✅博主简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,Matlab项目合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:海神之光
🏆代码获取方式:
海神之光Matlab王者学习之路—代码获取方式
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击👇
Matlab图像处理(进阶版)
路径规划(Matlab)
神经网络预测与分类(Matlab)
优化求解(Matlab)
语音处理(Matlab)
信号处理(Matlab)
车间调度(Matlab)
⛄一、简介
Gabor+SVM:利用Gabor程序实现对人脸的特征提取,然后用SVM进行分类;
1 Gabor
Gabor 特征提取算法可以在不同方向上描述局部人脸特征,对光照、遮挡以及表情变换等情况具有较强的鲁棒性,即Gabor算法在异常和危险情况下具有较强的系统生存的能力。
1.1 一维Gabor核:
其由一个高斯核与一个复数波的乘积定义为如下公式:
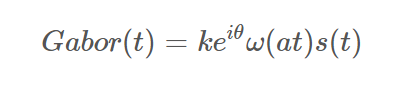
其中w(t)是高斯函数,s(t)是复数波,两者的一维数学表达式定义如下:
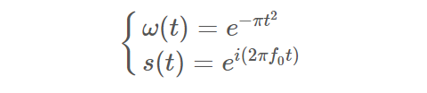
我们将s(t)代入一维Gabor公式可得下式:
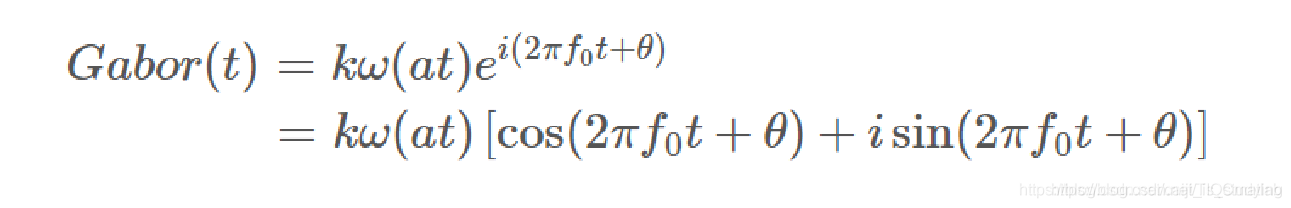
我们将上述一维情况推广到二维
二维复数波定义如下,其中(x,y)表示空间域坐标,(u0,v0)表示频率域坐标。
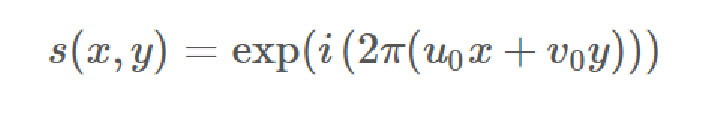
二维高斯函数定义如下,其中σx,σy 分别为在x,y两个方向上的尺度参数,用来控制高斯函数在两个方向上的“展布”形状。(x0,y0)为高斯函数的中心点。K为高斯核的幅度的比例。
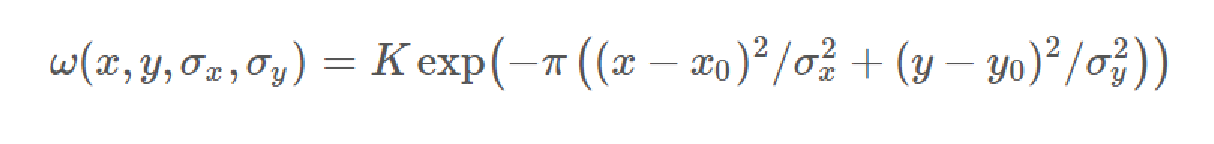
但是由于高斯函数还有旋转的操作,所以我们对坐标进行如下的变换:
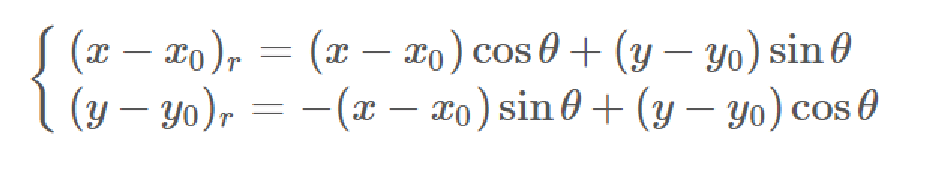
由此,我们得到了坐标变换后的高斯函数公式,其中θ表示高斯核顺时针旋转的角度。
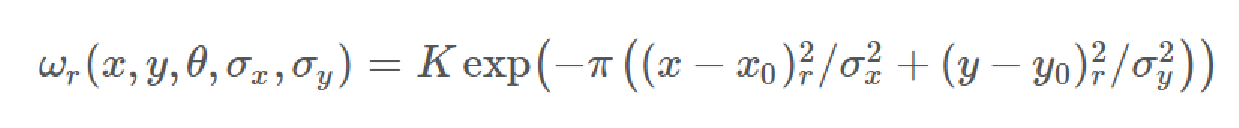
1.2 二维Gabor核
类似一维 Gabor 核,我们将二维高斯函数与二维复数波相乘,就得到了二维的Gabor核:
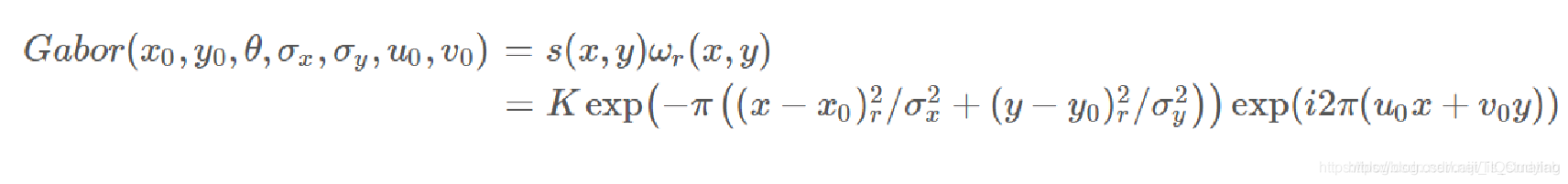
一个Gabor核能获取到图像某个频率邻域的响应情况,这个响应结果可以看做是图像的一个特征。如果我们用多个不同频率的Gabor核去获取图像在不同频率邻域的响应情况,最后就能形成图像在各个频率段的特征,这个特征就可以描述图像的频率信息了。
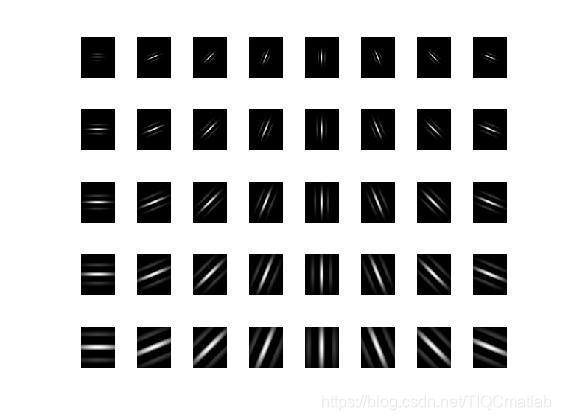
下图展示了一系列具有不同频率的 Gabor 核,用这些核与图像卷积,我们就能得到图像上每个点和其附近区域的频率分布情况。
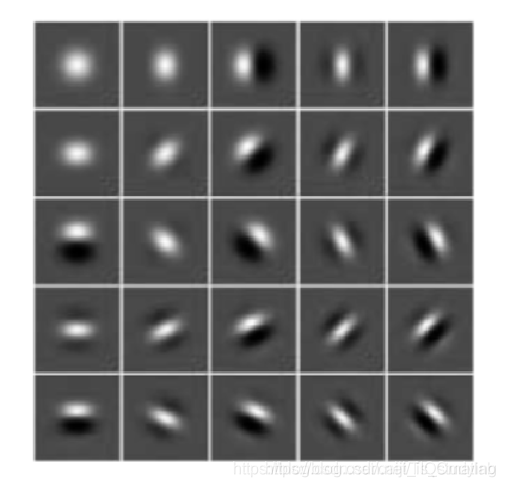
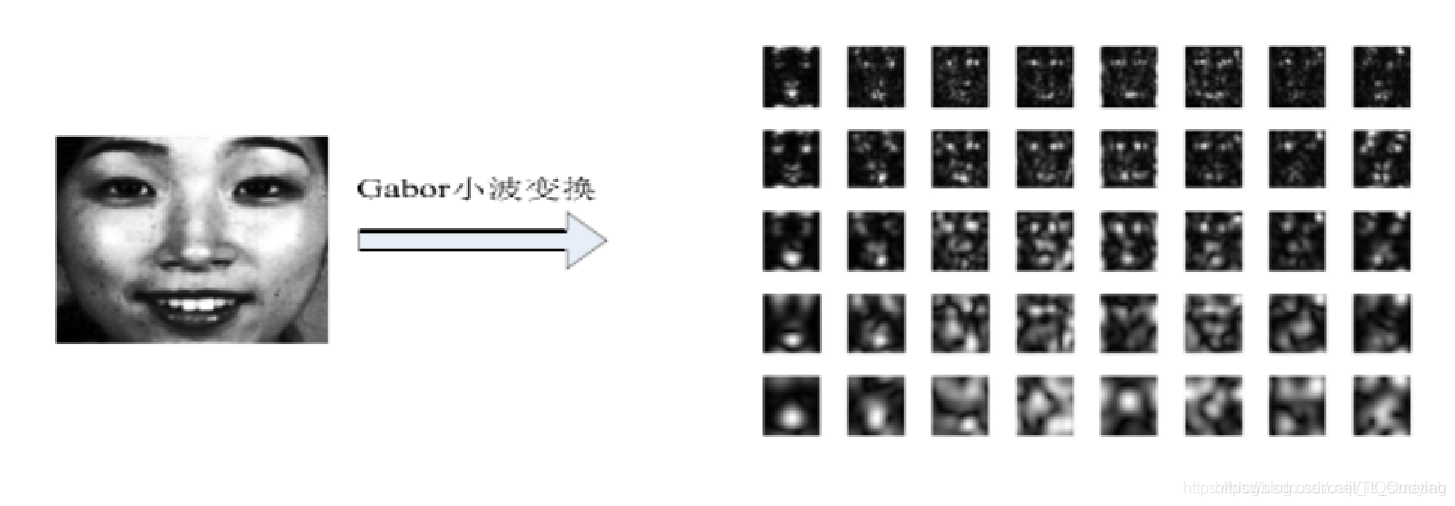
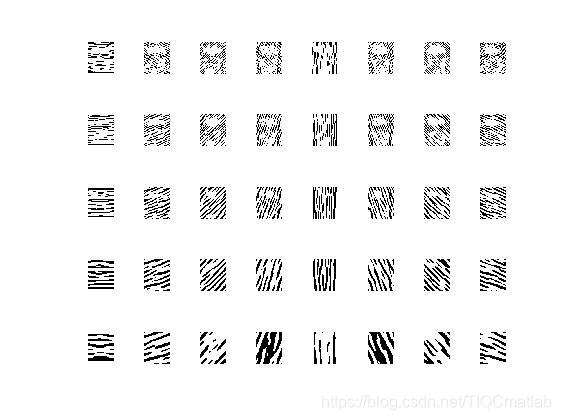
经过 Gabor 滤波获到的人脸图像信息包含实部和虚部两部分,分别代表不同局部的人脸特征信息,为了提取更加全面的人脸特征信息,一般会采用两种特征值相结合的方法,比如幅值和相位信息。但 Gabor 的相位信息会因为人脸空间位置发生改变而不太稳定。Gabor 幅值信息变化相对稳定,并且充分反映了人脸图像的能量谱。因此采取 Gabor 幅值特征。经过Gabor幅值特征处理,得到了人脸 Gabor 特征信息。5 个尺度,8 个方向的 Gabor 特征提取图如下所示:
2 PCA+SVM
2.1 PCA
主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis, 简称PCA)是常用的一种降维方法.
算法步骤:

2.2 SVM介绍
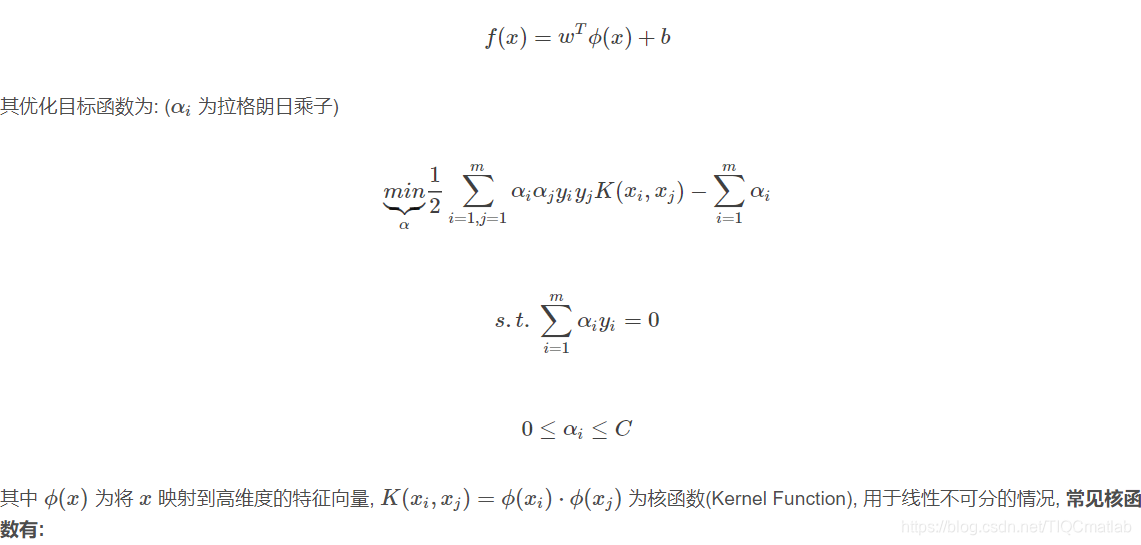
支持向量机(Support Vector Machines, 简称SVM)是一种二类分类模型.
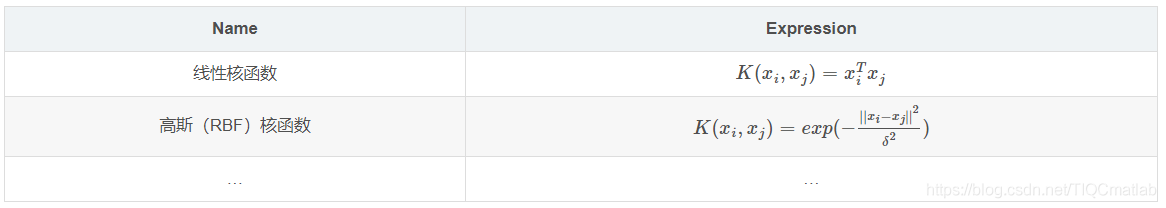
划分超平面为:
3 人脸识别步骤
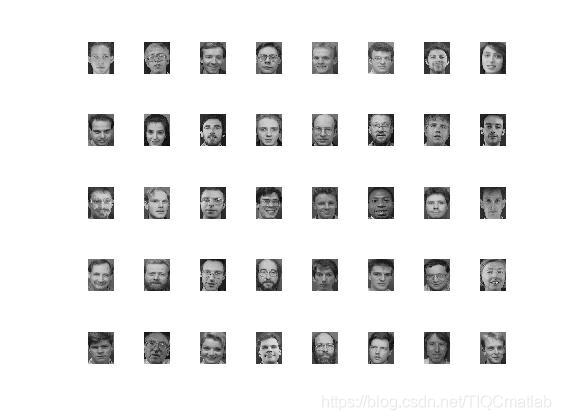
将每张人脸图片(m,nm,n)读取并展开成(m×n,1m×n,1), 假设总有ll张图片, 所有排列到一起, 一列为一张图片, 最终形成一个(m×n,l)(m×n,l) 的矩阵作为原始数据;
数据中心化: 计算平均脸, 所有列都减去张平均脸;
计算矩阵的协方差矩阵/散布矩阵, 求出特征值及特征向量, 并将其从大到小排列取前K个特征; (到这步特征已将至K维)
计算中心化后的数据在K维特征的投影;
基于上一步的数据进行 One-VS-One Multiclass SVM模型训练;
读取用于测试的人脸图片, 同训练图片一样处理;
利用训练出的模型对测试图片进行分类;
计算准确率.
⛄二、部分源代码
function varargout = pjimage(varargin)
% PJIMAGE MATLAB code for pjimage.fig
% PJIMAGE, by itself, creates a new PJIMAGE or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = PJIMAGE returns the handle to a new PJIMAGE or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% PJIMAGE(‘CALLBACK’,hObject,eventData,handles,…) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in PJIMAGE.M with the given input arguments.
%
% PJIMAGE(‘Property’,‘Value’,…) creates a new PJIMAGE or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before pjimage_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to pjimage_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE’s Tools menu. Choose “GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)”.
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help pjimage
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 11-Jun-2018 08:06:08
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct(‘gui_Name’, mfilename, …
‘gui_Singleton’, gui_Singleton, …
‘gui_OpeningFcn’, @pjimage_OpeningFcn, …
‘gui_OutputFcn’, @pjimage_OutputFcn, …
‘gui_LayoutFcn’, [] , …
‘gui_Callback’, []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% — Executes just before pjimage is made visible.
function pjimage_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to pjimage (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for pjimage
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes pjimage wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure_pjimage);
% — Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = pjimage_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function m_file_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to m_file (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function m_file_open_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to m_file_open (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function m_file_save_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to m_file_save (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function m_file_exit_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to m_file_exit (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% — Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
figure(1);
for i = 1:40
a = imread(strcat(‘C:\Users\lenovo\Desktop\人脸识别\人脸识别程序\ORL\s’, num2str(i), ‘\1.pgm’));
subplot(5,8,i);
imshow(a);
end
% — Executes on button press in pushbutton2.
function pushbutton2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
figure(2);
r = round(112 / 2);
c = round(92 / 2);
gamma = 0.5;
theta = pi / 8;
a = sqrt(2);
fmax = 0.22;
for u = 0 : 4
f = a ^ (-u) * fmax;
lambda = 1 / f;
for v = 0 : 7
sigma = 0.56 * lambda;
GK = getGaborKernel(r ,c ,v * theta ,sigma ,lambda ,gamma);%得到一个方向一个尺度的Gabor图像
subplot(5,8, u*8 + v + 1);
imshow(GK);
end
end
% — Executes on button press in pushbutton3.
function pushbutton3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
p = imread(‘C:\Users\lenovo\Desktop\人脸识别\人脸识别程序\ORL\s1\1.pgm’);
p = double§;
[m , n] = size§;
r = round(m / 2);
c = round(n / 2);
gamma = 0.5;
theta = pi / 8;
a = sqrt(2);
fmax = 0.22;
figure(3);
for u = 0 : 4
f = a ^ (-u) * fmax;
lambda = 1 / f;
for v = 0 : 7
sigma = 0.56 * lambda;
GK = getGaborKernel(r ,c ,v * theta ,sigma ,lambda ,gamma);%得到一个方向一个尺度的Gabor图像
x = conv2(p,GK,‘same’);%原图像与Gabor图像进行卷积 112 92
subplot(5, 8, u*8 + v +1);
imshow(x);
end
end
% — Executes during object deletion, before destroying properties.
function axes1_DeleteFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to axes1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
function edit1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit1 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
function edit2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit2 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit2 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
% — Executes on button press in pushbutton6.
function pushbutton6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
global ttlabel;
global prelabel;
% global ct;
% global gam;
trainLabel = [];
k = 1;
v = 1;
%共280张图片
for i = 1 : 40 %40个人
for j = 1 : 7 %每个人7张照片
a = imread(strcat(‘C:\Users\lenovo\Desktop\人脸识别\人脸识别程序\ORL\s’, num2str(i),‘’, num2str(j), ‘.pgm’));
a = double(a);
[m,n] = size(a);
trainvector = GetOneImageVector(a);
trainX(:, k) = trainvector;
k = k + 1;
%加标签
trainLabel = [trainLabel v]; %1X280
end
v = v + 1;
end
%归一化 均值向量 方差向量
trainx = Normalize(trainX); %6440X280
% ct =str2double(get(handles.edit3,‘String’));
% gam = str2double(get(handles.edit4,‘String’));
%使用SVM得到模型
model = svmtrain(trainLabel’, trainx’,‘-s 0 -t 2 -c 1000 -g 0.0001’);
% set(handles.edit1,‘string’,model);
%处理测试集
u = 1;
t = 1;
testLabel = [];
for i = 1:40
for j = 8:10
a = imread(strcat(‘C:\Users\lenovo\Desktop\人脸识别\人脸识别程序\ORL\s’, num2str(i),‘’, num2str(j), ‘.pgm’));
a = double(a);
[m,n] = size(a);
testvector = GetOneImageVector(a);
testX(:, u) = testvector;
u = u + 1;
testLabel = [testLabel t];
end
t = t + 1;
end
⛄三、运行结果

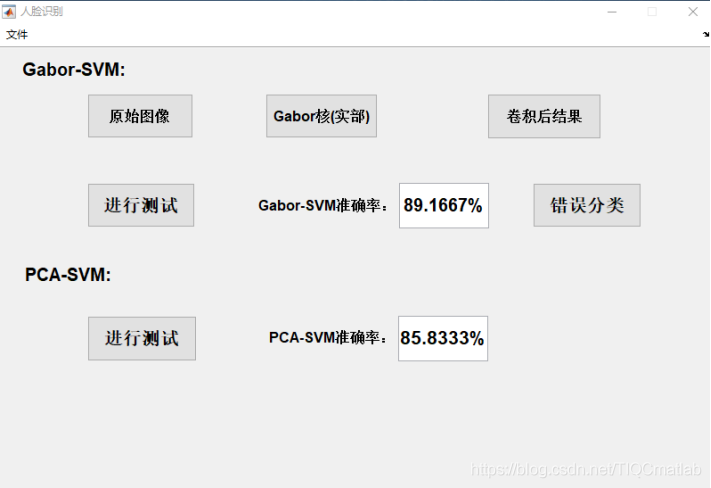
⛄四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1]孟逸凡,柳益君.基于PCA-SVM的人脸识别方法研究[J].科技视界. 2021,(07)
[2]张娜,刘坤,韩美林,陈晨.一种基于PCA和LDA融合的人脸识别算法研究[J].电子测量技术. 2020,43(13)
[3]陈艳.基于BP神经网络的人脸识别方法分析[J].信息与电脑(理论版). 2020,32(23)
[4]戴骊融,陈万米,郭盛.基于肤色模型和SURF算法的人脸识别研究[J].工业控制计算机. 2014,27(02)
3 备注
简介此部分摘自互联网,仅供参考,若侵权,联系删除
🍅 仿真咨询
1 各类智能优化算法改进及应用
生产调度、经济调度、装配线调度、充电优化、车间调度、发车优化、水库调度、三维装箱、物流选址、货位优化、公交排班优化、充电桩布局优化、车间布局优化、集装箱船配载优化、水泵组合优化、解医疗资源分配优化、设施布局优化、可视域基站和无人机选址优化
2 机器学习和深度学习方面
卷积神经网络(CNN)、LSTM、支持向量机(SVM)、最小二乘支持向量机(LSSVM)、极限学习机(ELM)、核极限学习机(KELM)、BP、RBF、宽度学习、DBN、RF、RBF、DELM、XGBOOST、TCN实现风电预测、光伏预测、电池寿命预测、辐射源识别、交通流预测、负荷预测、股价预测、PM2.5浓度预测、电池健康状态预测、水体光学参数反演、NLOS信号识别、地铁停车精准预测、变压器故障诊断
3 图像处理方面
图像识别、图像分割、图像检测、图像隐藏、图像配准、图像拼接、图像融合、图像增强、图像压缩感知
4 路径规划方面
旅行商问题(TSP)、车辆路径问题(VRP、MVRP、CVRP、VRPTW等)、无人机三维路径规划、无人机协同、无人机编队、机器人路径规划、栅格地图路径规划、多式联运运输问题、车辆协同无人机路径规划、天线线性阵列分布优化、车间布局优化
5 无人机应用方面
无人机路径规划、无人机控制、无人机编队、无人机协同、无人机任务分配
6 无线传感器定位及布局方面
传感器部署优化、通信协议优化、路由优化、目标定位优化、Dv-Hop定位优化、Leach协议优化、WSN覆盖优化、组播优化、RSSI定位优化
7 信号处理方面
信号识别、信号加密、信号去噪、信号增强、雷达信号处理、信号水印嵌入提取、肌电信号、脑电信号、信号配时优化
8 电力系统方面
微电网优化、无功优化、配电网重构、储能配置
9 元胞自动机方面
交通流 人群疏散 病毒扩散 晶体生长
10 雷达方面
卡尔曼滤波跟踪、航迹关联、航迹融合






















 4万+
4万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










