| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 11276 | Accepted: 8018 |
Description
In the Fibonacci integer sequence, F0 = 0, F1 = 1, and Fn = Fn − 1 + Fn − 2 for n ≥ 2. For example, the first ten terms of the Fibonacci sequence are:
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, …
An alternative formula for the Fibonacci sequence is
 .
.
Given an integer n, your goal is to compute the last 4 digits of Fn.
Input
The input test file will contain multiple test cases. Each test case consists of a single line containing n (where 0 ≤ n ≤ 1,000,000,000). The end-of-file is denoted by a single line containing the number −1.
Output
For each test case, print the last four digits of Fn. If the last four digits of Fn are all zeros, print ‘0’; otherwise, omit any leading zeros (i.e., print Fn mod 10000).
Sample Input
0 9 999999999 1000000000 -1
Sample Output
0 34 626 6875
Hint
As a reminder, matrix multiplication is associative, and the product of two 2 × 2 matrices is given by
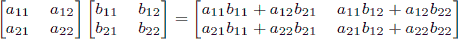 .
.
Also, note that raising any 2 × 2 matrix to the 0th power gives the identity matrix:
 .
.
<pre name="code" class="cpp"><span style="font-family:SimSun;font-size:12px;">#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<time.h>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<iterator>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<limits.h>
#include<map>
#include<memory.h>
//#define ONLINE_JUDGE
#define eps 1e-8
#define INF 0x7fffffff //INT_MAX
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f //int??????????????????
#define FOR(i,a) for((i)=0;i<(a);(i)++) //[i,a);
#define MEM(a) (memset((a),0,sizeof(a)))
#define sfs(a) scanf("%s",a)
#define sf(a) scanf("%d",&a)
#define sfI(a) scanf("%I64d",&a)
#define pf(a) printf("%d\n",a)
#define pfI(a) printf("%I64d\n",a)
#define pfs(a) printf("%s\n",a)
#define sfd(a,b) scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)
#define sft(a,b,c)scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c)
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<b;i++)
#define for2(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=b;i++)
#define for3(i,a,b)for(int i=(b);i>=a;i--)
#define MEM1(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define MEM2(a) memset(a,-1,sizeof(a))
#define LL __int64
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; }
template<class T> inline T Min(T a, T b) { return a < b ? a : b; }
template<class T> inline T Max(T a, T b) { return a > b ? a : b; }
using namespace std;
template<class T>
T Mint(T a, T b, T c) {
if (a>b) {
if (c>b)
return b;
return c;
}
if (c>a)
return a;
return c;
}
template<class T>
T Maxt(T a, T b, T c) {
if (a>b) {
if (c>a)
return c;
return a;
}
else if (c > b)
return c;
return b;
}
const int mod = 10000;
int T;
LL n;
struct Mat {
LL p[3][3];
}ta,tb;
Mat mat_mul(Mat a, Mat b) {
Mat c;
c.p[1][1] = (a.p[1][1] * b.p[1][1] + a.p[1][2] * b.p[2][1])%mod;
c.p[1][2] = (a.p[1][1] * b.p[1][2] + a.p[1][2] * b.p[2][2])%mod;
c.p[2][1] = (a.p[2][1] * b.p[1][1] + a.p[2][2] * b.p[2][1])%mod;
c.p[2][2] = (a.p[2][1] * b.p[1][2] + a.p[2][2] * b.p[2][2])%mod;
return c;
}
Mat mat_exp(Mat a, LL n) {
Mat temp;
temp.p[1][1] = temp.p[2][2] = 1;
temp.p[1][2] = temp.p[2][1] = 0;
while (n) {
if (n & 1)
temp = mat_mul(temp, a);
a = mat_mul(a, a);
n >>= 1;
}
return temp;
}
void init(LL n) {
ta.p[2][2] = 0;
ta.p[1][2] = ta.p[2][1] = ta.p[1][1] = 1;
tb = mat_exp(ta, n-1);
}
int main() {
while(~sfI(n)) {
if (n == -1)
break;
int a = 0;
int b = 1;
if (n == 0)
pf(a);
else if (n == 1)
pf(b);
else if (n == 2)
pf(b);
else {
init(n);
int m = b*tb.p[1][1]%mod + a*tb.p[2][1]%mod;
pf(m%mod);
}
}
return 0;
}</span>POJ 3070↑
hdu 2064↓
Queuing
Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 3644 Accepted Submission(s): 1648

Now we define that ‘f’ is short for female and ‘m’ is short for male. If the queue’s length is L, then there are 2 L numbers of queues. For example, if L = 2, then they are ff, mm, fm, mf . If there exists a subqueue as fmf or fff, we call it O-queue else it is a E-queue.
Your task is to calculate the number of E-queues mod M with length L by writing a program.
3 8 4 7 4 8
6 2 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<time.h>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<iterator>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<limits.h>
#include<map>
#include<memory.h>
//#define ONLINE_JUDGE
#define eps 1e-8
#define INF 0x7fffffff //INT_MAX
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f //int??????????????????
#define FOR(i,a) for((i)=0;i<(a);(i)++) //[i,a);
#define MEM(a) (memset((a),0,sizeof(a)))
#define sfs(a) scanf("%s",a)
#define sf(a) scanf("%d",&a)
#define sfI(a) scanf("%I64d",&a)
#define pf(a) printf("%d\n",a)
#define pfI(a) printf("%I64d\n",a)
#define pfs(a) printf("%s\n",a)
#define sfd(a,b) scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)
#define sft(a,b,c)scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c)
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<b;i++)
#define for2(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=b;i++)
#define for3(i,a,b)for(int i=(b);i>=a;i--)
#define MEM1(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define MEM2(a) memset(a,-1,sizeof(a))
#define ll __int64
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; }
template<class T> inline T Min(T a, T b) { return a < b ? a : b; }
template<class T> inline T Max(T a, T b) { return a > b ? a : b; }
using namespace std;
template<class T>
T Mint(T a, T b, T c) {
if (a>b) {
if (c>b)
return b;
return c;
}
if (c>a)
return a;
return c;
}
template<class T>
T Maxt(T a, T b, T c) {
if (a>b) {
if (c>a)
return c;
return a;
}
else if (c > b)
return c;
return b;
}
const int SIZE = 4;
int l, MOD;
struct Mat {
ll v[SIZE][SIZE];
Mat() {
memset(v, 0, sizeof(v));
}
void init(ll _v) {
for2(i, 0, SIZE)
v[i][i] = _v;
}
};
Mat operator * (Mat a, Mat b) {
Mat c;
for1(i, 0, SIZE) {
for1(j, 0, SIZE) {
c.v[i][j] = 0;
for1(k, 0, SIZE) {
c.v[i][j] += (a.v[i][k] * b.v[k][j]) % MOD;
c.v[i][j] %= MOD;
}
}
}
return c;
}
Mat operator ^ (Mat a, ll k) {
Mat c;
c.init(1);
while (k) {
if (k & 1) c = a * c;
a = a * a;
k >>= 1;
}
return c;
}
int main() {
Mat a, b, c;
a.v[0][0] = 9;
a.v[1][0] = 6;
a.v[2][0] = 4;
a.v[3][0] = 2;
b.v[0][0] = b.v[0][2] = b.v[0][3] = b.v[1][0] = b.v[2][1] = b.v[3][2] = 1;
while(~sfd(l,MOD)){
if (l == 0)
printf("0\n");
else if (l <= 4)
pf(a.v[1][4 - l+1] % MOD);
else {
c =( b ^ (l - 4))*a;
pf(c.v[0][0]%MOD);
}
}
return 0;
}






















 1155
1155

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








