一、基础知识点
1、Machine Learning definition
1)Field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed.
2)A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some task T and some performance measure P, if its performance on T, as measured by P, improves with experience E.
eg. Suppose your email program watches which emails you do or do not mark as spam, and based on that learns how to better filter spam. What is the task T in this setting? (a)
a.Classifying emails as spam or not spam. T
b.Watching you label emails as spam or not spam. E
c.The number (or fraction) of emails correctly classified as spam/not spam. P
d.None of the above—this is not a machine learning problem.
2、Machine learning algorithms
1)Supervised learning
①classification: Discrete valued output (0 or 1)
②regression: Predict continuous valued output
eg. You’re running a company, and you want to develop learning algorithms to address each of two problems.
Problem 1: You have a large inventory of identical items. You want to predict how many of these items will sell over the next 3 months.
Problem 2: You’d like software to examine individual customer accounts, and for each account decide if it has been hacked/compromised.Should you treat these as classification or as regression problems?(c)
a.Treat both as classification problems.
b.Treat problem 1 as a classification problem, problem 2 as a regression problem.
c.Treat problem 1 as a regression problem, problem 2 as a classification problem.
d.Treat both as regression problems.
2)Unsupervised learning
Unsupervised learning allows us to approach problems with little or no idea what our results should look like. We can derive structure from data where we don't necessarily know the effect of the variables by clustering the data based on relationships among the variables in the data.
3、Model and Cost Function
1)Model representation
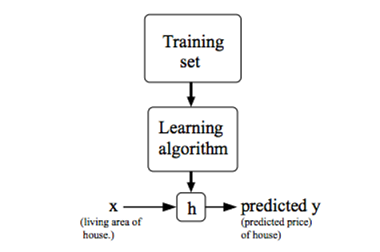

2)Cost function
① Hypothesis: 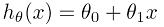
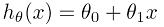
② Parameters: 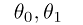
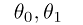
③ Cost Function:
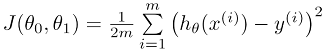
④ Goal:
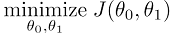
3)Gradient descent
①the gradient descent algorithm
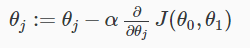
② about 
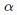
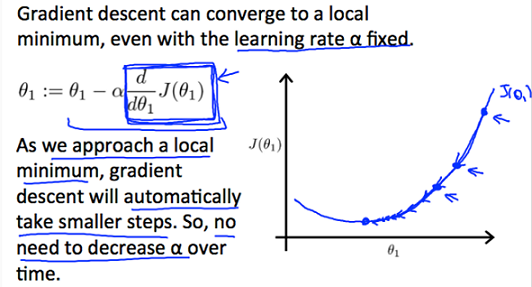
③ Gradient descent for linear regression
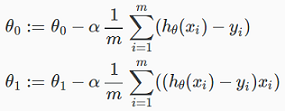
二、学习收获
week 1的课程相对比较简单,带我们初步进入机器学习的世界。
学习过程中视频教学固然简单易懂,但是学习速度较慢,学习时间较长。
同时我阅读了周志华教授的《机器学习》第1、2章,补充了一些机器学习的基础知识。
总体来说,这两周的学习以阅读和补充基础知识为主,还没有开始自己动手实现。
从下次开始,我会引入一些简单的编程练习。
不定期更新,这里是我的笔记小屋hhh~~~






















 1124
1124











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








