tflite_pose_classification
This notebook teaches you how to train a pose classification model using MoveNet and TensorFlow Lite. The result is a new TensorFlow Lite model that accepts the output from the MoveNet model as its input, and outputs a pose classification, such as the name of a yoga pose.
The procedure in this notebook consists of 3 parts:
- Part 1: Preprocess the pose classification training data into a CSV file that specifies the landmarks (body keypoints) detected by the MoveNet model, along with the ground truth pose labels.
- Part 2: Build and train a pose classification model that takes the landmark coordinates from the CSV file as input, and outputs the predicted labels.
- Part 3: Convert the pose classification model to TFLite.
原始数据:

训练集:
chair: 200
cobra: 200
dog: 200
tree: 200
warrior: 200
测试集:
chair: 84
cobra: 116
dog: 90
tree: 96
warrior: 109

经过 movenet_thunder 之后得到的数据:
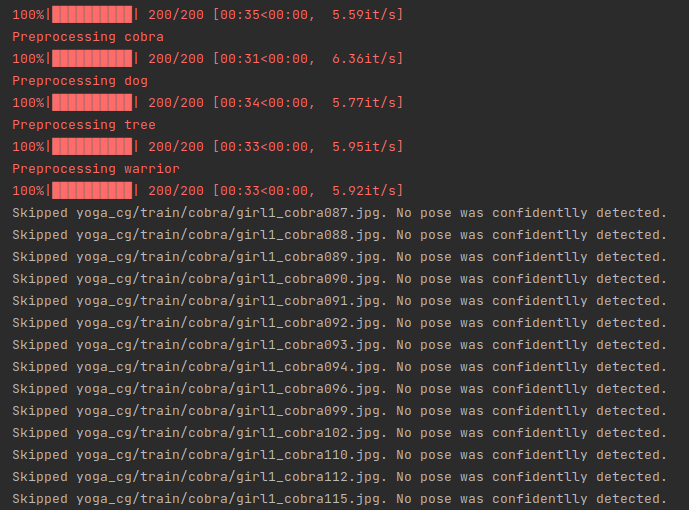
训练集:
chair: 200
cobra: 167
dog: 200
tree: 189
warrior: 193
测试集:
chair: 84
cobra: 116
dog: 90
tree: 56
warrior: 109
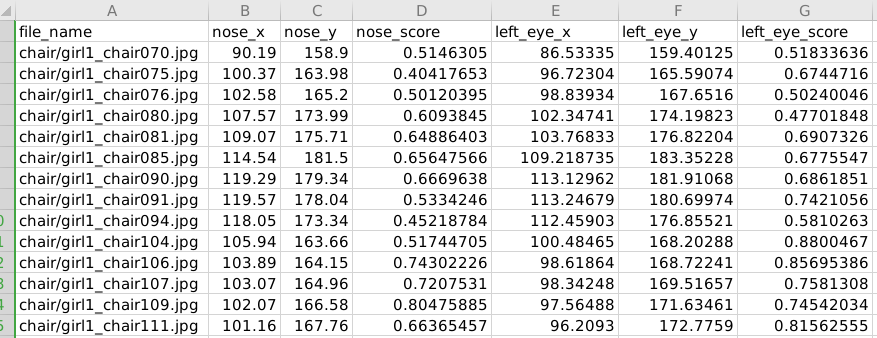
上面是一部分的 train_data.csv


Model size: 26KB
Accuracy of TFLite model: 0.9978021978021978
import csv
import cv2
import itertools
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import os
import sys
import tempfile
import tqdm
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.collections import LineCollection
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_hub as hub
from tensorflow import keras
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report, confusion_matrix
pose_sample_rpi_path = '/home/csdn/Downloads/examples/lite/examples/pose_estimation/raspberry_pi'
sys.path.append(pose_sample_rpi_path)
# Load MoveNet Thunder model
import utils
from movenet import Movenet
movenet = Movenet('movenet_thunder')
# Define function to run pose estimation using MoveNet Thunder.
# You'll apply MoveNet's cropping algorithm and run inference multiple times on
# the input image to improve pose estimation accuracy.
def detect(input_tensor, inference_count=3):
"""Runs detection on an input image.
Args:
input_tensor: A [1, height, width, 3] Tensor of type tf.float32.
Note that height and width can be anything since the image will be
immediately resized according to the needs of the model within this
function.
inference_count: Number of times the model should run repeatly on the
same input image to improve detection accuracy.
Returns:
A dict containing 1 Tensor of shape [1, 1, 17, 3] representing the
keypoint coordinates and scores.
"""
image_height, image_width, channel = input_tensor.shape
# Detect pose using the full input image
movenet.detect(input_tensor.numpy(), reset_crop_region=True)
# Repeatedly using previous detection result to identify the region of
# interest and only croping that region to improve detection accuracy
for _ in range(inference_count - 1):
keypoints_with_scores = movenet.detect(input_tensor.numpy(),
reset_crop_region=False)
return keypoints_with_scores
def draw_prediction_on_image(
image, keypoints_with_scores, crop_region=None, close_figure=True,
keep_input_size=False):
"""Draws the keypoint predictions on image.
Args:
image: An numpy array with shape [height, width, channel] representing the
pixel values of the input image.
keypoints_with_scores: An numpy array with shape [1, 1, 17, 3] representing
the keypoint coordinates and scores returned from the MoveNet model.
crop_region: Set the region to crop the output image.
close_figure: Whether to close the plt figure after the function returns.
keep_input_size: Whether to keep the size of the input image.
Returns:
An numpy array with shape [out_height, out_width, channel] representing the
image overlaid with keypoint predictions.
"""
height, width, channel = image.shape
aspect_ratio = float(width) / height
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12 * aspect_ratio, 12))
# To remove the huge white borders
fig.tight_layout(pad=0)
ax.margins(0)
ax.set_yticklabels([])
ax.set_xticklabels([])
plt.axis('off')
im = ax.imshow(image)
line_segments = LineCollection([], linewidths=(2), linestyle='solid')
ax.add_collection(line_segments)
# Turn off tick labels
scat = ax.scatter([], [], s=60, color='#FF1493', zorder=2)
# Calculate visualization items from pose estimation result
(keypoint_locs, keypoint_edges,
edge_colors) = utils.keypoints_and_edges_for_display(
keypoints_with_scores, height, width)
edge_colors = [(r / 255.0, g / 255.0, b / 255.0) for (r, g, b) in edge_colors]
line_segments.set_segments(keypoint_edges)
line_segments.set_color(edge_colors)
if keypoint_edges.shape[0]:
line_segments.set_segments(keypoint_edges)
line_segments.set_color(edge_colors)
if keypoint_locs.shape[0]:
scat.set_offsets(keypoint_locs)
if crop_region is not None:
xmin = max(crop_region['x_min'] * width, 0.0)
ymin = max(crop_region['y_min'] * height, 0.0)
rec_width = min(crop_region['x_max'], 0.99) * width - xmin
rec_height = min(crop_region['y_max'], 0.99) * height - ymin
rect = patches.Rectangle(
(xmin, ymin), rec_width, rec_height,
linewidth=1, edgecolor='b', facecolor='none')
ax.add_patch(rect)
fig.canvas.draw()
image_from_plot = np.frombuffer(fig.canvas.tostring_rgb(), dtype=np.uint8)
image_from_plot = image_from_plot.reshape(
fig.canvas.get_width_height()[::-1] + (3,))
if close_figure:
plt.close(fig)
if keep_input_size:
image_from_plot = cv2.resize(image_from_plot, dsize=(width, height),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
return image_from_plot
class MoveNetPreprocessor(object):
"""Helper class to preprocess pose sample images for classification."""
def __init__(self,
images_in_folder,
images_out_folder,
csvs_out_path):
"""Creates a preprocessor to detection pose from images and save as CSV.
Args:
images_in_folder: Path to the folder with the input images. It should
follow this structure:
yoga_poses
|__ downdog
|______ 00000128.jpg
|______ 00000181.bmp
|______ ...
|__ goddess
|______ 00000243.jpg
|______ 00000306.jpg
|______ ...
...
images_out_folder: Path to write the images overlay with detected
landmarks. These images are useful when you need to debug accuracy
issues.
csvs_out_path: Path to write the CSV containing the detected landmark
coordinates and label of each image that can be used to train a pose
classification model.
"""
self._images_in_folder = images_in_folder
self._images_out_folder = images_out_folder
self._csvs_out_path = csvs_out_path
self._messages = []
# Create a temp dir to store the pose CSVs per class
self._csvs_out_folder_per_class = tempfile.mkdtemp()
# Get list of pose classes and print image statistics
self._pose_class_names = sorted(
[n for n in os.listdir(self._images_in_folder) if not n.startswith('.')]
)
def process(self, per_pose_class_limit=None, detection_threshold=0.1):
"""Preprocesses images in the given folder.
Args:
per_pose_class_limit: Number of images to load. As preprocessing usually
takes time, this parameter can be specified to make the reduce the
dataset for testing.
detection_threshold: Only keep images with all landmark confidence score
above this threshold.
"""
# Loop through the classes and preprocess its images
for pose_class_name in self._pose_class_names:
print('Preprocessing', pose_class_name, file=sys.stderr)
# Paths for the pose class.
images_in_folder = os.path.join(self._images_in_folder, pose_class_name)
images_out_folder = os.path.join(self._images_out_folder, pose_class_name)
csv_out_path = os.path.join(self._csvs_out_folder_per_class,
pose_class_name + '.csv')
if not os.path.exists(images_out_folder):
os.makedirs(images_out_folder)
# Detect landmarks in each image and write it to a CSV file
with open(csv_out_path, 'w') as csv_out_file:
csv_out_writer = csv.writer(csv_out_file,
delimiter=',',
quoting=csv.QUOTE_MINIMAL)
# Get list of images
image_names = sorted(
[n for n in os.listdir(images_in_folder) if not n.startswith('.')])
if per_pose_class_limit is not None:
image_names = image_names[:per_pose_class_limit]
# Detect pose landmarks from each image
for image_name in tqdm.tqdm(image_names):
image_path = os.path.join(images_in_folder, image_name)
try:
image = tf.io.read_file(image_path)
image = tf.io.decode_jpeg(image)
except:
self._messages.append('Skipped ' + image_path + '. Invalid image.')
continue
else:
image = tf.io.read_file(image_path)
image = tf.io.decode_jpeg(image)
image_height, image_width, channel = image.shape
# Skip images that isn't RGB because Movenet requires RGB images
if channel != 3:
self._messages.append('Skipped ' + image_path +
'. Image isn\'t in RGB format.')
continue
keypoints_with_scores = detect(image)
# Save landmarks if all landmarks were detected
min_landmark_score = np.amin(keypoints_with_scores[:2])
should_keep_image = min_landmark_score >= detection_threshold
if not should_keep_image:
self._messages.append('Skipped ' + image_path +
'. No pose was confidentlly detected.')
continue
# Draw the prediction result on top of the image for debugging later
output_overlay = draw_prediction_on_image(
image.numpy().astype(np.uint8), keypoints_with_scores,
crop_region=None, close_figure=True, keep_input_size=True)
# Write detection result to into an image file
output_frame = cv2.cvtColor(output_overlay, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(images_out_folder, image_name), output_frame)
# Get landmarks and scale it to the same size as the input image
pose_landmarks = np.array(
[[lmk[0] * image_width, lmk[1] * image_height, lmk[2]]
for lmk in keypoints_with_scores],
dtype=np.float32)
# Write the landmark coordinates to its per-class CSV file
coordinates = pose_landmarks.flatten().astype(np.str).tolist()
csv_out_writer.writerow([image_name] + coordinates)
# Print the error message collected during preprocessing.
print('\n'.join(self._messages))
# Combine all per-class CSVs into a single output file
all_landmarks_df = self._all_landmarks_as_dataframe()
all_landmarks_df.to_csv(self._csvs_out_path, index=False)
def class_names(self):
"""List of classes found in the training dataset."""
return self._pose_class_names
def _all_landmarks_as_dataframe(self):
"""Merge all per-class CSVs into a single dataframe."""
total_df = None
for class_index, class_name in enumerate(self._pose_class_names):
csv_out_path = os.path.join(self._csvs_out_folder_per_class,
class_name + '.csv')
per_class_df = pd.read_csv(csv_out_path, header=None)
# Add the labels
per_class_df['class_no'] = [class_index] * len(per_class_df)
per_class_df['class_name'] = [class_name] * len(per_class_df)
# Append the folder name to the filename column (first column)
per_class_df[per_class_df.columns[0]] = (os.path.join(class_name, '')
+ per_class_df[per_class_df.columns[0]].astype(str))
if total_df is None:
# For the first class, assign its data to the total dataframe
total_df = per_class_df
else:
# Concatenate each class's data into the total dataframe
total_df = pd.concat([total_df, per_class_df], axis=0)
list_name = [[key + '_x', key + '_y', key + '_score']
for key in utils.KEYPOINT_DICT.keys()]
header_name = []
for columns_name in list_name:
header_name += columns_name
header_name = ['file_name'] + header_name
header_map = {total_df.columns[i]: header_name[i]
for i in range(len(header_name))}
total_df.rename(header_map, axis=1, inplace=True)
return total_df
# test_image_url = "./yoga-2114512_960_720.jpg"
#
# if len(test_image_url):
# image = tf.io.read_file(test_image_url)
# image = tf.io.decode_jpeg(image)
# keypoints_with_scores = detect(image)
# save_image = draw_prediction_on_image(image, keypoints_with_scores, crop_region=None,
# close_figure=False, keep_input_size=True)
# print(save_image)
#
# from PIL import Image
#
# im = Image.fromarray(save_image)
# im.save("your_file.jpeg")
is_skip_step_1 = True
use_custom_dataset = False
dataset_is_split = True
IMAGES_ROOT = "yoga_cg"
if not is_skip_step_1:
images_in_train_folder = os.path.join(IMAGES_ROOT, 'train')
images_out_train_folder = 'poses_images_out_train'
csvs_out_train_path = 'train_data.csv'
preprocessor = MoveNetPreprocessor(
images_in_folder=images_in_train_folder,
images_out_folder=images_out_train_folder,
csvs_out_path=csvs_out_train_path,
)
preprocessor.process(per_pose_class_limit=None)
if not is_skip_step_1:
images_in_test_folder = os.path.join(IMAGES_ROOT, 'test')
images_out_test_folder = 'poses_images_out_test'
csvs_out_test_path = 'test_data.csv'
preprocessor = MoveNetPreprocessor(
images_in_folder=images_in_test_folder,
images_out_folder=images_out_test_folder,
csvs_out_path=csvs_out_test_path,
)
preprocessor.process(per_pose_class_limit=None)
def load_pose_landmarks(csv_path):
"""Loads a CSV created by from the MoveNetPreprocessor.
Returns:
X: Detected landmark coordinates and scores of shape (N, 17 * 3)
y: Ground truth labels of shape of shape (N, label_count)
classes: The list of all class names found in the dataset
dataframe: The CSV loaded as a Pandas dataframe features (X) and ground
truth labels (y) to use later to train a pose classification model.
"""
# Load the CSV file
dataframe = pd.read_csv(csv_path)
df_to_process = dataframe.copy()
# Drop the file_name columns as you don't need it during training.
df_to_process.drop(columns=['file_name'], inplace=True)
# Extract the list of class names
classes = df_to_process.pop('class_name').unique()
# Extract the labels
y = df_to_process.pop('class_no')
# Convert the input features and labels into the correct format for training.
X = df_to_process.astype('float64')
y = keras.utils.to_categorical(y)
return X, y, classes, dataframe
csvs_out_train_path = 'train_data.csv'
csvs_out_test_path = 'test_data.csv'
# Load the train data
X, y, class_names, _ = load_pose_landmarks(csvs_out_train_path)
# Split training data (X, y) into (X_train, y_train) and (X_val, y_val)
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X, y,
test_size=0.15)
# Load the test data
X_test, y_test, _, df_test = load_pose_landmarks(csvs_out_test_path)
def get_center_point(landmarks, left_name, right_name):
"""Calculates the center point of the two given landmarks."""
left = tf.gather(landmarks, utils.KEYPOINT_DICT[left_name], axis=1)
right = tf.gather(landmarks, utils.KEYPOINT_DICT[right_name], axis=1)
center = left * 0.5 + right * 0.5
return center
def get_pose_size(landmarks, torso_size_multiplier=2.5):
"""Calculates pose size.
It is the maximum of two values:
* Torso size multiplied by `torso_size_multiplier`
* Maximum distance from pose center to any pose landmark
"""
# Hips center
hips_center = get_center_point(landmarks, "left_hip", "right_hip")
# Shoulders center
shoulders_center = get_center_point(landmarks,
"left_shoulder", "right_shoulder")
# Torso size as the minimum body size
torso_size = tf.linalg.norm(shoulders_center - hips_center)
# Pose center
pose_center_new = get_center_point(landmarks, "left_hip", "right_hip")
pose_center_new = tf.expand_dims(pose_center_new, axis=1)
# Broadcast the pose center to the same size as the landmark vector to
# perform substraction
pose_center_new = tf.broadcast_to(pose_center_new,
[tf.size(landmarks) // (17 * 2), 17, 2])
# Dist to pose center
d = tf.gather(landmarks - pose_center_new, 0, axis=0,
name="dist_to_pose_center")
# Max dist to pose center
max_dist = tf.reduce_max(tf.linalg.norm(d, axis=0))
# Normalize scale
pose_size = tf.maximum(torso_size * torso_size_multiplier, max_dist)
return pose_size
def normalize_pose_landmarks(landmarks):
"""Normalizes the landmarks translation by moving the pose center to (0,0) and
scaling it to a constant pose size.
"""
# Move landmarks so that the pose center becomes (0,0)
pose_center = get_center_point(landmarks, "left_hip", "right_hip")
pose_center = tf.expand_dims(pose_center, axis=1)
# Broadcast the pose center to the same size as the landmark vector to perform
# substraction
pose_center = tf.broadcast_to(pose_center,
[tf.size(landmarks) // (17 * 2), 17, 2])
landmarks = landmarks - pose_center
# Scale the landmarks to a constant pose size
pose_size = get_pose_size(landmarks)
landmarks /= pose_size
return landmarks
def landmarks_to_embedding(landmarks_and_scores):
"""Converts the input landmarks into a pose embedding."""
# Reshape the flat input into a matrix with shape=(17, 3)
reshaped_inputs = keras.layers.Reshape((17, 3))(landmarks_and_scores)
# Normalize landmarks 2D
landmarks = normalize_pose_landmarks(reshaped_inputs[:, :, :2])
# Flatten the normalized landmark coordinates into a vector
embedding = keras.layers.Flatten()(landmarks)
return embedding
# Define the model
inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(51))
embedding = landmarks_to_embedding(inputs)
layer = keras.layers.Dense(128, activation=tf.nn.relu6)(embedding)
layer = keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(layer)
layer = keras.layers.Dense(64, activation=tf.nn.relu6)(layer)
layer = keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(layer)
outputs = keras.layers.Dense(5, activation="softmax")(layer)
model = keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
model.summary()
model.compile(
optimizer='adam',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy']
)
# Add a checkpoint callback to store the checkpoint that has the highest
# validation accuracy.
checkpoint_path = "weights.best.hdf5"
checkpoint = keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(checkpoint_path,
monitor='val_accuracy',
verbose=1,
save_best_only=True,
mode='max')
earlystopping = keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor='val_accuracy',
patience=20)
# Start training
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train,
epochs=200,
batch_size=16,
validation_data=(X_val, y_val),
callbacks=[checkpoint, earlystopping])
# Visualize the training history to see whether you're overfitting.
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'])
plt.title('Model accuracy')
plt.ylabel('accuracy')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.legend(['TRAIN', 'VAL'], loc='lower right')
plt.show()
# Evaluate the model using the TEST dataset
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes,
normalize=False,
title='Confusion matrix',
cmap=plt.cm.Blues):
"""Plots the confusion matrix."""
if normalize:
cm = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
print("Normalized confusion matrix")
else:
print('Confusion matrix, without normalization')
plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)
plt.title(title)
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=55)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes)
fmt = '.2f' if normalize else 'd'
thresh = cm.max() / 2.
for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])):
plt.text(j, i, format(cm[i, j], fmt),
horizontalalignment="center",
color="white" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black")
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
plt.tight_layout()
# Classify pose in the TEST dataset using the trained model
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# Convert the prediction result to class name
y_pred_label = [class_names[i] for i in np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1)]
y_true_label = [class_names[i] for i in np.argmax(y_test, axis=1)]
# Plot the confusion matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(np.argmax(y_test, axis=1), np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1))
plot_confusion_matrix(cm,
class_names,
title='Confusion Matrix of Pose Classification Model')
# Print the classification report
print('\nClassification Report:\n', classification_report(y_true_label,
y_pred_label))
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model(model)
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
tflite_model = converter.convert()
print('Model size: %dKB' % (len(tflite_model) / 1024))
with open('pose_classifier.tflite', 'wb') as f:
f.write(tflite_model)
with open('pose_labels.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(class_names))
def evaluate_model(interpreter, X, y_true):
"""Evaluates the given TFLite model and return its accuracy."""
input_index = interpreter.get_input_details()[0]["index"]
output_index = interpreter.get_output_details()[0]["index"]
# Run predictions on all given poses.
y_pred = []
for i in range(len(y_true)):
# Pre-processing: add batch dimension and convert to float32 to match with
# the model's input data format.
test_image = X[i: i + 1].astype('float32')
interpreter.set_tensor(input_index, test_image)
# Run inference.
interpreter.invoke()
# Post-processing: remove batch dimension and find the class with highest
# probability.
output = interpreter.tensor(output_index)
predicted_label = np.argmax(output()[0])
y_pred.append(predicted_label)
# Compare prediction results with ground truth labels to calculate accuracy.
y_pred = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_pred)
return accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred)
# Evaluate the accuracy of the converted TFLite model
classifier_interpreter = tf.lite.Interpreter(model_content=tflite_model)
classifier_interpreter.allocate_tensors()
print('Accuracy of TFLite model: %s' %
evaluate_model(classifier_interpreter, X_test, y_test))




























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








