简介:
CNN(卷积神经网络)是一种特殊的对图像识别的方式,属于非常有效的带有前向反馈的网络。CNN主要用于对二维图像的识别,它的网络结构对平移、比例放缩、倾斜或其他的变形具有高度不变性。因为,每层关注的特征不一样,贴近原图的,关注像素级别的,而经过多次特征提取后,关联型、序列型或结构化等类型的特征(如拓扑结构)被提取出来,其一致性与事物本身的一致性就比较接近了。现在,卷积网络主要用于图像识别领域,也可以用于人脸识别、文字识别等方向。
1、tf.reshape([-1,28,28,1])
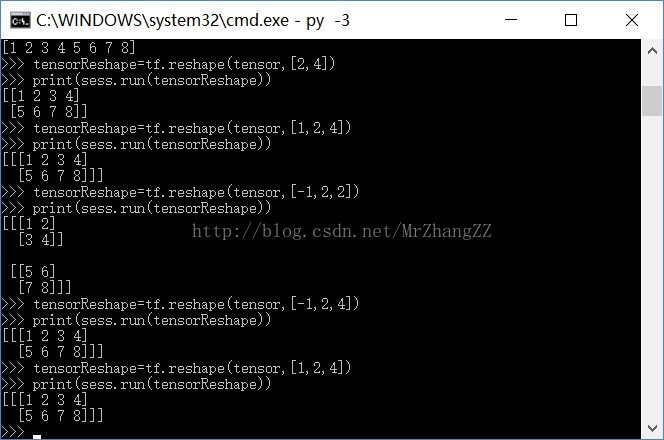
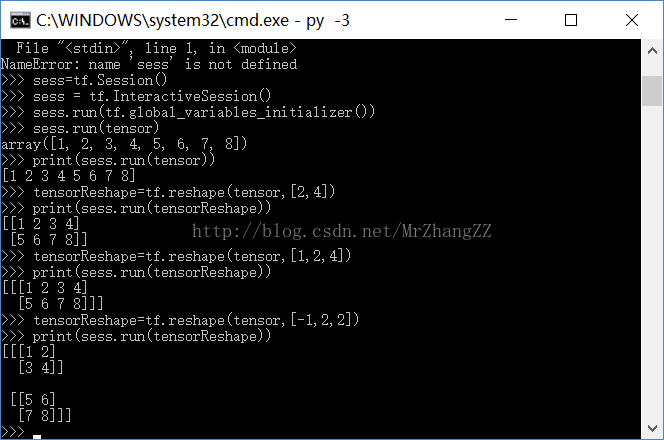


# create pooling ,in order to reduce the loss of info when cutting the imagedef max_pool_2x2(x): return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
tf.nn.max_pool(value, ksize, strides, padding, name=None)
参数是四个,和卷积很类似:第一个参数value:需要池化的输入,一般池化层接在卷积层后面,所以输入通常是feature map,依然是[batch, height, width, channels]这样的shape
第二个参数ksize:池化窗口的大小,取一个四维向量,一般是[1, height, width, 1],因为我们不想在batch和channels上做池化,所以这两个维度设为了1
第三个参数strides:和卷积类似,窗口在每一个维度上滑动的步长,一般也是[1, stride,stride, 1]
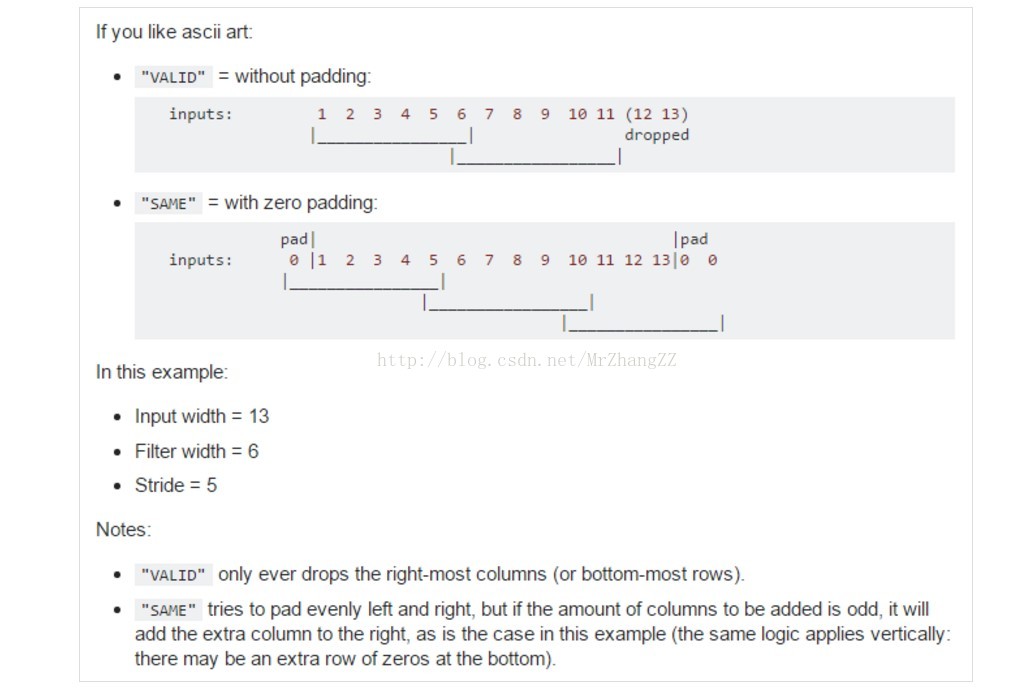
第四个参数padding:和卷积类似,可以取'VALID' 或者'SAME'
返回一个Tensor,类型不变,shape仍然是[batch, height, width, channels]这种形式
求平均值tf.reduce_mean(input_tensor, reduction_indices=None, keep_dims=False, name=None)
参数(1)input_tensor:待求值的tensor。
参数(2)reduction_indices:在哪一维上求解。
参数(3)(4)可忽略
举例说明:
# 'x' is [[1., 2.]
# [3., 4.]]
首先求平均值,
tf.reduce_mean(x) ==> 2.5 #如果不指定第二个参数,那么就在所有的元素中取平均值
tf.reduce_mean(x, 0) ==> [2., 3.] #指定第二个参数为0,则第一维的元素取平均值,即每一列求平均值
tf.reduce_mean(x, 1) ==> [1.5, 3.5] #指定第二个参数为1,则第二维的元素取平均值,即每一行求平均值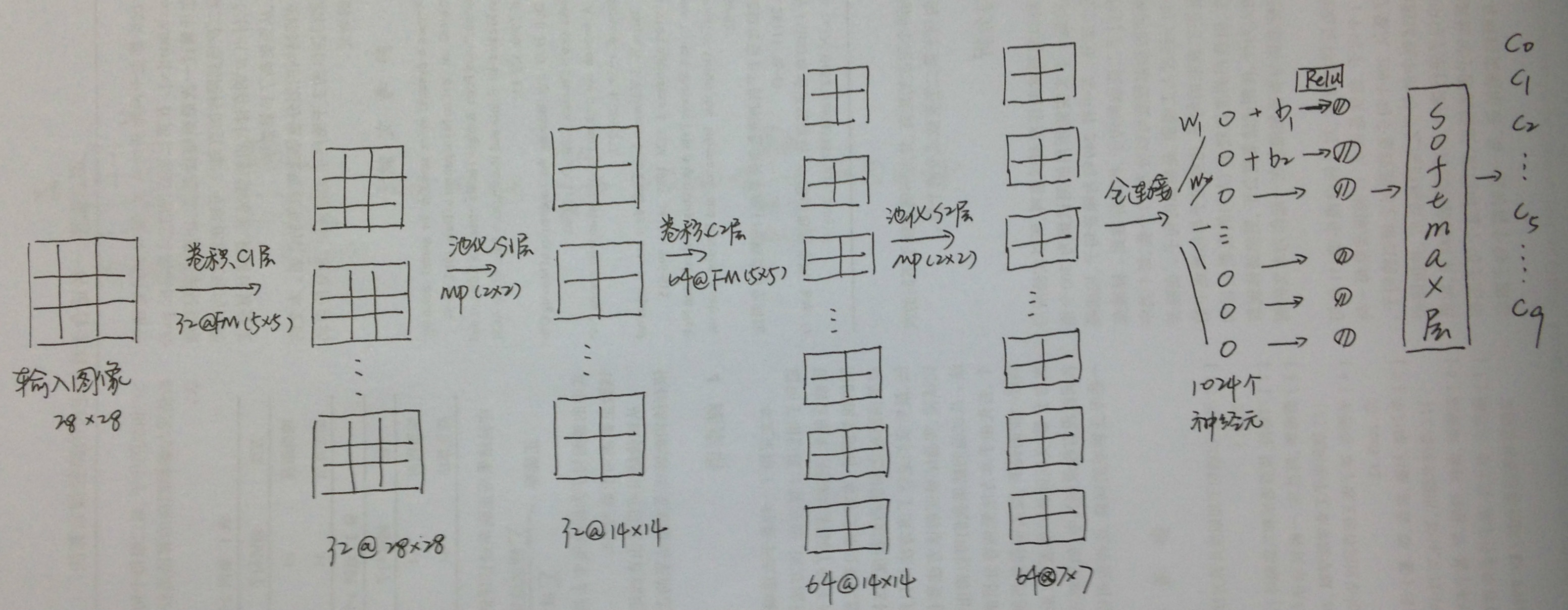
import tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data# 60000行的训练数据集(mnist.train)和10000行的测试数据集(mnist.test)# (每一行包含28*28=784个像素点)# Import datamnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)# init weightdef weight_variable(shape): initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.01) return tf.Variable(initial)# init biasdef bias_variable(shape): initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape) return tf.Variable(initial)# create CNN layerdef conv2d(x, W): # stride [1,x_movement,y_movement,1],stride[0] and stride[3] must be 1 return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') ### ???# create pooling ,in order to reduce the loss of info when cutting the imagedef max_pool_2x2(x): return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')# def compute_accuracydef comput_accuracy(v_xs, v_ys): global prediction y_pre = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: v_xs, keep_prob: 1}) correct_pre = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_pre, 1), tf.argmax(v_ys, 1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pre, tf.float32)) result = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={xs: v_xs, ys: v_ys, keep_prob: 1}) return result# define placeholder for inputs to networkxs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) # 28x28ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)x_image = tf.reshape(xs, [-1, 28, 28, 1])# print(x_image.shape) #[n_sample.28,28,1]# conv1 layerW_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32]) # patch 5x5,in size 1,out size 32b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])hide_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)# relu: let data nonlinear , output size 28x28x32hide_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(hide_conv1) # output size 14x14x32# conv2 layerW_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64]) # patch 5x5,in size 32,out size 64b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])hide_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(hide_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2) # relu: let data nonlinear , output size 14x14x64hide_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(hide_conv2) # output size 7x7x64# func1 layerW_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64, 1024]) # 全连接b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])# [n_samples,7,7,64] ->> [n_samples,7*7*64]h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(hide_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64]) # 转化为1维h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1) # 点积h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)# func2 layerW_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10])b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2)# the error between the prediction and real datacross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(ys*tf.log(prediction), reduction_indices=[1]))train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)# create sessionwith tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) for i in range(1000): batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: batch_xs, ys: batch_ys, keep_prob: 0.5}) if i % 40 == 0: print(comput_accuracy(mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels))





















 2329
2329











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








