- PAT排名
问题描述:每一个输入文件是一个考场的信息。在每个考场中,第一行包括一个正整数N(<=100),它表示考场数。在每个考场中,包括一个整数K(K<=300),它表示参加考试的人的数量,然后K行包括准考证号(13个数字)和每一个考试者总分的排名。每一行的数值用空格间隔。
要求:输出格式:准考证号,最后排名,考场号,考场内排名
输入样例:
2
5
1234567890001 95
1234567890005 100
1234567890003 95
1234567890002 77
1235467890004 85
4
1234567890013 65
1234567890011 25
1234567890014 100
1234567890012 85
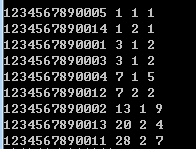
输出样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Student{
char id[15]; //准考证号
int score; //分数
int location_number; //考场号
int location_rank; //考场内排名
int total_rank;
}stu[100];
bool cmp(Student a,Student b){
// 按分数排名
return a.score>b.score;
}
int main(){
int location_size; // 考场数
scanf("%d",&location_size);
int location1_size; // 考场1学生数
scanf("%d",&location1_size);
for(int i=0;i<location1_size;i++){ // 获取学生数据
scanf("%s %d",stu[i].id,&stu[i].score);
stu[i].location_number = 1;
}
int location2_size; // 考场2学生数
scanf("%d",&location2_size);
// 获取学生数据
for(int i=location1_size;i<location2_size+location1_size;i++){
scanf("%s %d",stu[i].id,&stu[i].score);
stu[i].location_number = 2;
}
printf("\n");
// 得到考场1学生场内排名
sort(stu,stu+location1_size,cmp);
stu[0].location_rank = 1;
for(int i=1;i<location1_size;i++){
if(stu[i].score==stu[i-1].score)
stu[i].location_rank = stu[i-1].location_rank;
else
stu[i].location_rank = i + 1;
}
// 得到考场2学生场内排名
sort(stu+location1_size,stu+location1_size+location2_size,cmp);
stu[location1_size].location_rank = 1;
int k=1;
for(int i=location1_size+1;i<location2_size+location1_size;i++){
if(stu[i].score==stu[i-1].score)
stu[i].location_rank = stu[i-1].location_rank;
else
stu[i].location_rank = k + 1;
k++;
}
// 得到两个考场内学生的总排名
sort(stu,stu+location1_size+location2_size,cmp);
stu[0].total_rank = 1;
int j = 1;
for(int i=1;i<location1_size+location2_size;i++){
if(stu[i].score==stu[i-1].score)
stu[i].total_rank = stu[i-1].total_rank;
else
stu[i].total_rank = i + 1;
}
for(int i=0;i<location1_size+location2_size;i++){
printf("%s %d %d %d\n",stu[i].id,stu[i].total_rank,
stu[i].location_number,stu[i].location_rank);
}
return 0;
}
- 散列定义与整数散列
问M个数中每个数分别是否在N个数中出现过
#include <stdio.h>
const int max = 100010;
bool hash[max] = {false};
int main(){
int n,m,temp;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&temp);
hash[temp] = true;
}
scanf("%d",&m);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
scanf("%d",&temp);
if(hash[temp]==true){
printf("%s\n","Yes");
}
else{
printf("%s\n","No");
}
}
return 0;
}
问M个欲查询的数中每个数在N中出现的次数
#include <stdio.h>
const int max = 100010;
int hash[max] = {false};
int main(){
int n,m,temp;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&temp);
hash[temp]++;
}
scanf("%d",&m);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
scanf("%d",&temp);
printf("%d",hash[temp]);
}
return 0;
}
- 字符串hash初步:按照二十六进制转换为十进制的思路
#include <stdio.h>
int hashFunc(char c[],int len){
int id = 0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
id = id * 26 + (c[i] - 'A');
}
return id;
}
int main(){
char c[] = "AB";
printf("%d\n",hashFunc(c,2));
return 0;
}
- 给出N个字符串(恰好三位大写字母组成),再给出M个查询字符串,问每个查询字符串在N个字符串中出现的次数。
#include <stdio.h>
const int maxn = 100;
char S[maxn][5],temp[5];
int hash[62 * 62 * 62 + 10];
int hashFunc(char c[],int len){ // hash函数
int id = 0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(c[i]>='A'&&c[i]<='Z')
id = id * 62 + (c[i] - 'A');
else if(c[i]>='a'&&c[i]<='z')
id = id * 62 + (c[i] - 'a') + 26;
else
id = id * 62 + (c[i] - '0') + 52;
}
return id;
}
int main(){
int n,m;
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%s",S[i]);
int id = hashFunc(S[i],3);
hash[id]++;
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
scanf("%s",temp);
int id = hashFunc(temp,3);
printf("%d\n",hash[id]);
}
return 0;
}
5.全排列问题:输出1~n这n个整数的全排列
#include <stdio.h>
const int maxn = 11;
// 数组P是当前全排列,hash表示数字是否在数组中出现过
int P[maxn],n,hash[maxn] = {false};
void generateP(int index){
if(index == n+1){ // 递归边界,已经处理完排列的1~n位
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
printf("%d",P[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return;
}
for(int x=1;x<=n;x++){ //处理第1~n位
if(hash[x]==false){ //如果x不在当前排列中
P[index] = x; //把x加入当前排列
hash[x] = true; //更新hash函数
generateP(index+1); //处理index+1号位
hash[x] = false; //已处理完P[index]为x的子问题,还原状态
}
}
}
int main(){
n= 3;
generateP(1); // 从P(1)开始
return 0;
}
- n皇后问题:
暴力解法:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
const int maxn = 11;
// 数组P是当前全排列,hash表示数字是否在数组中出现过
int P[maxn],n,hash[maxn] = {false};
int count = 0; // 记录可行方案的个数
void generateP(int index){
if(index == n+1){ // 递归边界
bool flag = true; //假设可行
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<=n;j++){
if(abs(i-j)==abs(P[i]-P[j]))
flag = false; // 对角线存在不同元素,不可行
}
}
if(flag) count++;
return;
}
for(int x=1;x<=n;x++){ //处理第1~n位
if(hash[x]==false){ //如果x不在当前排列中
P[index] = x; //把x加入当前排列
hash[x] = true; //更新hash函数
generateP(index+1); //处理index+1号位
hash[x] = false; //已处理完P[index]为x的子问题,还原状态
}
}
}
int main(){
n= 4;
generateP(1); // 从P(1)开始
printf("%d",count);
return 0;
}
回溯法:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
const int maxn = 11;
// 数组P是当前全排列,hash表示数字是否在数组中出现过
int P[maxn],n,hash[maxn] = {false};
int count = 0; // 记录可行方案的个数
void generateP(int index){
if(index == n+1){ // 递归边界
count++;
return;
}
for(int x=1;x<=n;x++){ //处理第1~n位
if(hash[x]==false){ //考虑第x行
bool flag = true;
for(int pre=1;pre<index;pre++){ // 遍历前面的皇后
if(abs(index-pre)==abs(x-P[pre])){
flag = false; // 与x行形成对角线
break;
}
}
if(flag){
P[index] = x; //把x加入当前排列
hash[x] = true; //更新hash函数
generateP(index+1); //处理index+1号位
hash[x] = false; //已处理完P[index]为x的子问题,还原状态
}
}
}
}
int main(){
n= 4;
generateP(1); // 从P(1)开始
printf("%d",count);
return 0;
}
- 月饼
问题描述:现给定所有种类月饼的库存量、总售价以及市场的最大需求量,试计算可以获得的最大收益是多少。销售时允许取出一部分库存。样例给出的情况是这样的:假如有三种月饼,其库存量分别为18、15、10万吨,总售价分别为75、72、45亿元。如果市场的最大需求量只有20万吨,那么最大收益策略应该是卖出全部15万吨第二种月饼以及5万吨第三种月饼,获得72+45/2=94.5(亿元)
要求:每个输入包含1个测试用例。每个测试用例先出给一个不超过1000的正整数N表示月饼的种类数以及不超过500(以万吨为单位)的正整数D表示市场最大需求量;随后一行给出N个正数表示每种月饼的库存量(以万吨为单位);最后一行给出N个正数表示每种月饼的总售价(以亿元为单位)。数字间以空格分隔。
输入样例:
3 20
18 15 10
75 72 45
输出样例:
94.50
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct moon_cake{ // 存放月饼数据的结构体
int save;
int sale;
} moon[10];
bool cmp(moon_cake a,moon_cake b){ //比较函数,得到单价最大
return ((float)a.sale/a.save) > ((float)b.sale/b.save);
}
int main(){
int N,D;
scanf("%d %d",&N,&D);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
scanf("%d",&moon[i].save);
}
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
scanf("%d", &moon[i].sale);
}
sort(moon,moon+N,cmp); // 按单价最大排序
float total_sale;
int k=0;
while(D>0){
if(D > moon[k].save){ //需求量大于存储量
total_sale += moon[k].sale;
D = D - moon[k].save;
}
else{ //需求量小于存储量
total_sale = total_sale + (float)moon[k].sale* D / moon[k].save;
D = 0;
}
k ++;
}
printf("%.2f\n",total_sale);
return 0 ;
}
- 组个最小数
问题描述:给定数字0~9个若干个。可以任意顺序排列这些数字,但必须全部使用。目标是使得最后得到的数尽可能小(注意:0不能做首位)。例如,给定两个0、两个1、三个5和一个8,得到的最小的数就是10015558
要求:每个输入包含1个测试用例。每个测试用例在一行中给出十个非负整数,顺序表示所拥有数字0、数字1……数字9的个数。整数间用一个空格间隔。十个数字的总个数不超过50,且至少拥有一个非0的数字。
输入样例:
2 2 0 0 0 3 0 0 1 0
输出样例:
10015558
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int number[10];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ //得到0~9的个数
scanf("%d",&number[i]);
}
for(int i=1;i<10;i++){ //得到第一个不为0的最小的数
if(number[i]!=0){
printf("%d",i);
number[i]--;
break;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ // 按顺序得到后续的数
while(number[i]!=0){
printf("%d",i);
number[i]--;
}
}
return 0;
}





















 2087
2087











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








