1.背景介绍
HashMap在Java中是常用的数据结构之一。HashMap 是一个散列表,它存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射,并具有很快的访问速度。在JDK1.7中,HashMap是基于“数组+链表”实现的,而在JDK1.8以后,HashMap在底层实现中加入了红黑树用于提升查找速率。
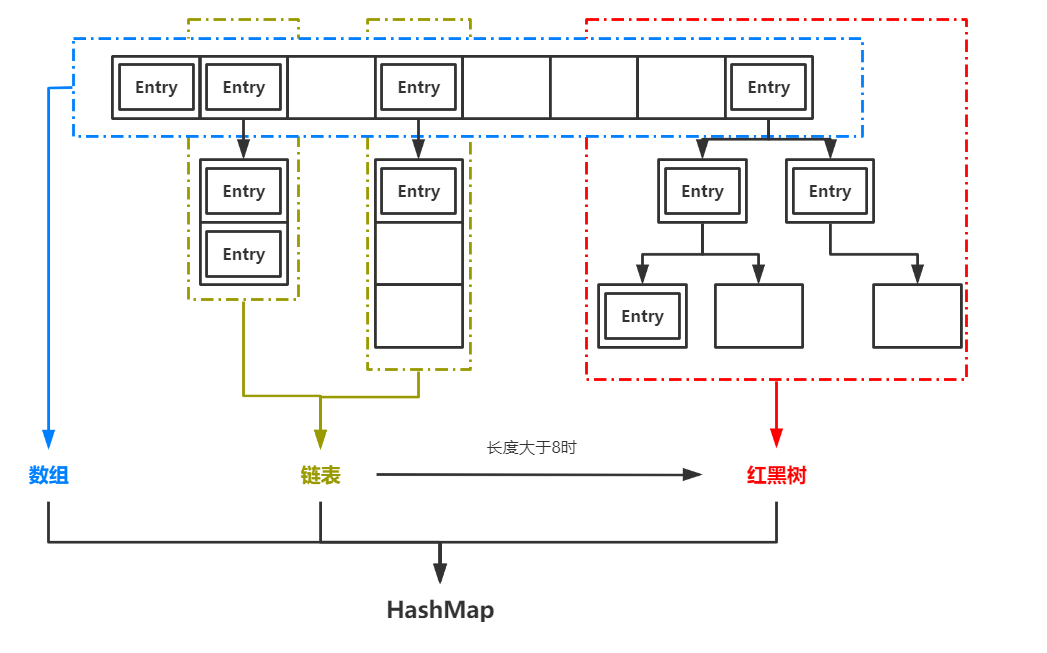
在JDK1.8中,当链表的长度大于阈值8时,这时这个链表将会转化成红黑树以提升查找效率。为什么阈值是8呢?请读者不妨思考一下这个问题,在文章末尾笔者将给出原因。(提示:想一想在红黑树和链表中查找一个元素的复杂度)
好了,关于HashMap就简单介绍到这里,接下来我们关注于自己实现一个HashMap—MyHashMap。
2.目标
在本次实现中,我们的目标如下:
- 实现put(k, v),该方法返回V类型的元素,这里返回为空即可。
- 实现get(k),该方法返回这个建对应的值v。
- 实现remove(k),该方法将这个键对应的键值对删除,并返回对应的值v,如果不存在对应的键,返回空。
- 实现size(),该方法返回HashMap中的键值对数目。
明确我们的目标后,就可以关注于具体实现了。
3.手写HashMap
3.1定义MyMap接口
这个接口定义了我们需要实现的具体行为。
public interface MyMap <K, V>{
V get(K k);
V put(K k, V v);
int size();
V remove(K k);
boolean isEmpty();
}
接下来我们要根据这个接口的定义完成我们的MyHashMap类去实现接口中定义的行为。
3.2定义链表节点
因为HashMap中存在着链表,所以我们也需要实现一个链表。我们以内部类的形式定义这样一个节点Entry,Entry类保存了"K-V"数据,next字段表明它可能会是一个链表节点。
参考形式如下:
public class MyHashMap <K,V> implements MyMap<K, V> {
//定义内部类Entry作为链表节点
class Entry<K, V>{
K k;
V v;
Entry<K,V> next;
public Entry(K k, V v){
this.k = k;
this.v = v;
}
}
}
3.2定义成员变量
这里参照HashMap设置一个默认的容量capacity和默认的加载因子loadFactor,table就是底层数组,另外,考虑到size方法的实现,这里肯定还需要一个成员变量size用于表示HashMap的大小。
//定义成员变量
final static int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16;
final static float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
private int capacity;
private float loadFactor;
private 







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 251
251











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








