对数域操作函数
class Logspace:
def __init__(self):
self.LOGZERO =np.nan
def eexp(self,x):
if np.isnan(x):
return 0
else:
return np.exp(x)
def eln(self,x):
if x == 0:
return self.LOGZERO
elif x>0:
return np.log(x)
else:
print 'Wrong!!!\n\t negative input error'
return np.nan
def elnsum(self,elnx,elny):
if np.isnan(elnx):
return elny
elif np.isnan(elny):
return elnx
elif elnx > elny:
return elnx + self.eln(1+np.exp(elny-elnx))
else:
return elny + self.eln(1+np.exp(elnx-elny))
def elnproduct(self,elnx,elny):
if np.isnan(elnx) or np.isnan(elny):
return self.LOGZERO
else:
return elnx + elny
def elnmatprod(self,elnx,elny):
#array([[ 0.]])其size是2
xsize = np.size(np.shape(elnx))
ysize = np.size(np.shape(elny))
if xsize == 1 and ysize == 1:
r = self.LOGZERO
for i in range(np.shape(elnx)[0]):
r = self.elnsum(r,self.elnproduct(elnx[i],elny[i]))
return r
elif xsize == 1 and not ysize == 1:
n = np.shape(elny)[1]
r = np.zeros(n)
for i in range(n):
r[i] = self.elnmatprod(elnx,elny[:,i])
return r
elif not xsize == 1 and ysize == 1:
n = np.shape(elnx)[0]
r = np.zeros(n)
for i in range(n):
r[i] = self.elnmatprod(elnx[i,:],elny)
return r
else:
m,n= np.shape(elnx)
p = np.shape(elny)[1]
r = np.zeros((m,p))
for i in range(m):
for j in range(p):
r[i][j] = self.elnmatprod(elnx[i,:],elny[:,j])
return r
def eexpmat(self,elny):
expy = np.copy(elny)
if np.size(np.shape(elny)) == 1:
for i in range(np.shape(elny)[0]):
expy[i] = self.eexp(expy[i])
else:
for i in range(np.shape(elny)[0]):
for j in range(np.shape(elny)[1]):
expy[i][j] = self.eexp(expy[i][j])
return expy
def elnmat(self,x):
elnx = np.copy(x)
if np.size(np.shape(x)) == 1:
for i in range(np.shape(x)[0]):
elnx[i] = self.eln(x[i])
else:
for i in range(np.shape(x)[0]):
for j in range(np.shape(x)[1]):
elnx[i,j] = self.eln(x[i,j])
return elnx # 测试举例
logspace = Logspace()
M1 = np.array([1,0.5])
M2 = np.array([[1.3,1.5],[1.8,0.5]])
M3 = np.array([[0.8,1.5],[1.8,0.7]])
M4 = np.array([0,0])
print logspace.eexpmat(logspace.elnmatprod(M1,M2))
print np.dot(logspace.eexpmat(M1),logspace.eexpmat(M2))[ 19.94836491 14.90077579]
[ 19.94836491 14.90077579]
条件随机场的函数
def read_corps(corpsfile='testchunk.data'):
#http://www.chokkan.org/software/crfsuite/tutorial.html,该页面有两个网址可下载数据集,该数据集量很大
#http://blog.dpdearing.com/2011/12/opennlp-part-of-speech-pos-tags-penn-english-treebank/
tagids = defaultdict(lambda: len(tagids))
tagids["<S>"] = 0
corps=[]
onesentence = []
words = [ "<S>" ]
tags = [ 0 ]
#wordnumcount = 0
with open(corpsfile,'r') as f:
for line in f:
if len(line)<=1:
pass
elif line != '. . O\n':
# '. . O\n'表示一句话结束,当一句话未结束则将该单词加入列表onesentence
onesentence.append(line)
else: #如果一句话结束,则对该句话的所有出现的单词进行处理,将处理结果存入列表corps
for texts in onesentence:
#wordnumcount += 1
w_t = texts.strip().split(" ")
#print w_t
try:
#由于表示数字的字符串变化较多,为了减少其干扰,这里将其检测出来并替换掉
float(w_t[0].strip().replace(',',''));
#print w_t
words.append('#CD#')
except:
words.append(w_t[0].lower())
#if w_t[1] in{ '``',',',"''",'$','#',')','('}:
# print w_t
tags.append(tagids[w_t[1]])
words.append("<S>") #words是一句话的单词组成的列表
tags.append(0) #tags是一句话的标注组成的列表,与单词列表words一一对应
if np.shape(words)[0] > 2: #排除掉空句子
corps.append((words,tags))
#对onesentence,words和tags重新初始化
onesentence = []
words = [ "<S>" ]
tags = [ 0 ]
#print '一共出现的单词个数:'+np.str(wordnumcount)
#一共出现的单词个数:40377
return corps,tagids
def getfeatureTS(corps):
featuresets = set() #特征的集合
featureT = [] #转移特征的列表,比如列表元素('T', 2, 3)表示从状态2转到特征3
featureS = [] #状态特征的列表,比如列表元素('S','Confidence', 1)
for corp in corps:
for i in range(np.shape(corp[0])[0]):
if corp[0][i] == '<S>':
continue
if ('S',corp[0][i],corp[1][i]) not in featuresets:
featuresets.add(('S',corp[0][i],corp[1][i]))
featureS.append(('S',corp[0][i],corp[1][i]))
if corp[0][i-1] != '<S>':
if ('T',corp[1][i-1],corp[1][i]) not in featuresets:
featuresets.add(('T',corp[1][i-1],corp[1][i]))
featureT.append(('T',corp[1][i-1],corp[1][i]))
featureTS = featureT+featureS
words2tagids = words2tagidfromfeatureS(featureS)
return featureTS,words2tagids
def getpriorfeatureE(corps,featureTS):
#计算先验特征期望值
N = np.shape(corps)[0] #训练样本数
K = np.shape(featureTS)[0] #特征数
priorfeatureE = np.zeros(K)
for corp in corps:
for i in range(np.shape(corp[0])[0]):
if corp[0][i] == '<S>':
continue
try:
idex = featureTS.index(('S', corp[0][i], corp[1][i]))
priorfeatureE[idex] += 1.0
except:
pass
try:
idex = featureTS.index(('T', corp[1][i-1], corp[1][i]))
priorfeatureE[idex] += 1.0
except:
pass
priorfeatureE /=N
#plt.plot(priorfeatureE)
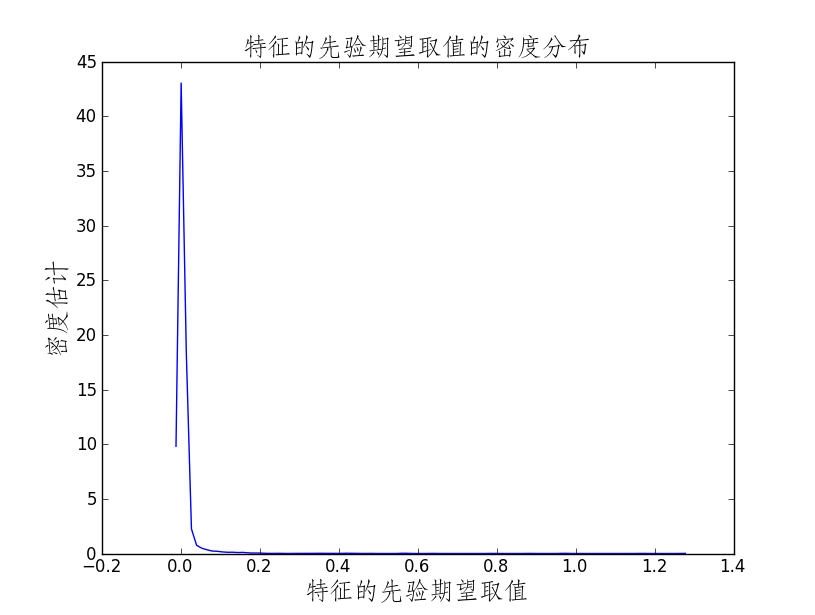
#从特征的先验期望值可以看出无论是转移特征(从横坐标0开始)还是状态特征(从横坐标318开始),先被记录的先验期望值越大
return priorfeatureE
def words2tagidfromfeatureS(featureS):
#统计所有单词分别对应的词性列表
words2tagids = {}
for feature in featureS:
word = feature[1]
state = feature[2]
if word in words2tagids:
words2tagids[word].append(state)
else:
words2tagids[word] = [state]
#lennums列表统计单词对应的词性的长度的分布
#lennums = [[lenlist.count(i) for i in range(1,max(lenlist)+1)]
# for lenlist in [[len(words2tagids[i]) for i in words2tagids]]][0]
#lennums = [3760, 389, 32, 1]
return words2tagids
def getpostfeatureE(weights,corps,featureTS,words2tagids):
K = np.shape(featureTS)[0] #特征数
postfeatureE = np.zeros(K) #特征的后验期望值
N = np.shape(corps)[0]
for corpidx in range(N):
corp = corps[corpidx][0][1:-1]
lencorp = np.size(corp) #语料长度,即句子中的单词数
Mlist = {}
Mlist['mat'] = ['']*(lencorp+1)
Mlist['dim'] = [words2tagids[corp[i]] for i in range(lencorp)]
Mlist['len'] = [np.size(words2tagids[corp[i]]) for i in range(lencorp)]
for i in range(lencorp+1):
if i == 0:#第一个矩阵,只有状态特征的行向量
d = Mlist['len'][0]
Mlist['mat'][i] = np.zeros((1,d))
for j in range(d):
Mlist['mat'][i][0,j] = weights[featureTS.index(('S', corp[0], words2tagids[corp[0]][j]))]
continue
if i == lencorp:#最后一个矩阵,元素为0的列向量矩阵
Mlist['mat'][i] = np.zeros((Mlist['len'][-1],1))
continue
#既非第一个矩阵,亦非第二个矩阵,每个元素要计算状态特征和转移特征
Mlist['mat'][i] = np.zeros((Mlist['len'][i-1],Mlist['len'][i]))
for d1 in range(Mlist['len'][i-1]):
for d2 in range(Mlist['len'][i]):
id1 = words2tagids[corp[i-1]][d1]
id2 = words2tagids[corp[i]][d2]
try:
Sweight = weights[featureTS.index(('S', corp[i], id2))]
except:
Sweight = 0
try:
Tweight = weights[featureTS.index(('T', id1, id2))]
except:
Tweight = 0
Mlist['mat'][i][d1,d2] = Sweight + Tweight
#return Mlist,corps[0]
#return 0
z = np.array([[0]])
for i in range(lencorp+1):
z = logspace.elnmatprod(z,Mlist['mat'][i])
Alphalist = ['']*(lencorp+2)
Betalist = ['']*(lencorp+2)
Alphalist[0] = np.zeros((1,1)) # 第一个前向向量:1*1的矩阵
Betalist[-1] = np.zeros((Mlist['len'][-1],1))
#Alphalist里的元素是单行矩阵,Betalist里的元素是单列矩阵
for i in range(1,lencorp+2):
#print i,np.shape(Alphalist[i-1]),np.shape(Mlist['mat'][i-1])
Alphalist[i] = logspace.elnmatprod(Alphalist[i-1],Mlist['mat'][i-1])
for i in range(lencorp,-1,-1):
Betalist[i] = logspace.elnmatprod(Mlist['mat'][i],Betalist[i+1])
for i in range(1,lencorp+1):
d1,d2 = np.shape(Mlist['mat'][i-1])
#print d1,d2,Mlist['dim'][i-2],Mlist['dim'][i-1] # 3,2,34
#print '================'
for di in range(d1):
for dj in range(d2):
# i=1时,没有转移特征;i=lencorp+1时,转移特征和状态特征都没有
plocal = logspace.eexp(logspace.elnproduct(logspace.elnproduct(logspace.elnproduct(Alphalist[i-1][0,di],
Mlist['mat'][i-1][di,dj]),Betalist[i][dj,0]),-z[0,0]))
if i == 1:#只有状态特征
try:
Sidex = featureTS.index(('S', corp[i-1], Mlist['dim'][i-1][dj]))
postfeatureE[Sidex] += plocal
except:
pass
else:
try:
Sidex = featureTS.index(('S', corp[i-1], Mlist['dim'][i-1][dj]))
postfeatureE[Sidex] += plocal
except:
pass
try:
Tidex = featureTS.index(('T', Mlist['dim'][i-2][di], Mlist['dim'][i-1][dj]))
postfeatureE[Tidex] += plocal
except:#如果该转移特征bucunza不存在,直接忽略
pass
#aM = logspace.elnmatprod(Alphalist[i-1],Mlist['mat'][i-1])
#aMb = logspace.elnmatprod(aM,Betalist[i])
#print promat
#backuppromat.append(promat)
postfeatureE /= N
return postfeatureE
def getliknegvalue(weights,corps,featureTS,words2tagids):
#目标函数是对对数似然函数取负,故要使其最小化
K = np.shape(featureTS)[0] #特征数
N = np.shape(corps)[0]
liknegvalue = 0
for corpidx in range(N):
corp = corps[corpidx][0][1:-1]
tag = corps[corpidx][1][1:-1]
lencorp = np.size(corp) #语料长度,即句子中的单词数
Mlist = {}
Mlist['mat'] = ['']*(lencorp+1)
Mlist['dim'] = [words2tagids[corp[i]] for i in range(lencorp)]
Mlist['len'] = [np.size(words2tagids[corp[i]]) for i in range(lencorp)]
for i in range(lencorp+1):
if i == 0:#第一个矩阵,只有状态特征的行向量
d = Mlist['len'][0]
Mlist['mat'][i] = np.zeros((1,d))
for j in range(d):
Mlist['mat'][i][0,j] = weights[featureTS.index(('S', corp[0], words2tagids[corp[0]][j]))]
continue
if i == lencorp:#最后一个矩阵,元素为0的列向量矩阵
Mlist['mat'][i] = np.zeros((Mlist['len'][-1],1))
continue
#既非第一个矩阵,亦非第二个矩阵,每个元素要计算状态特征和转移特征
Mlist['mat'][i] = np.zeros((Mlist['len'][i-1],Mlist['len'][i]))
for d1 in range(Mlist['len'][i-1]):
for d2 in range(Mlist['len'][i]):
id1 = words2tagids[corp[i-1]][d1]
id2 = words2tagids[corp[i]][d2]
try:
Sweight = weights[featureTS.index(('S', corp[i], id2))]
except:
Sweight = 0
try:
Tweight = weights[featureTS.index(('T', id1, id2))]
except:
Tweight = 0
Mlist['mat'][i][d1,d2] = Sweight + Tweight
numerator = 0
denominator= np.array([[0]])
for i in range(lencorp+1):
denominator = logspace.elnmatprod(denominator,Mlist['mat'][i])
if i == 0:
numerator = logspace.elnproduct(numerator,Mlist['mat'][i][0,Mlist['dim'][i].index(tag[i])])
elif i < lencorp:
numerator = logspace.elnproduct(numerator,Mlist['mat'][i][Mlist['dim'][i-1].index(tag[i-1]),Mlist['dim'][i].index(tag[i])])
liknegvalue += (denominator - numerator)/N
return liknegvalue[0,0]
def getgradients(priorfeatureE,weights,corps,featureTS,words2tagids):
postfeatureE = getpostfeatureE(weights,corps,featureTS,words2tagids)
return postfeatureE - priorfeatureEL-BFGS函数用于数值优化
def twoloop(s, y, rho,gk):
# 被lbfgs函数调用
n = len(s) #向量序列的长度
if np.shape(s)[0] >= 1:
#h0是标量,而非矩阵
h0 = 1.0*np.dot(s[-1],y[-1])/np.dot(y[-1],y[-1])
else:
h0 = 1
a = np.empty((n,))
q = gk.copy()
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
a[i] = rho[i] * np.dot(s[i], q)
q -= a[i] * y[i]
z = h0*q
for i in range(n):
b = rho[i] * np.dot(y[i], z)
z += s[i] * (a[i] - b)
return z
def lbfgs(fun = getliknegvalue,gfun = getgradients,x0 = weights,corps = corps,
featureTS = featureTS,words2tagids = words2tagids,
priorfeatureE = priorfeatureE,m=10,maxk = 20):
# fun和gfun分别是目标函数及其一阶导数,x0是初值,m为储存的序列的大小
rou = 0.55
sigma = 0.4
epsilon = 1e-5
k = 0
n = np.shape(x0)[0] #自变量的维度
s, y, rho = [], [], []
while k < maxk :
gk = gfun(priorfeatureE,x0,corps,featureTS,words2tagids)
if np.linalg.norm(gk) < epsilon:
break
dk = -1.0*twoloop(s, y, rho,gk)
m0=0;
mk=0
funcvalue = fun(x0,corps,featureTS,words2tagids)
while m0 < 20: # 用Armijo搜索求步长
if fun(x0+rou**m0*dk,corps,featureTS,words2tagids) < funcvalue+sigma*rou**m0*np.dot(gk,dk):
mk = m0
break
m0 += 1
x = x0 + rou**mk*dk
sk = x - x0
yk = gfun(priorfeatureE,x,corps,featureTS,words2tagids) - gk
if np.dot(sk,yk) > 0: #增加新的向量
rho.append(1.0/np.dot(sk,yk))
s.append(sk)
y.append(yk)
if np.shape(rho)[0] > m: #弃掉最旧向量
rho.pop(0)
s.pop(0)
y.pop(0)
k += 1
x0 = x
print '迭代次数:%d, 函数值:%f'%(k,funcvalue)
return x0, fun(x0,corps,featureTS,words2tagids)#,k#分别是最优点坐标,最优值,迭代次数条件随机场的测试
from collections import defaultdict
corps,tagids = read_corps('mycrfdata.data')
featureTS,words2tagids = getfeatureTS(corps) #得到总的特征列表featureTS
K = np.shape(featureTS)[0] #总的特征数
N = np.shape(corps)[0] #训练样本数
priorfeatureE = getpriorfeatureE(corps,featureTS) #计算特征的先验期望值
weights = np.array([1.0/K]*K)
#postfeatureE = getpostfeatureE(weights,corps,featureTS,words2tagids)
#liknegvalue = getliknegvalue(weights,corps,featureTS,words2tagids)
weights,likelyfuncvalue = lbfgs(fun = getliknegvalue,gfun = getgradients,x0 = weights,corps = corps,
featureTS = featureTS,words2tagids = words2tagids,
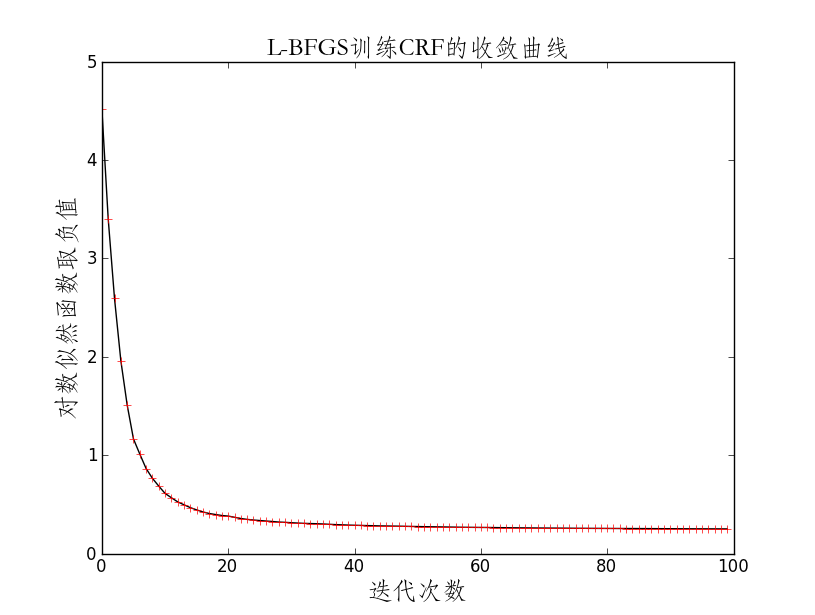
priorfeatureE = priorfeatureE,m=10,maxk = 40)迭代次数:1, 函数值:4.517425
迭代次数:2, 函数值:3.402287
迭代次数:3, 函数值:2.591947
迭代次数:4, 函数值:1.961000
迭代次数:5, 函数值:1.511211
迭代次数:6, 函数值:1.164718
迭代次数:7, 函数值:1.011021
迭代次数:8, 函数值:0.863806
迭代次数:9, 函数值:0.764431
迭代次数:10, 函数值:0.685292
迭代次数:11, 函数值:0.610862
迭代次数:12, 函数值:0.567107
迭代次数:13, 函数值:0.524796
迭代次数:14, 函数值:0.495254
迭代次数:15, 函数值:0.466203
迭代次数:16, 函数值:0.443137
迭代次数:17, 函数值:0.422248
迭代次数:18, 函数值:0.406402
迭代次数:19, 函数值:0.396005
迭代次数:20, 函数值:0.386036
迭代次数:21, 函数值:0.380390
迭代次数:22, 函数值:0.380207
迭代次数:23, 函数值:0.376401
迭代次数:24, 函数值:0.375102
迭代次数:25, 函数值:0.370988
迭代次数:26, 函数值:0.366604
迭代次数:27, 函数值:0.360824
迭代次数:28, 函数值:0.355004
迭代次数:29, 函数值:0.351590
迭代次数:30, 函数值:0.347119
迭代次数:31, 函数值:0.344447
迭代次数:32, 函数值:0.341149
迭代次数:33, 函数值:0.337679
迭代次数:34, 函数值:0.335245
迭代次数:35, 函数值:0.332701
迭代次数:36, 函数值:0.329436
迭代次数:37, 函数值:0.326451
迭代次数:38, 函数值:0.324949
迭代次数:39, 函数值:0.321441
迭代次数:40, 函数值:0.319166
迭代次数:41, 函数值:0.315978
迭代次数:42, 函数值:0.312033
迭代次数:43, 函数值:0.308039
迭代次数:44, 函数值:0.305588
迭代次数:45, 函数值:0.302214import codecs
#读取中文文本,首先要把文本文件保存成utf-8格式,默认的ANSI格式文件读取后不能正确打印中文字符
likelihoodlist = []
with codecs.open('loglikelihood.txt','r','utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
#u'\uff1a'是中文符号“:”
likelihoodlist.append(float(line.split(u'\uff1a')[-1].split()[0]))
plt.plot(likelihoodlist[:100],'-k')
plt.plot(likelihoodlist[:100],'+r')
plt.title(u'L-BFGS训练CRF的收敛曲线',{'fontname':'STFangsong','fontsize':18})
plt.xlabel(u'迭代次数',{'fontname':'STFangsong','fontsize':18})
plt.ylabel(u'对数似然函数取负值',{'fontname':'STFangsong','fontsize':18})from scipy.stats.kde import gaussian_kde
# this create the kernel, given an array it will estimate the probability over that values
kde = gaussian_kde(priorfeatureE)
# these are the values over wich your kernel will be evaluated
dist_space = linspace( min(priorfeatureE)-0.01*(max(priorfeatureE)-min(priorfeatureE)), max(priorfeatureE), 100 )
# plot the results
plt.plot(dist_space, kde(dist_space))
plt.title(u'特征的先验期望取值的密度分布',{'fontname':'STFangsong','fontsize':18})
plt.xlabel(u'特征的先验期望取值',{'fontname':'STFangsong','fontsize':18})
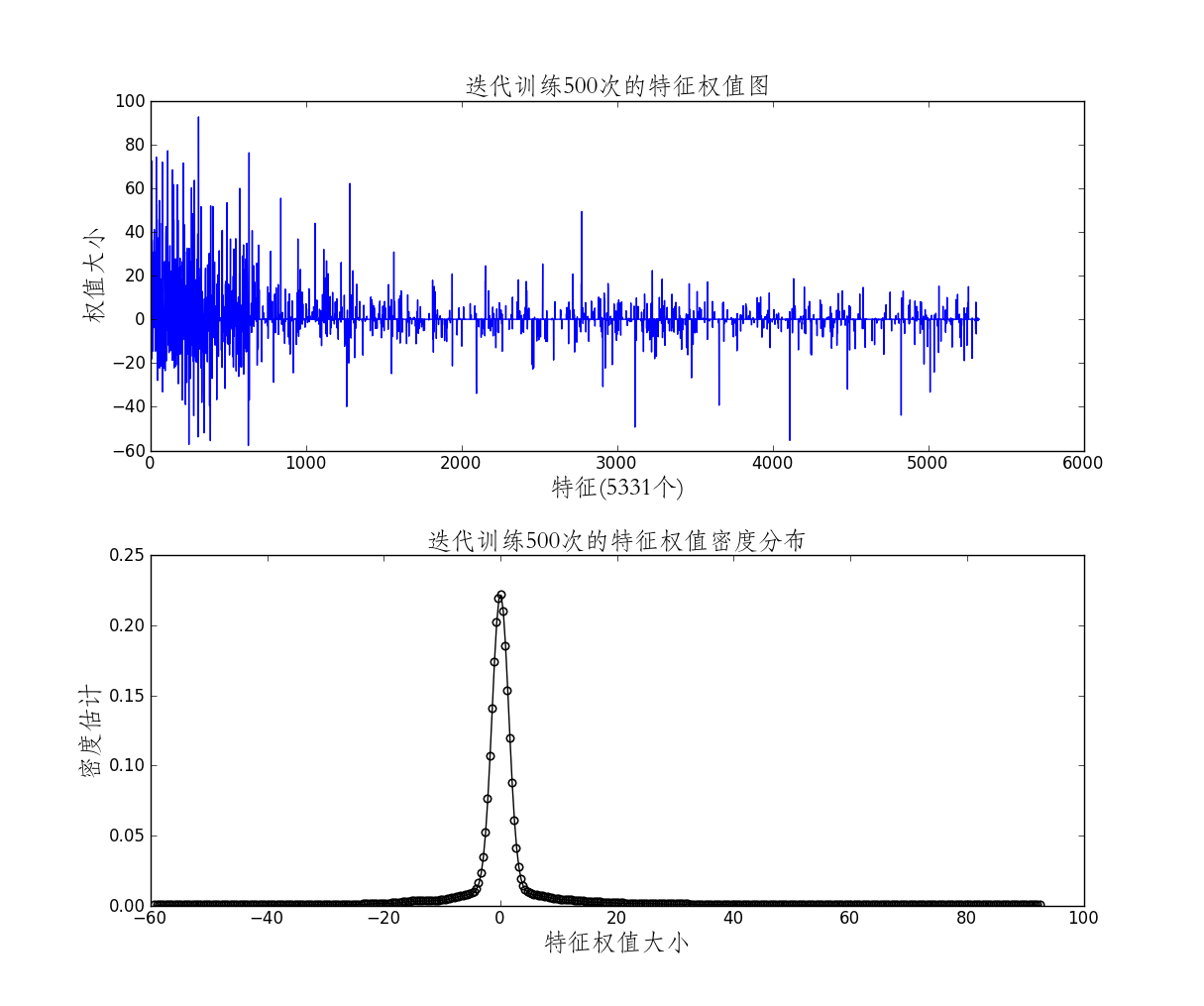
plt.ylabel(u'密度估计',{'fontname':'STFangsong','fontsize':18})from scipy.stats.kde import gaussian_kde
#weights是训练的权值列表,由于训练时间长,得到并不容易,故先保存
np.savetxt('crfweights.out', weights, delimiter=',') #
data = np.genfromtxt('crfweights.out', delimiter=',')
# this create the kernel, given an array it will estimate the probability over that values
kde = gaussian_kde(data)
# these are the values over wich your kernel will be evaluated
dist_space = linspace( min(data)-0.01*(max(data)-min(data)), max(data), 400 )
fig,axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2,ncols=1,figsize=(12,10))
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace = None,hspace=0.3)
axes[0].plot(data)
axes[0].set_title(u'迭代训练500次的特征权值图',{'fontname':'STFangsong','fontsize':18})
axes[0].set_xlabel(u'特征(5331个)',{'fontname':'STFangsong','fontsize':18})
axes[0].set_ylabel(u'权值大小',{'fontname':'STFangsong','fontsize':18})
axes[1].plot(dist_space, kde(dist_space),'k',marker = u'$\circ$')
axes[1].set_title(u'迭代训练500次的特征权值密度分布',{'fontname':'STFangsong','fontsize':18})
axes[1].set_xlabel(u'特征权值大小',{'fontname':'STFangsong','fontsize':18})
axes[1].set_ylabel(u'密度估计',{'fontname':'STFangsong','fontsize':18})势函数:势,英语potential,就是有一种潜力,由一种能量转化为别的能量的潜力,描述这种潜力的函数,应该就是叫势函数。势函数到处可见,凡是涉及到能量描述和转换的地方,都会涉及到势函数,还有生物势、化学势。统计物理里面涉及到很多这方面的知识。
标注问题:在自然语言处理中有一个常见的任务,即标注。常见的有:1)词性标注(Part-Of-Speech Tagging),将句子中的每个词标注词性,例如名词、动词等;2)实体标注(Name Entity Tagging),将句子中的特殊词标注,例如地址、日期、人物姓名等。
http://blog.csdn.net/lanxu_yy/article/details/36245161
条件随机场(Conditional random fields)
http://blog.csdn.net/chlele0105/article/details/14897761
条件随机场简介(Introduction to Conditional Random Fields)
说明了特征函数的内容
http://blog.echen.me/2012/01/03/introduction-to-conditional-random-fields/
条件随机场的Python例子
https://github.com/huangzhengsjtu/pcrf/
http://flexcrfs.sourceforge.net/flexcrfs.pdf
CRF++的简单使用
http://blog.csdn.net/felomeng/article/details/4288492
Using CRF for Image Segmentation in Python
http://sloblog.io/~ankl/B-SrKYr2qJw/using-crf-for-image-segmentation-in-python-step-1
http://www.inference.phy.cam.ac.uk/hmw26/crf/
《Conditional Random Fields: An Introduction》内容不错






















 2428
2428











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








