-
Image Processing (imgproc module)
In this section you will learn about the image processing (manipulation) functions inside OpenCV.
边缘检测
-
Compatibility: > OpenCV 2.0
Author: Ana Huamán
Where we learn a sophisticated alternative to detect edges.
Canny Edge detector,也叫optimal detector,是由John F. Canny于1986年开发的。这种算法旨在满足下面三个标尺:
- Low error rate: Meaning a good detection of only existent edges.
- 低错误率:仅仅在边缘检测出轮廓
- Good localization: The distance between edge pixels detected and real edge pixels have to be minimized.
- 精准定位:检测出的边缘尽可能的与实际边缘重合
- Minimal response: Only one detector response per edge.
- 最小回应:一个边缘只产生一个检测结果
步骤
过滤噪声:参见平滑处理
发现图像梯度大的部分:参见梯度;额外的,真正的梯度应有方向,这里是计算了方向的。
截取非最大部分:保存轮廓线边缘
Hysteresis(迟滞):对于高于阈值上线的部分视为边界,低于阈值下线的被忽视,处于两个阈值之间的,且于高于阈值上线部分相连的,也被视为边界。
Create some needed variables 声明所需变量
Loads the source image 装载图片
Create a matrix of the same type and size of src (to be dst) 为输出图像开辟空间
Convert the image to grayscale (using the function cv::cvtColor 灰度转换
Create a window to display the results 创建显示窗口
Create a Trackbar for the user to enter the lower threshold for our Canny detector 创建Trackbar对象,输入阈值下线
Let's check the CannyThreshold function, step by step Canny算法实现
We fill a dst image with zeros (meaning the image is completely black) 初始化输出图像矩阵
Finally, we will use the function cv::Mat::copyTo to map only the areas of the image that are identified as edges 将处理结果拷贝到输出图像中
We display our result:显示结果
Hough变换
-
Compatibility: > OpenCV 2.0
Author: Ana Huamán
Where we learn how to detect lines
-
Compatibility: > OpenCV 2.0
Author: Ana Huamán
Where we learn how to detect circles
重映射
-
Compatibility: > OpenCV 2.0
Author: Ana Huamán
Where we learn how to manipulate pixels locations
假如有一个图像表达式:h(x,y),表示在一定区间内,给定一个坐标(x,y),则对应于该坐标的图像的值为h(x,y),这是原图像在坐标上的映射。
现在把他重映射了,即有一个映射函数f,输入参数为原图像中的某点,能得到对应输出图像中的另外一点。
补充:我觉得吧,这里看似多此一举的绘制map_x、map_y,实际上是一种高效开发的必然。这样可以让操作和功能分离,保证了功能的自由拓展能力,而避免了重复的对操作(remap)过程的调试开发。
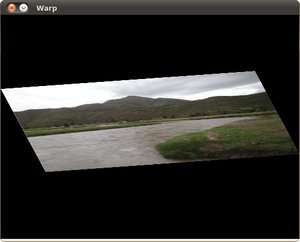
仿射变换
-
Compatibility: > OpenCV 2.0
Author: Ana Huamán
Where we learn how to rotate, translate and scale our images
理论请自行查看,这是一种相对于重映射更为固定化的过程,因此具有更具描述性的操作。
cv::warpAffine cv::getRotationMatrix2D
像素均衡、直方图均衡化 Histogram Equalization
-
Compatibility: > OpenCV 2.0
Author: Ana Huamán
Where we learn how to improve the contrast in our images
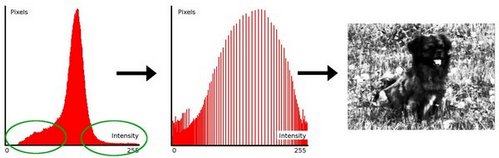
理论:像素直方图是一个分布不太均匀的东西,这让我们感觉图像不够饱满。现在强行把他们之间的距离拉大,比如原先只有深红、猩红、血红这样色差不大的一些颜色,现在为了增加表现力,我把他们改为红黑、亮红、浅红这样差别比较大的颜色。
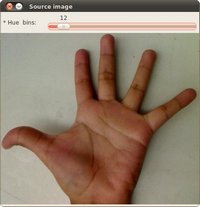
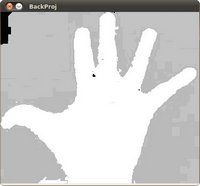
背景投影
-
Compatibility: > OpenCV 2.0
Author: Ana Huamán
Where we learn how to use histograms to find similar objects in images
。。。貌似能抓住图像中的鲜艳部分,有挖出背景的功能。各位大神原谅我这弱鳥,实在是啃不动这些图形图像专业的东西。我尽量把更多直接明了的部分放进来,有需要用到这些功能的可以方便检索。

模式匹配(模板搜索)
-
Compatibility: > OpenCV 2.0
Author: Ana Huamán
Where we learn how to match templates in an image
功能:找到src中与目标最为匹配的区域
这里提出了六种匹配方式:
-
method=CV_TM_SQDIFF
R(x,y)=∑x′,y′(T(x′,y′)−I(x+x′,y+y′))2 -
method=CV_TM_SQDIFF_NORMED
R(x,y)=∑x′,y′(T(x′,y′)−I(x+x′,y+y′))2∑x′,y′T(x′,y′)2⋅∑x′,y′I(x+x′,y+y′)2‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾√ -
method=CV_TM_CCORR
R(x,y)=∑x′,y′(T(x′,y′)⋅I(x+x′,y+y′)) -
method=CV_TM_CCORR_NORMED
R(x,y)=∑x′,y′(T(x′,y′)⋅I(x+x′,y+y′))∑x′,y′T(x′,y′)2⋅∑x′,y′I(x+x′,y+y′)2‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾√ -
method=CV_TM_CCOEFF
R(x,y)=∑x′,y′(T′(x′,y′)⋅I′(x+x′,y+y′))where
T′(x′,y′)=T(x′,y′)−1/(w⋅h)⋅∑x″,y″T(x″,y″)I′(x+x′,y+y′)=I(x+x′,y+y′)−1/(w⋅h)⋅∑x″,y″I(x+x″,y+y″) -
method=CV_TM_CCOEFF_NORMED
R(x,y)=∑x′,y′(T′(x′,y′)⋅I′(x+x′,y+y′))∑x′,y′T′(x′,y′)2⋅∑x′,y′I′(x+x′,y+y′)2‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾√
寻找轮廓
-
Finding contours in your image
Compatibility: > OpenCV 2.0
Author: Ana Huamán
Where we learn how to find contours of objects in our image
- Use the OpenCV function cv::findContours
- Use the OpenCV function cv::drawContours


凸包
-
Compatibility: > OpenCV 2.0
Author: Ana Huamán
Where we learn how to get hull contours and draw them!

创建边界区域、圆
-
Creating Bounding boxes and circles for contours
Compatibility: > OpenCV 2.0
Author: Ana Huamán
Where we learn how to obtain bounding boxes and circles for our contours.
-
Creating Bounding rotated boxes and ellipses for contours
Compatibility: > OpenCV 2.0
Author: Ana Huamán
Where we learn how to obtain rotated bounding boxes and ellipses for our contours.
关键看这里
-
For every found contour we now apply approximation to polygons with accuracy +-3 and stating that the curve must me closed.
After that we find a bounding rect for every polygon and save it to boundRect.
At last we find a minimum enclosing circle for every polygon and save it to center and radius vectors.
for( size_t i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++ ){approxPolyDP( Mat(contours[i]), contours_poly[i], 3, true );boundRect[ i] = boundingRect( Mat(contours_poly[i]) );minEnclosingCircle( contours_poly[i], center[i], radius[i] );}We found everything we need, all we have to do is to draw.
效果:
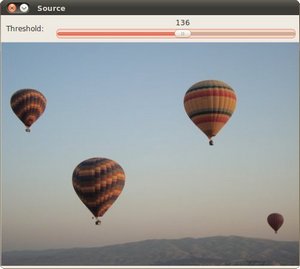
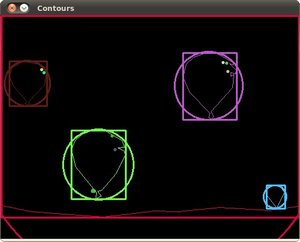





















 906
906

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








