背景
让我们来了解一下HashMap吧
过程
简介
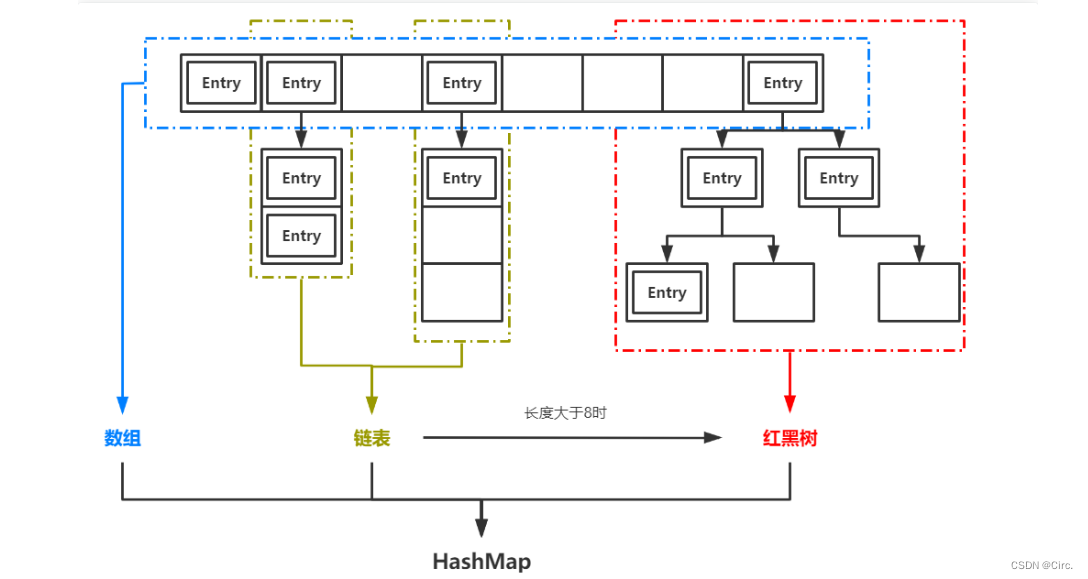
HashMap是Java中一中非常常用的数据结构,也基本是面试中的“必考题”。它实现了基于“K-V”形式的键值对的高效存取。JDK1.7之前,HashMap是基于数组+链表实现的,1.8以后,HashMap的底层实现中加入了红黑树用于提升查找效率。
HashMap根据存入的键值对中的key计算对应的index,也就是它在数组中的存储位置。当发生哈希冲突时,即不同的key计算出了相同的index,HashMap就会在对应位置生成链表。当链表的长度超过8时,链表就会转化为红黑树。
手写HashMap
1、定义接口
public interface MyMap<K,V> {
V put(K k, V v);
V get(K k);
int size();
V remove(K k);
boolean isEmpty();
void clear();
}
2、实现接口,实现这个接口,并实现里面的方法。
final static int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16;
final static float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
int capacity;
float loadFactor;
int size = 0;
Entry<K,V>[] table;
Copy
class Entry<K, V>{
K k;
V v;
Entry<K,V> next;
public Entry(K k, V v, Entry<K, V> next){
this.k = k;
this.v = v;
this.next = next;
}
}
我们参照HashMap设置一个默认的容量capacity和默认的加载因子loadFactor,table就是底层数组,Entry类保存了"K-V"数据,next字段表明它可能会是一个链表节点。
3、构造方法
public MyHashMap(){
this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public MyHashMap(int capacity, float loadFactor){
this.capacity = upperMinPowerOf2(capacity);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.table = new Entry[capacity];
}
这里的upperMinPowerOf2的作用是获取大于capacity的最小的2次幂。在HashMap中,开发者采用了更精妙的位运算的方式完成了这个功能,效率比这种方式要更高。
private static int upperMinPowerOf2(int n){
int power = 1;
while(power <= n){
power *= 2;
}
return power;
}
为什么HashMap的capacity一定要是2次幂呢?这是为了方便HashMap中的数组扩容时已存在元素的重新哈希(rehash)考虑的。
4、put方法
@Override
public V put(K k, V v) {
// 通过hashcode散列
int index = k.hashCode() % table.length;
Entry<K, V> current = table[index];
// 判断table[index]是否已存在元素
// 是
if(current != null){
// 遍历链表是否有相等key, 有则替换且返回旧值
while(current != null){
if(current.k == k){
V oldValue = current.v;
current.v = v;
return oldValue;
}
current = current.next;
}
// 没有则使用头插法
table[index] = new Entry<K, V>(k, v, table[index]);
size++;
return null;
}
// table[index]为空 直接赋值
table[index] = new Entry<K, V>(k, v, null);
size++;
return null;
}
put方法中,我们通过传入的K-V值构建一个Entry对象,然后判断它应该被放在数组的那个位置。回想我们之前的论断:
想要提高HashMap的效率,最重要的就是尽量避免生成链表,或者说尽量减少链表的长度
想要达到这一点,我们需要Entry对象尽可能均匀地散布在数组table中,且index不能超过table的长度,很明显,取模运算很符合我们的需求int index = k.hashCode() % table.length。关于这一点,HashMap中也使用了一种效率更高的方法——通过&运算完成key的散列,有兴趣的同学可以查看HashMap的源码。
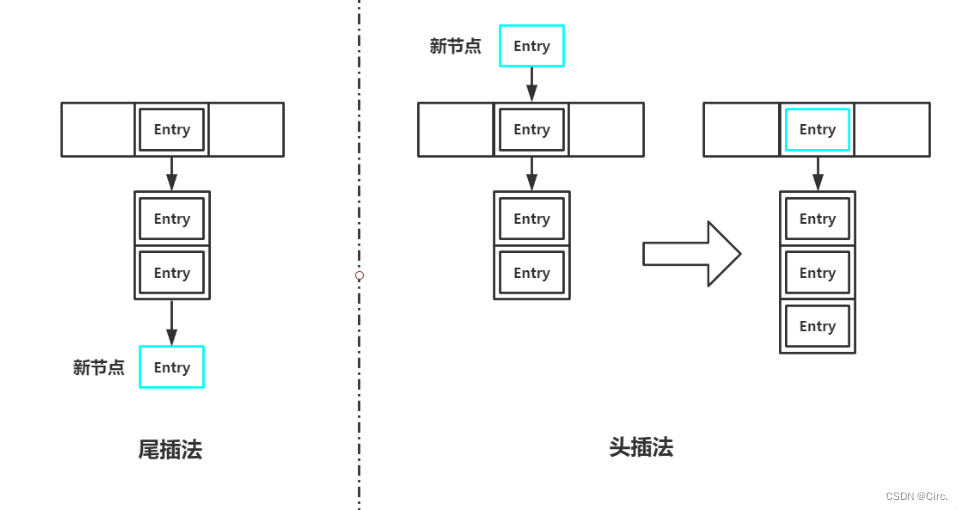
如果table[index]处已存在元素,说明将要形成链表。我们首先遍历这个链表(长度为1也视作链表),如果存在key与我们存入的key相等,则替换并返回旧值;如果不存在,则将新节点插入链表。插入链表又有两种做法:头插法和尾插法。如果使用尾插法,我们需要遍历这个链表,将新节点插入末尾;如果使用头插法,我们只需要将table[index]的引用指向新节点,然后将新节点的next引用指向原来table[index]位置的节点即可,这也是HashMap中的做法。
5、get方法
@Override
public V get(K k) {
int index = k.hashCode() % table.length;
Entry<K, V> current = table[index];
// 遍历链表
while(current != null){
if(current.k == k){
return current.v;
}
current = current.next;
}
return null;
}
5、remove方法
@Override
public V remove(K k) {
int index = k.hashCode() % table.length;
Entry<K, V> current = table[index];
// 如果直接匹配第一个节点
if(current.k == k){
table[index] = null;
size--;
return current.v;
}
// 在链表中删除节点
while(current.next != null){
if(current.next.k == k){
V oldValue = current.next.v;
current.next = current.next.next;
size--;
return oldValue;
}
current = current.next;
}
return null;
}
移除某个节点时,如果该key对应的index处没有形成链表,那么直接置为null。如果存在链表,我们需要将目标节点的前驱节点的next引用指向目标节点的后继节点。由于我们的Entry节点没有previous引用,因此我们要基于目标节点的前驱节点进行操作,即:
Copy
current.next = current.next.next;
current代表我们要删除的节点的前驱节点。
还有一些简单的size()、isEmpty()等方法都很简单,这里就不再赘述。现在,我们自定义的MyHashMap基本可以使用了。
总结
关于HashMap的实现,还有几点我们没有解决:
扩容问题。在HashMap中,当存储的元素数量超过阈值(threshold = capacity * loadFactor)时,HashMap就会发生扩容(resize),然后将内部的所有元素进行rehash,使hash冲突尽可能减少。在我们的MyHashMap中,虽然定义了加载因子,但是并没有使用它,capacity是固定的,虽然由于链表的存在,仍然可以一直存入数据,但是数据量增大时,查询效率将急剧下降。
树化问题(treeify)。我们之前讲过,链表节点数量超过8时,为了更高的查询效率,链表将转化为红黑树。但是我们的代码中并没有实现这个功能。
null值的判断。HashMap中是允许存null值的key的,key为null时,HashMap中的hash()方法会固定返回0,即key为null的值固定存在table[0]处。这个实现起来很简单,不实现的情况下MyHashMap中如果存入null值会直接报NullPointerException异常。
一些其他问题。
























 580
580











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










