1;
}
std::cout << "threads create finish" << std::endl;
double sum = 0;
for (auto& r : results) {
sum += r.get(); // 通过future获取每个任务的结果,即获取共享状态
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
auto start_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
double r = concurrent_task(1, 10e8);
auto end_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto ms = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end_time - start_time).count();
std::cout << "Concurrent task finish, " << ms << " ms consumed, Result: " << r << std::endl;
return 0;
}耗时结果如下:
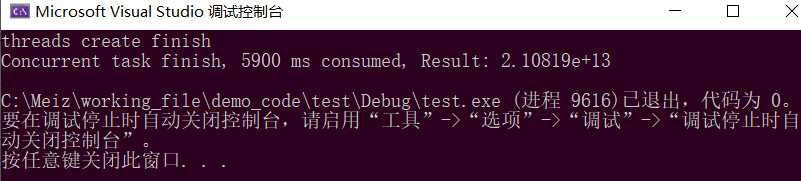
2.std::async和std::future
#include <thread>
#include <future>
#include <numeric>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <chrono>
double accumulate(int min, int max)
{
double sum = 0;
for (int i = min; i <= max; ++i)
{
sum += sqrt(i);
}
return sum;
}
double concurrent_async(int min, int max)
{
std::vector<std::future<double>> results;
unsigned concurrent_count = std::thread::hardware_concurrency();
double sum = 0;
min = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < concurrent_count; i++)
{
int range = max / concurrent_count * (i + 1);
auto f = std::async(std::launch::async, accumulate, min, range);
results.push_back(std::move(f));
min = range + 1;
}
int size = results.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
//如果选择异步执行策略,调用get时,如果异步执行没有结束,get会阻塞当前调用线程,
//直到异步执行结束并获得结果,如果异步执行已经结束,不等待获取执行结果;
//如果选择同步执行策略,只有当调用get函数时,同步调用才真正执行,这也被称为函数调用被延迟
sum += results[i].get();
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
std::cout << "waiting for the result..." << std::endl;
auto start_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
double r = concurrent_async(1, 10e8);
auto end_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto ms = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end_time - start_time).count();
std::cout << "Concurrent task finish, " << ms << " ms consumed, Result: " << r << std::endl;
return 0;
}耗时结果如下:
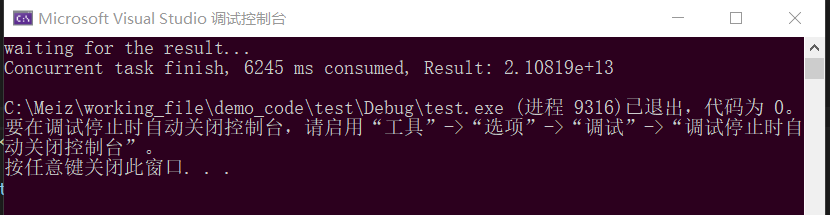
3. OpenMP算法
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
double calculate(int min, int max) {
double sum = 0.0;
#pragma omp parallel for reduction(+:sum)
for (int i = min; i <= max; ++i)
{
sum += sqrt(i);
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
std::cout << "waiting for the result..." << std::endl;
auto time1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto sum = calculate(1, 10e8);
auto time2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto duration = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::milliseconds>(time2 - time1).count();
cout << "Concurrent task finish, " << duration << "ms consumed, Result: " << sum << endl;
}耗时结果如下:























 692
692











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








