// by rappizit@yahoo.com.cn
// 2007-11-02
#include < vector >
#include < list >
#include < stack >
#include < algorithm >
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
#define pause system("pause")
typedef vector < int > vi;
typedef list < int > li;
typedef vector < li > vli;
vi EulerCircle (vli G)
{
int n = G.size ();
int edge = 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++ )
{
int degree = G [i].size ();
if (degree % 2 || ! degree)
{
return vi ( 0 );
}
edge += degree;
}
vi path (edge / 2 + 1 );
stack < int > s;
int p = 0 , i = 0 ;
do {
if (G [i].empty ())
{
do {
s.pop ();
path [p ++ ] = i;
} while ( ! s.empty () && (i = s.top (), G [i].empty ()));
}
else {
int t = * (G [i].begin ());
G [i].erase (G [i].begin ());
G [t].erase (find (G [t].begin (), G [t].end (), i));
// 使用带有十字链接的双向邻接表可以常数时间地删除边 e(t, i)?!
s.push (t);
i = t;
}
} while ( ! s.empty ());
return path;
}
void main ()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vli G (n);
while (m -- )
{
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
G [u].push_back (v); // 这里为了迎合书上的例子,每条无向边分两次输入
}
vi path = EulerCircle (G);
if (path.size ())
{
for ( int i = 0 ; i < path.size (); i ++ )
{
cout << path [i] << " " ;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
无向图的欧拉回路
采用邻接表存储,vector <list <int>> 类型。
1.如果某点的度数为奇数或零,则没有欧拉回路,返回空的 vector。
2.否则,从标号为 i = 0 的点开始。
3.如果 i 没有邻接点,那么堆栈中所有没有邻接点的点弹出到 vector path 中,如果堆栈非空则 i 赋值为栈顶元素。
否则取 i 的第一个邻接点 t ,删除它们的边(要在 G 中的两处都删除)。将 t 压栈。i 赋值为 t 。
4.如果堆栈为空,返回 path,否则转 3。
算法时间复杂度为 O (E)。
测试数据:
7 20
0 1
0 2
0 5
0 6
1 0
1 2
2 0
2 3
2 4
2 1
3 4
3 2
4 6
4 5
4 3
4 2
5 4
5 0
6 4
6 0
测试结果:
0 6 4 2 3 4 5 0 2 1 0
过程图示:
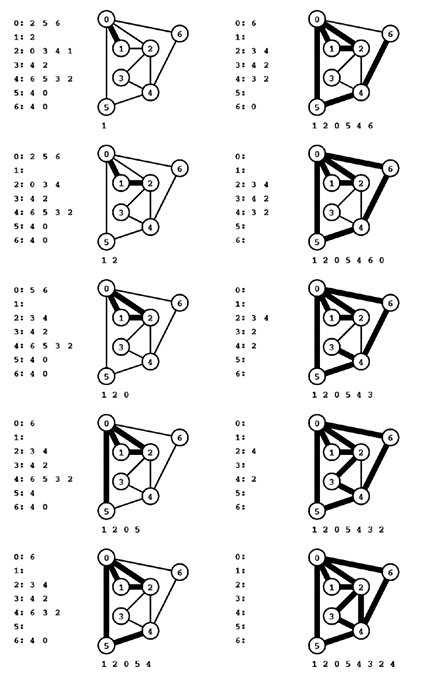
First, the program adds the edge 0-1 to the tour and removes it from the adjacency lists (in two places) (top left, lists at left). Second, it adds 1-2 to the tour in the same way (left, second from top). Next, it winds up back at 0 but continues to do another cycle 0-5-4-6-0, winding up back at 0 with no more edges incident upon 0 (right, second from top). Then it pops the isolated vertices 0 and 6 from the stack until 4 is at the top and starts a tour from 4 (right, third from from top), which takes it to 3, 2, and back to 4, where upon it pops all the now-isolated vertices 4, 2, 3, and so forth. The sequence of vertices popped from the stack defines the Euler tour 0-6-4-2-3-4-5-0-2-1-0 of the whole graph.
Algorithms In Java, Part 5 Graph Algorithms , Chapter 17.7 / Java 算法(第 3 版,第 2 卷)——图算法,章节 17.7
PS:但是我是用 C++ 实现的^_^

























 964
964











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








