目录
一、计算机底层层面是逻辑图,然后再深刻理解:程序、进程、线程、纤程
一、计算机底层层面是逻辑图,然后再深刻理解:程序、进程、线程、纤程
进程(重)->线程(普通)->纤程(轻)
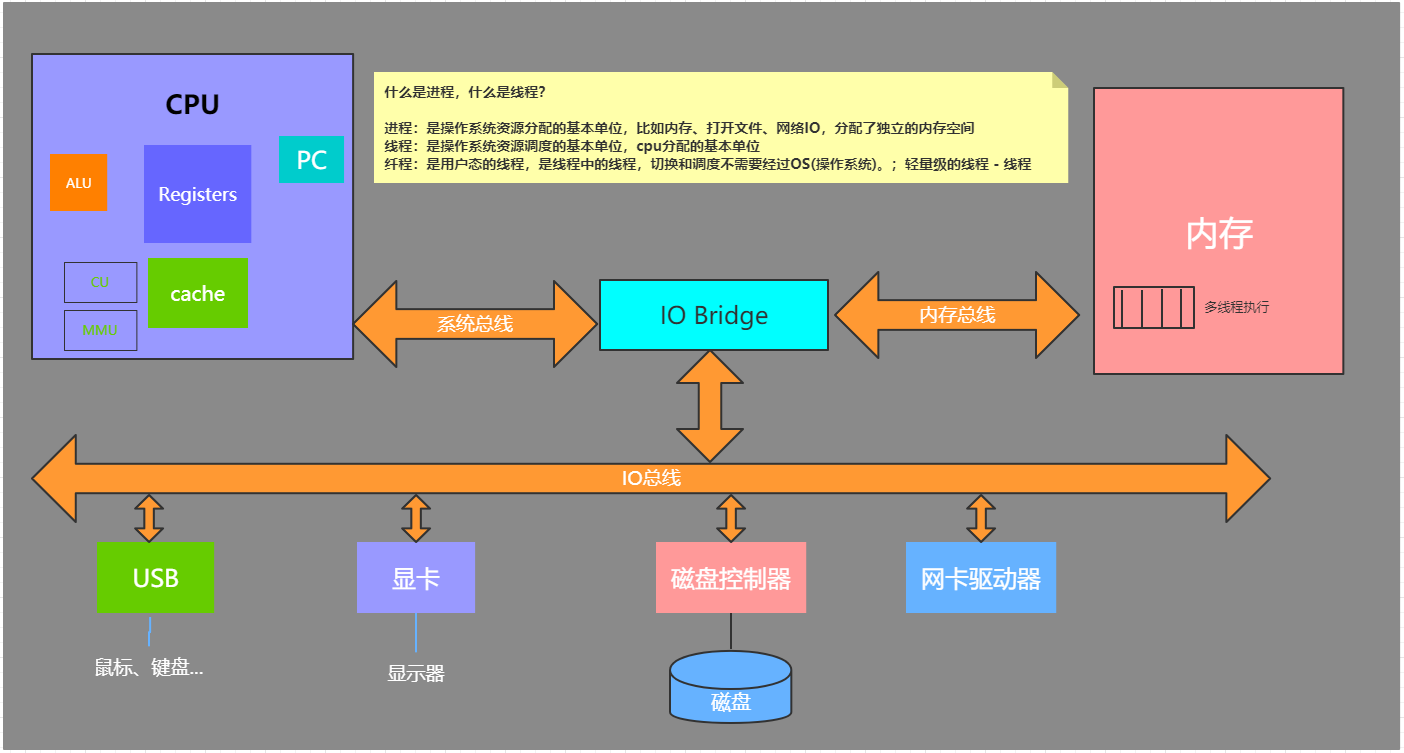
- 进程:是操作系统资源分配的基本单位,比如内存、打开文件、网络IO,分配了独立的内存空间
- 线程:是操作系统资源调度的基本单位,cpu分配的基本单位
- 纤程:是用户态的线程,是线程中的线程,切换和调度不需要经过OS(操作系统)。;轻量级的线程 - 线程
// 进程:是操作系统资源分配的基本单位,比如内存、打开文件、网络IO,分配了独立的内存空间
public class T0_Process {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("hello world");
}
}// 线程:是操作系统资源调度的基本单位,cpu分配的基本单位
public class T01_HelloFiber {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Runnable r = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
calc();
}
};
int size = 10000;
Thread[] threads = new Thread[size];
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(r);
}
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i].start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i].join();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
private static void calc() {
int result = 0;
for (int m = 0; m < 10000; m++) {
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
result += i;
}
}
}
}// 纤程:是用户态的线程,是线程中的线程,切换和调度不需要经过OS(操作系统)。;轻量级的线程 - 线程 ; java 原生没有提供纤程支持,需要依赖于 Quasar的库
public class T02_HelloFiberV2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int size = 10000;
Fiber<Void>[] fibers = new Fiber[size];
for (int i = 0; i < fibers.length; i++) {
fibers[i] = new Fiber<Void>(new SuspendableRunnable() {
@Override
public void run() throws SuspendExecution, InterruptedException {
calc();
}
});
}
for (int i = 0; i < fibers.length; i++) {
fibers[i].start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < fibers.length; i++) {
fibers[i].join();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
private static void calc() {
int result = 0;
for (int m = 0; m < 10000; m++) {
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
result += i;
}
}
}
}
纤程的应用场景:纤程 vs 线程池:很短的计算任务,不需要和内核打交道,并发量高!
二、线程数设多少
N(t)=N(cpu)*U(cpu)*(1+W/C)
N核数
U cpu利用率
W/C 等待时间/计算时间
等待和计算时间 :部署统计后;测试可用Profiler统计,上线后可用arthas
三、线程创建方式
1)继承Thread类创建线程
2)实现Runnable接口创建线程
3)使用Callable和Future创建线程
4)使用lambda表达式创建线程
4)使用线程池例如用Executor框架
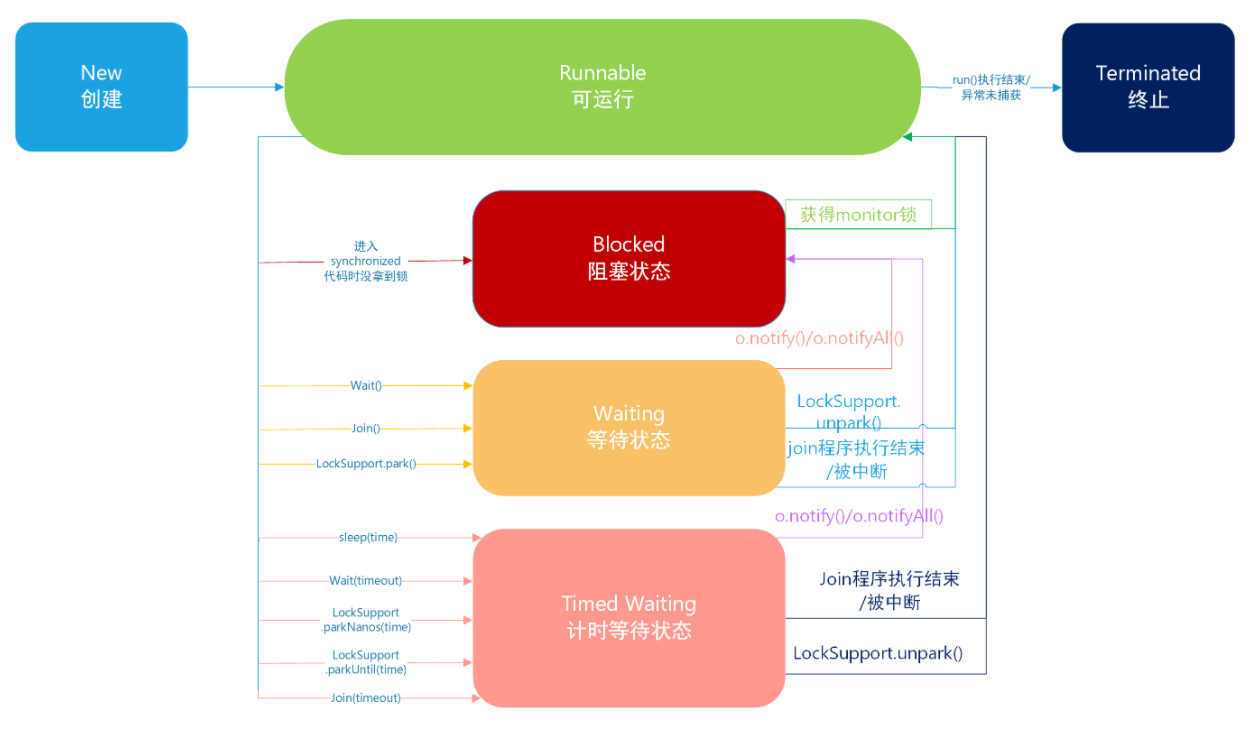
四、线程状态
- NEW : 线程刚刚创建,还没有启动
- RUNNABLE : 可运行状态,由线程调度器可以安排执行
- 包括READY和RUNNING两种细分状态
- WAITING: 等待被唤醒
- TIMED WAITING: 隔一段时间后自动唤醒
- BLOCKED: 被阻塞,正在等待锁
- TERMINATED: 线程结束
五、线程的打断(interrupt)
- interrupt() :实例方法,设置线程中断标志(设置标志位)
- isInterrupted():实例方法,有没有人打扰我?(查询标志位)
- interrupted():静态方法,有没有人打扰我(当前线程)?复位!
优雅的结束线程
- 自然结束(能自然结束就尽量自然结束)
- stop()(已废除,不建议使用,粗暴,造成数据不一致) suspend() resume() 也废除了,容易产生死锁
- volatile标志
- 不适合某些场景(比如还没有同步的时候,线程做了阻塞操作,没有办法循环回去)
- 打断时间也不是特别精确,比如一个阻塞容器,容量为5的时候结束生产者, 但是,由于volatile同步线程标志位的时间控制不是很精确,有可能生产者还继续生产一段儿时间
-
public class T03_VolatileFlag { private static volatile boolean running = true; public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t = new Thread(() -> { long i = 0L; while (running) { //wait recv accept i++; } System.out.println("end and i = " + i); //4168806262 4163032200 }); t.start(); SleepHelper.sleepSeconds(1); running = false; } }
- interrupt() and isInterrupted(比较优雅)
public class T04_Interrupt_and_NormalThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
//sleep wait
}
System.out.println("t1 end!");
});
t.start();
SleepHelper.sleepSeconds(1);
t.interrupt();
}
}




















 267
267











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








