文章目录
Boost搜索引擎
项目背景
什么是搜索引擎?
我们平时使用的百度、google搜索、360搜索、搜狗搜索本质上就是搜索引擎,这些搜索引擎都是成熟的产品,具有很高的技术门槛。
全网搜索与站内搜索
百度、google等搜索引擎使用的是全网搜索,需要爬取到全网的资源,难度很大,我们的Boost搜索引擎使用的是站内搜索,相比而言难度要低很多,站内搜索的资源总量相对较少。站内搜索得到的结果更垂直(也就是相关性更强),例如在cplusplus.com中搜索到的都是C++的内容。
Boost搜索引擎最终要达到的效果
Boost搜索引擎最终要达到可以展示网页的标题、网页的内容摘要、显示即将跳
转的网址,效果如下:

竞价排名
现代搜索引擎在显示搜索结果时,使用竞价排名的机制,谁出得钱多,在搜索相同关键字时谁的结果排在前面。
小结:Boost搜索引擎是一个站内的搜索引擎,搜索结果更垂直,更简单。
搜索引擎宏观原理
搜索引擎的宏观原理如图:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-XfHUDXCI-1680706818358)(.\picture\image-20230322143411742.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/041069c0350c4a4aab6cb187f44ab8c2.png)
- 客户端通过GET方法上传关键字,发起HTTP请求
- 服务器收到HTTP请求后,根据关键字进行索引,在磁盘上找到相关的HTML,将HTML的标题+描述+URL进行返回,由于根据索引可能找到多个相关的HTML,所以返回的HTTP响应是拼接多个网页标题+描述+URL的结果
- 服务端在爬取网页资源时,会进行
去标签、数据清洗、建立索引
搜索引擎的技术栈和项目环境
技术栈
C/C++、STL、C++11、Boost准标准库、Jsoncpp库、cppjieba库、cpp-httplib库。HTML5、CSS、js、jQuery、Ajex库(前端内容,选学)。
jsoncpp:使用其中序列化与反序列化的接口
Boost库:主要使用其中文件相关的函数
cppjieba库:结巴分词库,主要使用其中提取关键字相关的函数
cpp-httplib库:cpp-httplib中包含封装好的的http服务器,这样就不用从0开始手写http服务器了
项目环境
Linux环境,ubuntu/centos均可,vim/gcc/g++/Makefile/vs2019/vscode
正排索引与倒排索引
正排索引:根据文档ID找到文档内容,在正排索引中,文档ID与文档内容之间的关系是一对一的。
倒排索引:根据关键字索引对应的文档ID,关键字与文档ID之间的关系可以是一对多。
查找的过程:根据用户输入的关键字,倒排索引到文档的ID(可能包含多个),在根据文档的ID正排索引到文档的内容。根据文档内容,提取title + content(摘要) + URL,构建HTTP响应,进行返回。在这个过程中,根据关键字可能查找到多个文档ID,每一个文档ID都有一个权重,这就是竞价排名的原理。
数据去标签与数据清洗模块Parser(解析器)
数据源
Boost搜索引擎项目使用的是站内搜索,搜索的数据源从boost官网进行下载。
Boost官网是没有自带的搜索功能的,我们的Boost搜索引擎要做的就是提供一个搜索功能。
下载完成以后,使用rz或rz -E将文件上传到Linux机器(如果找不到rz命令,使用sudo apt install lrzsz进行安装),接着使用tar -xzf(或xzvf)进行解压,得到文件。
文件中的内容就是Boost官网中的所有内容。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-TuS7zzBk-1680706818359)(.\picture\image-20230322160643078.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fbac3960b4c348ebb8e40ec67d5cab8f.png)
我们需要的是目录下的所有HTML文件作为数据源,boost_1_81_0中的大部分HTML文件在doc/html目录下。使用命令cp boost_1_81_0/doc/html/* data/input/ -rf将数据源进行拷贝。
去标签
创建一个parser.cc,完成对数据源的去标签工作
touch parser.cc
常见的HTML文件格式:
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Auxiliary Components</title>
在HTML文件中,<>中的内容表示的是格式控制,所谓去标签,指的是将去除<>中的内容,只保留网页的内容,例如上面的HTML去标签之后有效的网页内容只有Auxiliary Components
parser.cc的任务是把数据源中的每一个HTML进行去标签,然后将去标签之后的结果写入到同一个文件中,每一个HTML去标签之后的结果使用\3作为分隔符。在进行读取的时候,以\3作为一段内容的结束标志进行读取。
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX\3YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY\3ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ\3
parser.cc
parser.cc需要将data/input/的全部HTML递归读取,然后将每一个HTML文件做去标签动作,完成之后将数据写入到一个特定的文件。parser.cc的整体框架如下:
int main() {
// 1.递归遍历文件
if (!EnumFiles()) {
cerr << "递归遍历文件失败" << endl;
exit(0);
}
cout << "递归遍历文件成功" << endl;
// 2.解析
if (!ParseHtml()) {
cerr << "解析失败" << endl;
exit(0);
}
cout << "解析成功" << endl;
// 3.回写
if (!SaveHtml()) { // 将results的结果回写到dst_file
cerr << "回写到dst_file失败" << endl;
exit(0);
}
cout << "回写到dst_file成功" << endl;
return 0;
}
parser.cc主要实现EnumFiles、ParseHtml、SaveHtml这三个函数。
EnumFiles:由于C++的STL对于文件系统支持的不太好,要进行遍历文件比较麻烦,因此EnumFiles使用Boost库中的FileSystem来完成递归遍历文件。安装Boost库:
sudo apt-get install libboost-all-dev
bool EnumFiles() { // 将src_path(data/input/)下的所有.html文件的文件名放入file_list中
namespace fs = boost::filesystem;
fs::path root_path(src_path); // 定义起始目录,从起始目录开始遍历
if (!fs::exists(root_path)) {
cerr << "路径不存在" << endl;
return false;
}
fs::recursive_directory_iterator end; // 定义结束迭代器
fs::recursive_directory_iterator start(root_path); // 定义起始迭代器
while (start != end) {// 递归遍历文件夹
if (!fs::is_regular(*start)) { // 如果是一个目录
start++;
continue;
}
// 是普通文件
if (start->path().extension() == ".html") { // 如果文件后缀是html,就添加到file_list中
// cout << start->path().string() << endl; // 测试
file_list.push_back(start->path().string());
}
start++;
}
return true;
}
注意:使用了Boost库在链接时需要加上选项-lboost_system和-lboost_filesystem
ParseHtml:对每一个.html文件进行解析
要完成ParseHtml总体上需要3步:
- 要把文件内容读取到内存,需要自己设计ReadFile函数
- 解析指定的文件,解析指定的文件需要进行3个操作:提取标题、提取摘要、构建URL。需要自己实现ParseTitle、ParseContent、ParseUrl函数
- 将每一个.html解析完成后的结果push到result中
这里将文件操作封装到一个FileUtil类中,提取标题(ParseTitle)、提取摘要(ParserContent)、构建URL(ParseUrl)单独作为函数给出。
// 工具类
class FileUtil { // FileUtil中提供文件的相关操作
public:
static bool ReadFile(const string &filepath, string &result) {
// 将filepath中的内容读取到result中
}
};
ParseHtml整体框架如下:
static bool ParseTitle(const string &result, string &title) {
return true;
}
static bool ParseContent(const string &result, string &content) {
return true;
}
static bool ParseUrl(const string &pathname, string &url) {
return true;
}
bool ParseHtml() { // 对.html文件进行解析,将结果保存到results中
for (const auto &file : file_list) { // file表示文件的路径
// 1.将文件中的内容读出来
string result;
if (!FileUtil::ReadFile(file, result)) {
cerr << "读取文件内容失败" << endl;
continue;
}
// 读取文件内容成功
DockInfo temp;
// 2.提取标题、提取摘要、构建URL
if (!ParseTitle(result, temp.title)) {
cerr << "提取标题失败" << endl;
continue;
}
if (!ParseContent(result, temp.content)) {
cerr << "提取摘要失败" << endl;
continue;
}
if (!ParseUrl(file, temp.url)) {
cerr << "构建Url失败" << endl;
continue;
}
// 调试
// cout << "标题: " << temp.title << endl;
// cout << "摘要: " << temp.content << endl;
// cout << "URL: " << temp.url << endl;
// break;
// 3.将结果push到result
results.push_back(std::move(temp));
}
return true;
}
下面考虑如何实现ReadFile(读取文件内容,存放到result中)、ParseTitle(提取标题)、ParseContent(提取摘要)、ParseUrl(构建URL)。
读取文件ReadFile:考虑使用C++的ifstream输入流读取文件:
static bool ReadFile(const string &filepath, string &result) {
// 将filepath中的内容读取到result中
ifstream in(filepath);
if (!in.is_open()) {
cerr << "打开文件 " << filepath << " 失败" << endl;
return false;
}
string tmp;
while (std::getline(in, tmp)) { // getline的返回值是一个istream的对象,其内部重载了强制类型转换
result += tmp;
}
in.close();
return true;
}
获取标题ParseTitle
在HTML文件中,标题位于<title>和</title>之间,例如下面的例子中,标题就是"Acknowledgements"
<title>Acknowledgements</title>
ParseTitle的主逻辑就是找到<title>的最后一个>的位置x,找到</title>的第一个<的位置y,位于x和y之间的内容就属于标题。
static bool ParseTitle(const string &result, string &title) {
size_t x = result.find("<title>");
if (x == string::npos) {
cerr << "找不到标题的开始" << endl;
return false;
}
size_t start = x + 7; // 标题的开始下标
size_t y = result.find("</title>");
if (y == string::npos) {
cerr << "找不到标题的结束" << endl;
return false;
}
size_t end = y - 1; // 标题的结束下标
title = result.substr(start, end - start + 1);
return true;
}
获取摘要ParseContent
获取摘要的过程就是进行去标签的过程,例如对于下面的HTML,去除标签以后就是"User’s Guide"
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>User's Guide</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../../../doc/src/boostbook.css" type="text/css">
ParseContent函数可以使用状态机完成
static bool ParseContent(const string &result, string &content) {
enum status {
LABLE, // 标签
CONTENT // 摘要
};
// 使用一个简单的状态机完成去标签
enum status s = LABLE;
for (char c : result) {
switch (s) {
case LABLE:
if (c == '>') { // 表示当前标签处理完毕
s = CONTENT;
}
break;
case CONTENT:
if (c == '<') { // 表示又遇到了一个标签
s = LABLE;
} else {
if (c == '\n') { // 文本中的'\n'将其去除,因为我们使用'\n'作为解析之后的文本分隔符
c = ' ';
}
content += c; // 添加到摘要中
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return true;
}
ParseUrl构建URL
我们想要构建出的URL是Boost官网中的一个URL,Boost官网中一个普通的URL格式如下:
https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_81_0/doc/html/accumulators.html
其对应在"boost_1_81_0"文件中的路径如下
boost_1_81_0/doc/html/accumulators.html
其对应在本地路径如下
data/input/accumulators.html
也就是说,我们将本地路径下的地址去掉data/input/,然后拼接到https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_81_0/doc/html/后面即可形成一个Boost官网的URL。
static bool ParseUrl(const string &filepath, string &url) {
string url_head = "https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_81_0/doc/html/";
// 使用boost库提供的FileSystem进行文件遍历得到的filepath的格式是"./data/input/..."
url += url_head;
int size = src_path.size();
url += filepath.substr(size); // 从./data/input/后面一直截取到结尾
return true;
}
使用打印进行初步调试
bool ParseHtml() { // 对.html文件进行解析,将结果保存到results中
for (const auto &file : file_list) { // file表示文件的路径
// 1.将文件中的内容读出来
string result;
if (!FileUtil::ReadFile(file, result)) {
cerr << "读取文件内容失败" << endl;
continue;
}
// 读取文件内容成功
DockInfo temp;
// 2.提取标题、提取摘要、构建URL
if (!ParseTitle(result, temp.title)) {
cerr << "提取标题失败" << endl;
continue;
}
if (!ParseContent(result, temp.content)) {
cerr << "提取摘要失败" << endl;
continue;
}
if (!ParseUrl(file, temp.url)) {
cerr << "构建Url失败" << endl;
continue;
}
//调试
cout << "标题: " << temp.title << endl;
cout << "摘要: " << temp.content << endl;
cout << "URL: " << temp.url << endl;
break;
// 3.将结果push到result
results.push_back(std::move(temp));
}
return true;
}
SaveHtml:将处理完毕的数据保存到指定文件(dst_file)中
SaveHtml实际上是将vector<DockInfo> results;中的内容写入到const string dst_file = "./data/raw_html/raw.txt";文件中,在进行写入时,每一个DockInfo之间用\n作为分隔符,DockInfo内部的title、content和url用\3作为分割符,这样做的目的是方便在使用getline进行读取时,一次可以读取一个完整的DockInfo,并且可以以\3作为分割对读取到的内容进行解释。
bool SaveHtml() { // 将results的结果回写到dst_file
std::ofstream out(dst_file, std::ios::out | std::ios::binary);
if (!out.is_open()) {
cerr << "打开文件失败" << endl;
return false;
}
for (const auto &doc : results) {
out << doc.title << '\3' << doc.content << '\3' << doc.url << '\n';
}
out.close();
return true;
}
建立索引Index
建立索引从宏观上需要建立正排索引和倒排索引,正排索引建立文档id与文档内容之间的索引,倒排索引建立关键字与文档id之间的索引。将建立索引的逻辑在index.h中进行实现。
index.h的主要结构:
namespace ns_index {
struct DocInfo { // 正排索引对应结构体
string title; // 文档标题
string content; // 文档内容
string url; // 在Boost官网中的URL
size_t doc_id; // 文档id
};
struct InvertedElme { // 倒排索引对应结构体
int doc_id; // 文档id
string word; // 关键字
size_t weight; // 文档id的权值
};
// 倒排拉链
using InvertedList = vector<InvertedElme>;
class Index {
public:
DocInfo *GetForwardIndex(const size_t doc_id) { // 根据文档id获取文档相关信息
}
InvertedList *GetInvertedList(const string &word) { // 根据关键字获得倒排拉链
}
// 根据raw.txt文件的内容构建索引,raw.txt中存放的是所有HTML文件解析完毕之后的数据
bool BulidIndex(const string &raw_filepath) {
}
private:
vector<DocInfo> forward_index; // 正排索引,forward_index[i]表示文档id为i的DocInfo信息
unordered_map<string, InvertedList> inverted_index; // 倒排索引,一个关键字对应多个InvertedElme结构(多个文档id)
};
} // namespace ns_index
建立索引的过程主要就是实现Index类中的函数。
正排与倒排
GetForwardIndex与GetInvertedList函数的实现较简单:
DocInfo *GetForwardIndex(const size_t doc_id) { // 根据文档id获取文档相关信息
if (doc_id < size(forward_index)) {
return forward_index.data() + doc_id;
}
return nullptr;
}
InvertedList *GetInvertedList(const string &word) { // 根据关键字获得倒排拉链
if (inverted_index.count(word) == 0) {
return nullptr;
}
return &inverted_index[word];
}
构建索引
构建索引需要构建正排索引和倒排索引,需要将raw.txt的数据读取到内存,分析数据,进行构建索引。
BulidIndex的框架:
bool BulidIndex(const string &raw_filepath) {
// 1.按行读取文件中的内容
ifstream ifs(raw_filepath, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary);
if (!ifs.is_open()) {
cerr << "打开文件失败" << endl;
return false;
}
string line; // 按行读取
while (getline(ifs, line)) {
// 2.建立正排索引
DocInfo *doc = BulidForwardIndex(line);
if (doc == nullptr) {
cerr << "建立正排索引失败" << endl;
continue;
}
// 3.建立倒排索引
if (BulidInvertedIndex(doc) == false) {
cerr << "建立倒排索引失败" << endl;
}
}
}
DocInfo *BulidForwardIndex(const string line) {
}
bool BulidInvertedIndex(DocInfo *doc) {
}
正排索引
建立正排索引时,在BulidForwardIndex函数的内部会根据line构建出对应的DockInfo结构体,将其插入到forward_index中,并返回forward_index中对应的DocInfo的地址。
BulidForwardIndex的步骤:
- 对line进行解析,按照\3作为分隔符,提取出title、content、url
- 将解析完毕的内容填充到DocInfo
- 插入到forward_index中
其中第一步解析字符串的函数作为字符串相关操作在util.h文件中单独给出,并将其封装在StringUtil类中,这里我们使用Boost库中的split函数直接完成字符串的切分。
class StringUtil {
public:
static void CutString(const string &str, vector<string> &vs, string sep /*分隔符*/) {
boost::split(vs /*切分完毕放到vs中*/, str /*要切分的串*/, boost::is_any_of(sep) /*分隔符*/, boost::token_compress_on);
}
};
建立正排索引整体代码如下:
DocInfo *BulidForwardIndex(const string line) {
DocInfo info;
// 1.将line按照\3为分割进行切分
vector<string> vs; // 切分完成的数据放到vs中
StringUtil::CutString(line, vs, "\3");
if (size(vs) != 3) {
return nullptr;
}
// 2.解析完毕的内容填入到DocInfo中
info.title = move(vs[0]);
info.content = move(vs[1]);
info.url = move(vs[2]);
info.doc_id = size(forward_index);
// 3.插入到vector中
forward_index.push_back(move(info));
return &forward_index.back();
}
倒排索引步骤
倒排索引是将关键字映射到文档id中,倒排索引函数的声明如下:
bool BulidInvertedIndex(DocInfo *doc);
根据传入的doc,即可建立倒排索引,doc中含有title、content、url以及文档id(doc_id)。
-
首先根据title、content提取出关键词。例如title=“鲤鱼”,content=“红鲤鱼与绿鲤鱼与驴”
vector<string> title_word; title_word.push_back("鲤鱼"); title_word.push_back("鱼"); vector<string> content_word; content_word.push_back("红鲤鱼"); content_word.push_back("鲤鱼"); content_word.push_back("鱼"); content_word.push_back("绿鲤鱼"); content_word.push_back("鲤鱼"); content_word.push_back("鱼"); content_word.push_back("驴"); -
进行词频统计,需要分别统计标题和内容中关键词出现的次数,例如"鲤鱼"在标题中出现了1次,在内容中出现了2次
struct word_cnt{ size_t title_cnt=0;//某一个关键词在标题中出现的次数 size_t content_cnt=0;//某一个关键词在内容中出现的次数 }; unordered_map<string,word_cnt> word_hash; for(const string& word:title_word){//统计标题中的关键词出现的次数 word_hash[word].title_cnt++; } for(const string& word:content_word){//统计内容中的关键词出现的次数 word_hash[word].content_cnt++; } -
统计完毕每一个词在标题和内容中出现的次数,就可以进行自定义相关性。
关键词 在标题中出现的次数 在内容中出现的次数 鱼 1 2 鲤鱼 1 2 红鲤鱼 0 1 绿鲤鱼 0 1 驴 0 1 所谓自定义相关性,就是通过关键字出现的次数,为每一个关键字计算出一个权值,例如在文档A中,关键字"葡萄"出现了3次,葡萄在文档A中的权值是3;而在文档B中,关键字葡萄出现了5次,葡萄在文档B中的权值是5,那么在根据葡萄这个关键字进行搜索时,优先显示文档B,第二个显示文档A。
struct InvertedElme { // 倒排索引对应结构体 int doc_id; // 文档id string word; // 关键字 size_t weight; // 权值(文档中特定关键字的权值) };上面的例子中,关键词的数目为5,那么就需要5个InvertedElme结构,表示不同的关键词,它们的doc_id相同,根据出现的次数按照一定规则计算出权值,并添加到倒排索引中。
for(auto& w_pair:word_hash){ InvertedElme temp; temp.doc_id=1; temp.word=w_pair.first; //认为如果关键词出现在了标题中,那么权值计算大一点 temp.weight=w_pair.second.title_cnt*10+w_pair.second.content_cnt; //将其添加到倒排拉链中(倒排索引:根据词找到doc_id) inverted_index[temp.word].push_back(move(temp)); }
倒排索引实现
-
根据标题和内容,提取关键词(分词)。这里使用jieba分词库,jieba是一个开源的,head-only的开源第三方库。在util.h文件中实现一个JiebaUtil类,用于实现分词。
// 词库 static const char *const TEST_FILE = "./ThirdPart/cppjieba/test/testdata/testlines.utf8"; static const char *const JIEBA_DICT_FILE = "./ThirdPart/cppjieba/dict/jieba.dict.utf8"; static const char *const HMM_DICT_FILE = "./ThirdPart/cppjieba/dict/hmm_model.utf8"; static const char *const USER_DICT_FILE = "./ThirdPart/cppjieba/dict/user.dict.utf8"; class JiebaUtil { public: static void CutString(const string &words, vector<string> &vs) { seg.cut(words, vs); } private: inline static MixSegment seg = MixSegment(JIEBA_DICT_FILE, HMM_DICT_FILE); }; -
能够进行分词以后,就可以按照倒排索引的步骤进行建立索引,在建立索引时应该注意:关键字不区分大小写,例如搜索"hello world"与"HELLO WORlD"的结果应该是一样的,因此在倒排拉链中,作为key值的关键字统一使用小写。
bool BulidInvertedIndex(DocInfo *doc) { // 建立倒排索引 // 1.提取关键词 vector<string> title_words; JiebaUtil::CutString(doc->title, title_words); vector<string> content_words; JiebaUtil::CutString(doc->content, content_words); // 2.进行词频统计 struct word_cnt { size_t title_cnt = 0; // 某一个关键词在标题中出现的次数 size_t content_cnt = 0; // 某一个关键词在内容中出现的次数 }; unordered_map<string, word_cnt> word_hash; for (string &word : title_words) { // 统计标题中的关键词出现的次数 boost::to_lower(word); // 转化为小写,忽略大小写 word_hash[word].title_cnt++; } for (string &word : content_words) { // 统计内容中的关键词出现的次数 boost::to_lower(word); // 转化为小写,忽略大小写 word_hash[word].content_cnt++; } // 3.自定义相关性 for (auto &w_pair : word_hash) { InvertedElme temp; temp.doc_id = doc->doc_id; temp.word = w_pair.first; #define X 10 #define Y 1 // 认为如果关键词出现在了标题中,那么权值计算大一点 temp.weight = w_pair.second.title_cnt * X + w_pair.second.content_cnt; // 将其添加到倒排拉链中(倒排索引:根据词找到doc_id) inverted_index[temp.word].push_back(move(temp)); } }
搜索模块searcher
搜索模块的宏观思路:
- 首先根据处理完毕的数据构建出来索引(正排和倒排)
- 提供一个search函数,根据用户输入的关键词,返回相应的结果,这个结果是一个序列化后的字符串,后序会根据序列化后的字符串构建出json
将Index类设计为单例,全局只有一份,将search函数封装在Searcher类中,Search类整体框架如下:
namespace ns_searcher {
class Searcher {
public:
void InitSearch(const string &file_path) { // 进行初始化,构建索引
ns_index::Index::GetInst()->BulidIndex(file_path);
}
string Search(const string &query) { // 根据用户请求,返回结果
}
};
} // namespace ns_searcher
Search
-
需要将用户的请求进行分词,例如用户搜索的词是"vector and string",需要将其分词为"vector"和"string"
-
触发,根据用户提供的关键词,进行Index查找,注意在查找时需要统一转化为小写,然后进行查找。在查找时,使用倒排索引,根据关键词获得对应的倒排拉链,从中提取出文档id,在根据文档id进行正排索引,获得相关数据。
string Search(const string &query) { // 根据用户请求,返回序列化后的字符串 // 1.分词 vector<string> words; JiebaUtil::CutString(query, words); // 2.触发 using namespace ns_index; vector<InvertedElme> allElme; // 保存所有根据关键词拿到的结果 for (string &word : words) { boost::to_lower(word); // 根据词进行查找 auto Invertedlist = ns_index::Index::GetInst()->GetInvertedList(word); // 获取倒排拉链 if (Invertedlist == nullptr) { continue; // 表示这个关键字不存在 } allElme.insert(std::end(allElme), Invertedlist->begin(), Invertedlist->end()); } // 对allElem中的结果按照权值进行排序(降序) std::sort(begin(allElme), end(allElme), [](const InvertedElme &l, const InvertedElme &r) { return l.weight > r.weight; }); // 3.根据结果构建序列化后的字符串并进行返回 }在allElme中,可能存在文档id重复的InvertedElme(权值可能不同),此时可以考虑去重或者将文档id重复的InvertedElme的权值进行合并,该操作后续完成。
sort的升序与降序记忆方案
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-z5eMTiOv-1680706818361)(.\picture\image-20230401180348541.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1c9dd570b0e041fba47c7b2fb27ae4f3.png)
左边大于右边,降序,反之升序。
-
将allElme中的内容进行序列化。
allElme中保存的是倒排的结果,保存了文档id(doc_id),关键字(word)和权值(weight),需要根据文档id进行正排索引获取到文档信息,将文档信息进行序列化。序列化使用jsoncpp库,安装jsoncpp库:
sudo apt-get install libjsoncpp-dev,使用时需要包含头文件<jsoncpp/json/json.h>,链接时需要带选项-ljsoncpp。序列化的代码:
string Search(const string &query) { // 1.分词 // 2.触发 // 3.将结果序列化 Json::Value root; for (auto &item : allElme) { // item中保存了id,word和权值 auto doc = Index::GetInst()->GetForwardIndex(item.doc_id); assert(doc != nullptr); // 理论上doc不可能为nullptr,因为item是根据倒排索引得到的,倒排索引又依赖于正排索引构建 Json::Value temp; temp["title"] = doc->title; temp["desc"] = doc->content;//文档的描述。conten是文档去标签之后的结果,后续需要对content进行操作得到摘要 temp["url"] = doc->url; root.append(temp); } return Json::StyledWriter().write(root);//返回序列化后的结果 }
测试搜索模块
可以使用以下代码对搜索模块进行简单测试:
#include "Searcher.h"
int main() {
ns_searcher::Searcher s;
s.InitSearch("./data/raw_html/raw.txt");
while (1) {
string key;
cout << "Please Input#";
cin >> key;
cout << s.Search(key);
}
return 0;
}
当输入关键字后,虽然可以得到结果,但是由于文档的描述过长,信息混乱,因此需要对文档的content进行分析,只提取出其中的关键数据作为摘要,即序列化的代码应该进行修改:
string Search(const string &query) {
// 1.分词
// 2.触发
// 3.将结果序列化
Json::Value root;
for (auto &item : allElme) {
// item中保存了id,word和权值
auto doc = Index::GetInst()->GetForwardIndex(item.doc_id);
assert(doc != nullptr); // 理论上doc不可能为nullptr,因为item是根据倒排索引得到的,倒排索引又依赖于正排索引构建
Json::Value temp;
temp["title"] = doc->title;
temp["content"] = GetDesc(doc->content,item.word);//获取摘要
temp["url"] = doc->url;
root.append(temp);
}
return Json::StyledWriter().write(root);//返回序列化后的结果
}
GetDesc函数根据关键字word对content的内容提取摘要,其步骤如下:
- 在content中找到word,提取前50字节和后100字节的的内容,进行返回
- 如果前面不够50字节,那么有多少字节拿多少
- 如果后面不够100字节,有多少拿多少
- 在最后添加上省略号
GetDesc函数的实现:
static string GetDesc(string &content, const string &word) {
boost::to_lower(content);//将content转换为小写,进行忽略大小写的查找
size_t firstpos = content.find(word);
assert(firstpos != string::npos);
#define PREV_SIZE 50
#define NEXT_SIZE 100
size_t start = 0;
size_t end = size(content) - 1;
if (start + PREV_SIZE < firstpos) {
start = firstpos - PREV_SIZE;
}
if (firstpos + NEXT_SIZE <= end) {
end = firstpos + NEXT_SIZE;
}
return content.substr(start, end - start + 1) + "......";
}
上面代码中Boost::to_lower可以进行改进,我们的目的是忽略大小写在content中找到word首次出现的位置,可以使用STL中的search。
auto it = std::search(begin(content), end(content), begin(word), end(word), [](char x, char y) -> bool { return std::tolower(x) == std::tolower(y); });
assert(it != end(content));
size_t firstpos = std::distance(begin(content), it);
至此,搜索模块编写完成,通过Boost网页测试可以发现,某些关键字在进行搜索时,其权值与网页中出现的次数不一样,主要是因为jieba库在进行分词时,存在一定的误差,例如针对以下文档:
Format: The format library provides a type-safe mechanism for formatting arguments according to a printf-like format-string.
jieba在进行分词时不会将单词formatting拆分为format 和ting,这样就会导致在网页使用Ctrl + F进行搜索时,得到format关键字出现的次数是2,但是搜索引擎在进行搜索format时,得到的format关键字的权值是1。
HTTP-Server模块编写
搜索模块编写完成之后,需要编写HTTP服务端进行网络通信,获取到用户发送过来的关键字,将结果返回给用户。这里使用现有的cpp-httplib库来完成HTTP服务的编写。
cpp-httplib是一个head-only的开源库,简单的demo:
#include "../ThirdPart/cpp-httplib/httplib.h"
const std::string root_path = "../wwwroot";
int main() {
httplib::Server ser;
ser.set_base_dir(root_path); //设置Web根目录
ser.Get("/hi", [](const httplib::Request &req, httplib::Response &rsp) {
rsp.set_content("你好", "text/plain;charset=UTF-8");
});
ser.listen("0.0.0.0", 8081); //设置全连接队列的最大长度
return 0;
}
Get函数:当用户请求Web根目录下的某一文件夹下的资源时,用户的请求保存在req中,lambda表达式函数体中会根据用户的请求和目录构建响应写入到rsp中,最终rsp中的内容会返回给用户。这个工作由库完成,在使用Get函数时只需要编写好对应的lambda表达式或回调函数即可。
HTTP-Server编写步骤:
- 根据清洗完毕的数据建立正排索引和倒排索引(前面已经完成)
- 读取用户发送过来的关键字,根据关键字进行搜索
- 将搜索结果进行返回
整体代码如下:
#include "./ThirdPart/cpp-httplib/httplib.h"
#include "Searcher.h"
const std::string root_path = "./wwwroot";
int main() {
ns_searcher::Searcher::InitSearch("./data/raw_html/raw.txt"); // 初始化搜索引擎
httplib::Server ser;
ser.set_base_dir(root_path);
ser.Get("/s", [](const httplib::Request &req, httplib::Response &rsp) {
if (!req.has_param("word")) { // 表示URL中没有携带关键字(参数)
rsp.set_content("输入的URL中不携带任何关键字!", "text/plain; charset=UTF-8");
return;
}
std::string word = req.get_param_value("word"); // 提取用户传递的关键字
cout << "用户搜索的关键字是 " << word << endl;
// 根据关键字构建响应
string json_str = ns_searcher::Searcher::Search(word);
rsp.set_content(json_str, "application/json");
});
ser.listen("0.0.0.0", 8081);
return 0;
}
由于我们返回的是序列化后的字符串,显示在网页上不美观,因此接下来编写前端模块使显示内容更加美观,且可以实现网页跳转。(由于Get函数的第一个参数表明了路径,因此在使用浏览器访问服务器时,除了需要指明IP+PORT,还需要指明要访问资源的路径"/s",除此之外,若要携带关键字,应该添加"?word=关键字")
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-oTmHD4ek-1680706818362)(.\picture\image-20230403201222924.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8cfdf2c73e304e4ab51ed7563aa2d503.png)
编写前端模块
前面模块编写html、css、js
- vscode中新建.html文件,使用
'!'加上Tab键补全可以形成网页骨架 - 网页由大量标签构成,标签分为单标签和双标签,例如
<meta charset="UTF-8">就是典型的单标签,而<title>Boost 搜索引擎</title>就是典型的双标签。 - html负责网页的结构,css负责网页的美观,js(javascript)负责网页的动态效果与前后端交互
前端模块代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/3.5.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<title>Boost 搜索引擎</title>
<style>
/*去掉网页中所有的内外边距*/
* {
margin: 0;
/*设置外边距*/
padding: 0;
/*设置内边距*/
}
html,
body {
/*将body的内容100%与网页的呈现吻合*/
height: 100%;
}
/* 类选择器 */
.container {
width: 800px;
margin: 0px auto;
margin-top: 15px;
}
/* 复合选择器 */
.container .search {
width: 100%;
height: 52px;
}
.container .search input {
float: left;
/*设置框的属性*/
width: 600px;
height: 27px;
border: 3px solid skyblue;
/*设置边框边缘线*/
border-right: none;
padding-left: 10px;
}
.container .search button {
float: left;
width: 50px;
height: 33px;
background-color: #4e6ef2;
color: aliceblue;
font-size: medium;
font-family: 'Segoe UI', Tahoma, Geneva, Verdana, sans-serif
}
.container .result {
width: 100%;
}
.container .result .item {
margin-top: 15px;
}
.container .result .item a {
display: block;
text-decoration: none;
/*去掉标题下划线*/
font-size: 20px;
/*设置标题字体大小*/
/* 设置标题字体颜色 */
color: #4e6ef2;
}
.container .result .item a:hover {
/* 设置鼠标放在文字上的动态效果 */
text-decoration: underline;
}
.container .result .item p {
font-size: 17px;
font-family: 'Segoe UI', Tahoma, Geneva, Verdana, sans-serif;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.container .result .item i {
display: block;
font-style: normal;
color: burlywood;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="search">
<input type="text" value="">
<button onclick="Search()">搜索</button>
</div>
<div class="result">
<!-- <div class="item">
<a href="#">这是标题</a>
<p>这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要</p>
<i>这是URL</i>
</div> -->
</div>
</div>
<script>
function Search() {
// alert("hello")
let query = $(".container .search input").val();
// console.log("query =" + query);
$.ajax({
type: "GET",
url: "/s?word=" + query,
success: function (data) {
console.log(data);
BuildHtml(data);
}
});
}
function BuildHtml(data) {
let result_table = $(".container .result");
result_table.empty();
for (let elem of data) {
let a_lable = $("<a>", {
text: elem.title,
href: elem.url,
/*跳转*/
target: "_blank"
});
let p_lable = $("<p>", {
text: elem.content
});
let i_table = $("<i>", {
text: elem.url
});
let div_lable = $("<div>", {
class: "item"
});
a_lable.appendTo(div_lable);
p_lable.appendTo(div_lable);
i_table.appendTo(div_lable);
div_lable.appendTo(result_table);
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
优化
去除重复结果
在实际进行搜索时,可能出现重复的结果:
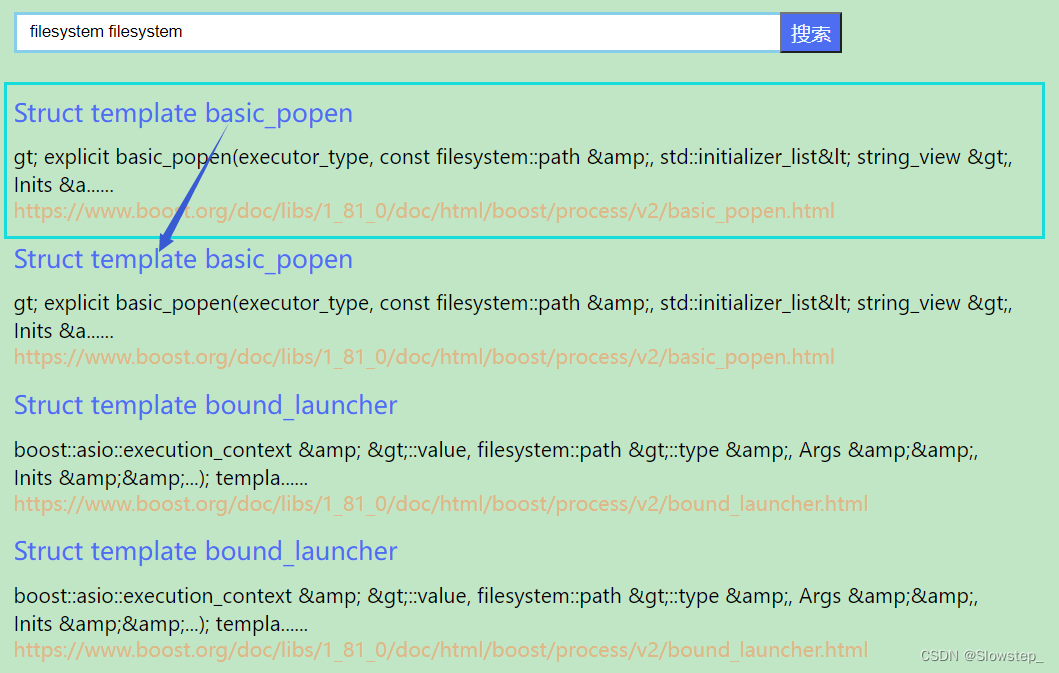
原因:在搜索"filesystem filesystem"时,搜索模块会对query进行分词,分词为2个filesystem,进行2次重复的检索,因此需要对Search函数进行优化,去除掉重复的结果。此外,在进行搜索时,即使搜索关键字中没有出现重复,但是根据关键字检索
得出的结果也有可能出现重复,此时可以考虑将重复的结果进行合并,权值累加。
增加一个InvertedElmePrint结构,并对Search函数进行修改,达到去重的效果
struct InvertedElmePrint {
int doc_id; // 关键字检索出来的相同结果
vector<string> words; // 关键字
size_t weight; // 权值
};
修改后的Search函数:
static string Search(const string &query) { // 根据用户请求,返回结果
// 1.分词
vector<string> words;
JiebaUtil::CutString(query, words);
// 将words中的所有空串去掉,例如" "、" "
for (auto it = begin(words); it != end(words);) {
bool flag = false;
for (char c : *it) {
if (c != ' ') {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if (flag) {
it++;
} else {
it = words.erase(it);
}
}
// 2.触发
using namespace ns_index;
unordered_map<int, InvertedElmePrint> hash; // doc_id ---> doc_id + vector<string> words + weight
for (string &word : words) {
boost::to_lower(word);
// 根据词进行查找
auto Invertedlist = ns_index::Index::GetInst()->GetInvertedList(word); // 获取倒排拉链
if (Invertedlist == nullptr) {
continue; // 表示这个关键字不存在
}
// cout << "关键字" << word << "对应的文档有" << Invertedlist->size() << "篇" << endl;
for (auto &epair : *Invertedlist) { // 遍历文档
hash[epair.doc_id].doc_id = epair.doc_id;
hash[epair.doc_id].weight += epair.weight; // 权值进行累加
hash[epair.doc_id].words.push_back(word);
}
// cout << "存储key-val哈希表的表大小为: " << hash.size() << endl;
}
vector<InvertedElmePrint> allElme;
for (auto &epair : hash) {
allElme.push_back(move(epair.second));
}
// 对allElem中的结果按照权值进行排序(降序)
std::sort(begin(allElme), end(allElme), [](const InvertedElmePrint &l, const InvertedElmePrint &r) { return l.weight > r.weight; });
Json::Value root;
for (auto &item : allElme) {
// item中保存了id,word和权值
auto doc = Index::GetInst()->GetForwardIndex(item.doc_id);
assert(doc != nullptr); // 理论上doc不可能为nullptr,因为item是根据倒排索引得到的,倒排索引又依赖于正排索引构建
Json::Value temp;
temp["title"] = doc->title;
temp["content"] = GetDesc(doc->content, item.words[0]); // 获取摘要
temp["url"] = doc->url;
// temp["weight"] = item.weight;
// temp["doc_id"] = item.doc_id;
root.append(temp);
}
return Json::FastWriter().write(root); // 返回序列化后的结果
}
由于在jieba分词中,会将空格也分词为一个关键字,这样会导致大量的无关文档被查询到,因此应该去除掉空格。
添加日志信息
可以通过C语言的预处理指令和__LINE__、__TIME__、__FILE__、__DATE__等宏封装一个日志,将程序输出的信息都打印到日志上。
log.h
#pragma once
// 封装一个日志
#include <cstdarg> //va_start,va_list,va_end宏的头文件
#include <cstdio>
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
// 日志级别
#define DEBUG 0
#define NORMAL 1
#define WARNING 2
#define ERROR 3
#define FATAL 4 // 致命
static const char *levelmap[] = {"DEBUG", "NORMAL", "WARNING", "ERROR", "FATAL"};
static void logMessage(int level, const char *format, ...) {
#ifdef DEBUG_SHOW // 可通过gcc编译选项添加宏
if (level == DEBUG) {
return;
}
#endif
static char buffer[BUFSIZ]; // 可反复使用
va_list args;
va_start(args, format);
vsnprintf(buffer, sizeof buffer, format, args); // 将可变参数存放至buffer中
va_end(args);
FILE *pf = fopen("README.log", "a"); // 追加方式打开,不存在就创建
if (pf == nullptr) {
// 直接将日志输出到屏幕
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n%s\n%s\n%s\n", buffer, __FILE__, __DATE__, __TIME__);
return;
}
// 否则将日志写到文件
fprintf(pf, "%s\n%s\n%s\n%s\n", buffer, __FILE__, __DATE__, __TIME__);
fclose(pf);
return;
}
补充一个C语言中宏的用法
#define DEBUG 0
#define NORMAL 1
#define WARNING 2
#define ERROR 3
#define FATAL 4 // 致命
#define LOG(LEVEL) log(#LEVEL) //将宏替换过程中的LEVEL参数转化为字符串
void log(string level){
cout<<level<<endl;
}
LOG(DEBUG); //--->log("DEBUG")
守护进程化
将服务作为守护进程部署到后台,只要Linux机器不关机,就可以一直提供服务。守护进程具有如下特点:
- 自成一个会话,可以不依赖于终端
- 组长进程不能是守护进程
- 守护进程不能向显示器打印消息,否则可能会被暂停或终止
- 调用
setsid函数可以让一个进程变成守护进程
可以通过以下代码让服务进程守护进程化:
static void MyDaemon() {
signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_IGN);
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
int fd = open("/dev/null", O_RDWR);
dup2(fd, 0);//将标准输入重定向到/dev/null
close(fd);
fd=open("./log/README.log",O_RDWR);
dup2(fd,1);
dup2(fd,2);//将标准输出和标准错误重定向到日志文件
close(fd);
if (fork() > 0) {
exit(0);
}
// 走到这里的就是子进程,此时子进程变为孤儿进程,且子进程一定不是组长进程
setsid(); // 子进程调用setsid变成守护进程,进行服务器端的服务
}
在服务器进程启动之前,调用MyDaemon函数即可。另外,使用命令nohup也可以创建一个守护进程:
nohup ./httpserver > log/README.log 2>&1 & #2>&1表示重定向,最后一个&表示后台进程
去掉暂停词
我们的程序在进行搜索时,可以考虑去掉暂停词,例如搜索is,会出现大量结果。![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-e7Dpb4d9-1680706818364)(.\picture\image-20230405193930674.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e195a4daaee3439d999caa6f0b19f4fb.png)
可以考虑将所有的暂停词存入到unordered_map中,在进行jieba分词时,直接将暂停词去掉。在cppjeba/dict下存在一个文件stop_words.utf8,该文件中存放了几乎所有的暂停次,只需要将该文件中的数据读取到内存即可,可以对JiebaUtil类进行如下修改:
class JiebaUtil {
public:
static void CutString(const string &words, vector<string> &vs) {
seg.cut(words, vs);
int x = 0;
for (auto it = begin(vs); it != end(vs);) {
if (stop_words.count(*it)) {
it = vs.erase(it);
} else {
it++;
}
// cout << x++ << endl;
}
}
static void ReadStopWords() {
// 读取暂停词
ifstream in(STOP_WORDS_PATH, std::ios::in);
assert(in.is_open());
string temp;
int cnt = 0;
while (getline(in, temp)) {
stop_words.insert(temp);
cnt++;
}
}
private:
inline static MixSegment seg = MixSegment(JIEBA_DICT_FILE, HMM_DICT_FILE);
inline static unordered_set<string> stop_words; // 存放暂停词
};
注意:由于有的文档中content字段较大,因此在BulidInvertedIndex函数中调用JiebaUtil::CutString函数花费的时间较长,需要7~8min。
扩展
-
项目在对数据源进行去标签时,html文件全部是从data/input/目录下得到的,可以考虑提取boost_1_81_0/目录下的所有html文件,建立整站搜索
-
在项目中使用到了cpp-httplib的库,可以考虑不使用组件,自己实现设计一个http服务器
-
可以设计在线更新方案,通过网页爬虫定时更新boost_1_81_0/文件,同时可以考虑引入信号机制达到更新正排索引和到倒排索引的目的
-
可以在搜索引擎中增加竞价排名的机制,本质上就是人为操控根据关键字得到的文档的权值
-
可以设置热词统计,使用字典树或优先级队列等数据结构,达到智能显示搜索关键词的目的
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-nQmEhEP1-1680706818364)(.\picture\image-20230405175105511.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e9d12270db964159bc83dfab537a23ed.png)
-
设置登录注册,考虑引入MySQL
项目代码:github





















 621
621











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








