简述
一个应用程序为了适应不同场合、不同人的偏好,常常需要在程序的运行过程中能够灵活地改变控件的排布方式。
动态布局介绍了如何在程序运行的过程中改变控件的布局,控件的排布方式依赖于程序运行过程中的设置。
实现
下面用一个小例子来介绍这种效果的实现方式
效果
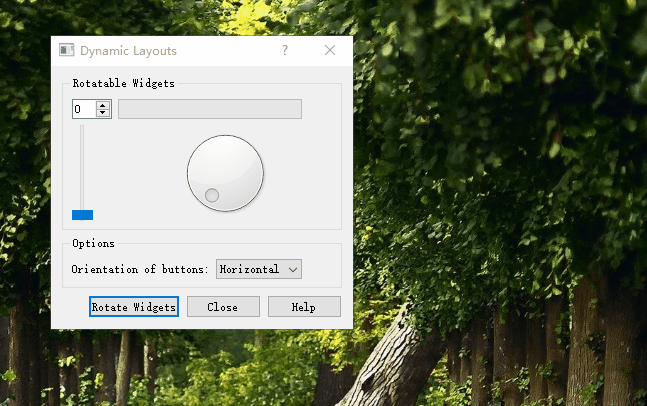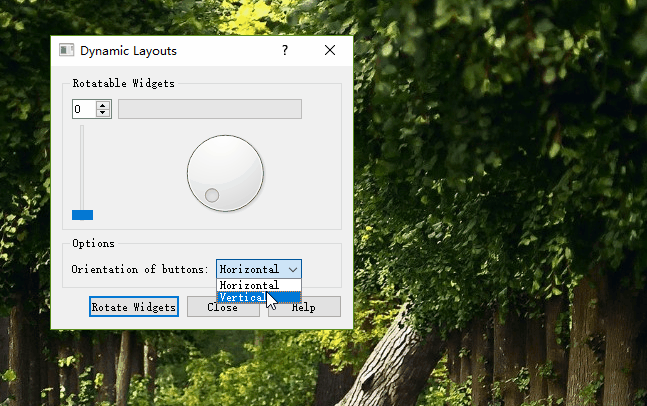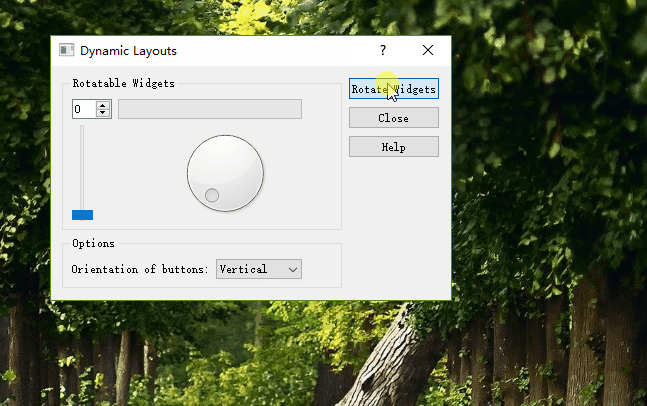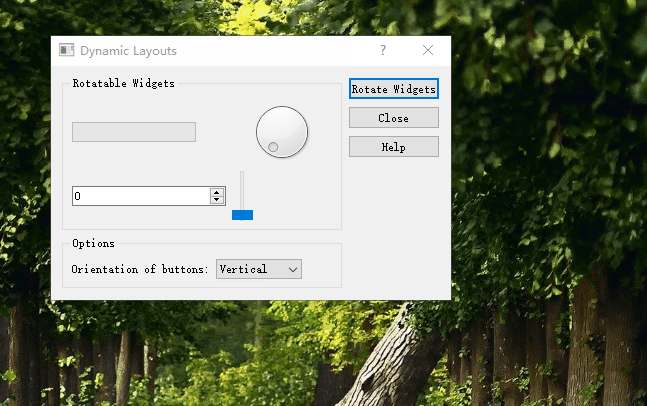
通过方向选择按钮实现按钮面板的垂直与水平排布。
通过点击RotateWidgets按钮来实现Rotatable Widgets内部控件的旋转排布。
源码
dialog.h
#ifndef DIALOG_H
#define DIALOG_H
#include <QDialog>
#include <QQueue>
class QComboBox;
class QDialogButtonBox;
class QGridLayout;
class QGroupBox;
class QLabel;
class QPushButton;
class Dialog : public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
Dialog(QWidget *parent = 0);
private slots:
void buttonsOrientationChanged(int index);
void rotateWidgets();
void help();
private:
void createRotatableGroupBox();
void createOptionsGroupBox();
void createButtonBox();
QGroupBox *rotatableGroupBox;
QQueue<QWidget *> rotatableWidgets;
QGroupBox *optionsGroupBox;
QLabel *buttonsOrientationLabel;
QComboBox *buttonsOrientationComboBox;
QDialogButtonBox *buttonBox;
QPushButton *closeButton;
QPushButton *helpButton;
QPushButton *rotateWidgetsButton;
QGridLayout *mainLayout;
QGridLayout *rotatableLayout;
QGridLayout *optionsLayout;
};
#endif // DIALOG_H
dialog.cpp
#include <QtWidgets>
#include "dialog.h"
Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
{
createRotatableGroupBox();
createOptionsGroupBox();
createButtonBox();
mainLayout = new QGridLayout;
mainLayout->addWidget(rotatableGroupBox, 0, 0);
mainLayout->addWidget(optionsGroupBox, 1, 0);
mainLayout->addWidget(buttonBox, 2, 0);
setLayout(mainLayout);
mainLayout->setSizeConstraint(QLayout::SetMinimumSize);
setWindowTitle(tr("Dynamic Layouts"));
}
void Dialog::buttonsOrientationChanged(int index)
{
mainLayout->setSizeConstraint(QLayout::SetNoConstraint);
setMinimumSize(0, 0);
Qt::Orientation orientation = Qt::Orientation(
buttonsOrientationComboBox->itemData(index).toInt());
if (orientation == buttonBox->orientation())
return;
mainLayout->removeWidget(buttonBox);
int spacing = mainLayout->spacing();
QSize oldSizeHint = buttonBox->sizeHint() + QSize(spacing, spacing);
buttonBox->setOrientation(orientation);
QSize newSizeHint = buttonBox->sizeHint() + QSize(spacing, spacing);
if (orientation == Qt::Horizontal) {
mainLayout->addWidget(buttonBox, 2, 0);
resize(size() + QSize(-oldSizeHint.width(), newSizeHint.height()));
} else {
mainLayout->addWidget(buttonBox, 0, 3, 2, 1);
resize(size() + QSize(newSizeHint.width(), -oldSizeHint.height()));
}
mainLayout->setSizeConstraint(QLayout::SetDefaultConstraint);
}
void Dialog::rotateWidgets()
{
Q_ASSERT(rotatableWidgets.count() % 2 == 0);
foreach (QWidget *widget, rotatableWidgets)
rotatableLayout->removeWidget(widget);
rotatableWidgets.enqueue(rotatableWidgets.dequeue());
const int n = rotatableWidgets.count();
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; ++i) {
rotatableLayout->addWidget(rotatableWidgets[n - i - 1], 0, i);
rotatableLayout->addWidget(rotatableWidgets[i], 1, i);
}
}
void Dialog::help()
{
QMessageBox::information(this, tr("Dynamic Layouts Help"),
tr("This example shows how to change layouts "
"dynamically."));
}
void Dialog::createRotatableGroupBox()
{
rotatableGroupBox = new QGroupBox(tr("Rotatable Widgets"));
rotatableWidgets.enqueue(new QSpinBox);
rotatableWidgets.enqueue(new QSlider);
rotatableWidgets.enqueue(new QDial);
rotatableWidgets.enqueue(new QProgressBar);
int n = rotatableWidgets.count();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
connect(rotatableWidgets[i], SIGNAL(valueChanged(int)),
rotatableWidgets[(i + 1) % n], SLOT(setValue(int)));
}
rotatableLayout = new QGridLayout;
rotatableGroupBox->setLayout(rotatableLayout);
rotateWidgets();
}
void Dialog::createOptionsGroupBox()
{
optionsGroupBox = new QGroupBox(tr("Options"));
buttonsOrientationLabel = new QLabel(tr("Orientation of buttons:"));
buttonsOrientationComboBox = new QComboBox;
buttonsOrientationComboBox->addItem(tr("Horizontal"), Qt::Horizontal);
buttonsOrientationComboBox->addItem(tr("Vertical"), Qt::Vertical);
connect(buttonsOrientationComboBox,
QOverload<int>::of(&QComboBox::currentIndexChanged),
this,
&Dialog::buttonsOrientationChanged);
optionsLayout = new QGridLayout;
optionsLayout->addWidget(buttonsOrientationLabel, 0, 0);
optionsLayout->addWidget(buttonsOrientationComboBox, 0, 1);
optionsLayout->setColumnStretch(2, 1);
optionsGroupBox->setLayout(optionsLayout);
}
void Dialog::createButtonBox()
{
buttonBox = new QDialogButtonBox;
closeButton = buttonBox->addButton(QDialogButtonBox::Close);
helpButton = buttonBox->addButton(QDialogButtonBox::Help);
rotateWidgetsButton = buttonBox->addButton(tr("Rotate &Widgets"),
QDialogButtonBox::ActionRole);
connect(rotateWidgetsButton, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &Dialog::rotateWidgets);
connect(closeButton, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &Dialog::close);
connect(helpButton, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &Dialog::help);
}
引用
[1] Qt助手






















 3159
3159

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








