Faster-Whisper 实时识别电脑语音转文本
前言
以前做的智能对话软件接的Baidu API,想换成本地的,就搭一套Faster-Whisper吧。
下面是B站视频实时转写的截图

项目
搭建环境
所需要的CUDANN已经装好了,如果装的是12.2应该是包含cuBLAS了
没装的,可以从下面链接下载装一下,文末的参考视频中也有讲解
https://github.com/Purfview/whisper-standalone-win/releases/tag/libs

Ancanda的运行环境去Clone一下之前配好的环境,用之前BertVits的即可
安装Faster-Whisper
输入即可安装
pip install faster-whisper
下载模型
https://huggingface.co/Systran/faster-whisper-large-v3
下载完放到代码旁边就可以了

编写测试代码
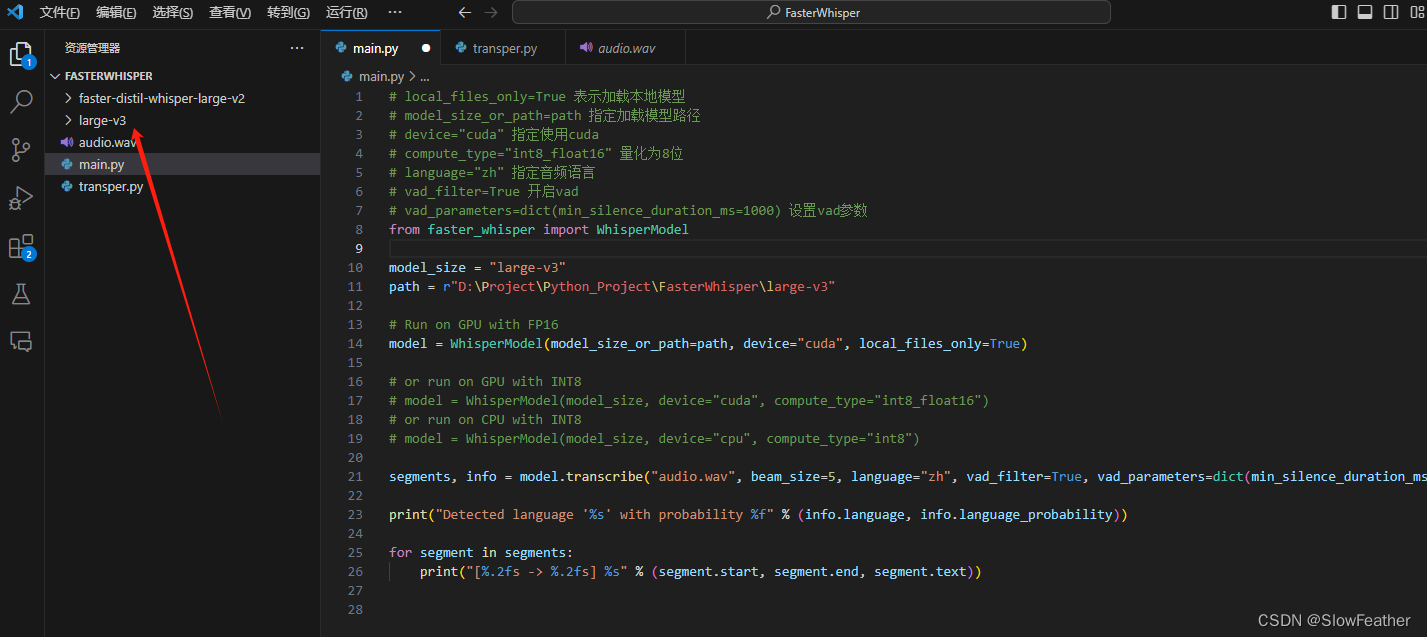
# local_files_only=True 表示加载本地模型
# model_size_or_path=path 指定加载模型路径
# device="cuda" 指定使用cuda
# compute_type="int8_float16" 量化为8位
# language="zh" 指定音频语言
# vad_filter=True 开启vad
# vad_parameters=dict(min_silence_duration_ms=1000) 设置vad参数
from faster_whisper import WhisperModel
model_size = "large-v3"
path = r"D:\Project\Python_Project\FasterWhisper\large-v3"
# Run on GPU with FP16
model = WhisperModel(model_size_or_path=path, device="cuda", local_files_only=True)
# or run on GPU with INT8
# model = WhisperModel(model_size, device="cuda", compute_type="int8_float16")
# or run on CPU with INT8
# model = WhisperModel(model_size, device="cpu", compute_type="int8")
segments, info = model.transcribe("audio.wav", beam_size=5, language="zh", vad_filter=True, vad_parameters=dict(min_silence_duration_ms=1000))
print("Detected language '%s' with probability %f" % (info.language, info.language_probability))
for segment in segments:
print("[%.2fs -> %.2fs] %s" % (segment.start, segment.end, segment.text))
运行测试代码
找个音频放入文件夹内,输入python main.py即可运行!
可以看到正确(不太正确)的识别出了音频说了什么。

实时转写脚本
新建一个脚本transper.py
运行即可
此处特别感谢开源项目
https://github.com/MyloBishop/transper
import os
import sys
import time
import wave
import tempfile
import threading
import torch
import pyaudiowpatch as pyaudio
from faster_whisper import WhisperModel as whisper
# A bigger audio buffer gives better accuracy
# but also increases latency in response.
# 表示音频缓冲时间的常量
AUDIO_BUFFER = 5
# 此函数使用 PyAudio 库录制音频,并将其保存为一个临时的 WAV 文件。
# 使用 pyaudio.PyAudio 实例创建一个音频流,通过指定回调函数 callback 来实时写入音频数据到 WAV 文件。
# time.sleep(AUDIO_BUFFER) 会阻塞执行,确保录制足够的音频时间。
# 最后,函数返回保存的 WAV 文件的文件名。
def record_audio(p, device):
"""Record audio from output device and save to temporary WAV file."""
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(suffix=".wav", delete=False) as f:
filename = f.name
wave_file = wave.open(filename, "wb")
wave_file.setnchannels(device["maxInputChannels"])
wave_file.setsampwidth(pyaudio.get_sample_size(pyaudio.paInt16))
wave_file.setframerate(int(device["defaultSampleRate"]))
def callback(in_data, frame_count, time_info, status):
"""Write frames and return PA flag"""
wave_file.writeframes(in_data)
return (in_data, pyaudio.paContinue)
stream = p.open(
format=pyaudio.paInt16,
channels=device["maxInputChannels"],
rate=int(device["defaultSampleRate"]),
frames_per_buffer=pyaudio.get_sample_size(pyaudio.paInt16),
input=True,
input_device_index=device["index"],
stream_callback=callback,
)
try:
time.sleep(AUDIO_BUFFER) # Blocking execution while playing
finally:
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
wave_file.close()
# print(f"{filename} saved.")
return filename
# 此函数使用 Whisper 模型对录制的音频进行转录,并输出转录结果。
def whisper_audio(filename, model):
"""Transcribe audio buffer and display."""
# segments, info = model.transcribe(filename, beam_size=5, task="translate", language="zh", vad_filter=True, vad_parameters=dict(min_silence_duration_ms=1000))
segments, info = model.transcribe(filename, beam_size=5, language="zh", vad_filter=True, vad_parameters=dict(min_silence_duration_ms=1000))
os.remove(filename)
# print(f"{filename} removed.")
for segment in segments:
# print(f"[{segment.start:.2f} -> {segment.end:.2f}] {segment.text.strip()}")
print("[%.2fs -> %.2fs] %s" % (segment.start, segment.end, segment.text))
# main 函数是整个脚本的主控制函数。
# 加载 Whisper 模型,选择合适的计算设备(GPU 或 CPU)。
# 获取默认的 WASAPI 输出设备信息,并选择默认的扬声器(输出设备)。
# 使用 PyAudio 开始录制音频,并通过多线程运行 whisper_audio 函数进行音频转录。
def main():
"""Load model record audio and transcribe from default output device."""
print("Loading model...")
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print(f"Using {device} device.")
# model = whisper("large-v3", device=device, compute_type="float16")
model = whisper("large-v3", device=device, local_files_only=True)
print("Model loaded.")
with pyaudio.PyAudio() as pya:
# Create PyAudio instance via context manager.
try:
# Get default WASAPI info
wasapi_info = pya.get_host_api_info_by_type(pyaudio.paWASAPI)
except OSError:
print("Looks like WASAPI is not available on the system. Exiting...")
sys.exit()
# Get default WASAPI speakers
default_speakers = pya.get_device_info_by_index(
wasapi_info["defaultOutputDevice"]
)
if not default_speakers["isLoopbackDevice"]:
for loopback in pya.get_loopback_device_info_generator():
# Try to find loopback device with same name(and [Loopback suffix]).
# Unfortunately, this is the most adequate way at the moment.
if default_speakers["name"] in loopback["name"]:
default_speakers = loopback
break
else:
print(
"""
Default loopback output device not found.
Run `python -m pyaudiowpatch` to check available devices.
Exiting...
"""
)
sys.exit()
print(
f"Recording from: {default_speakers['name']} ({default_speakers['index']})\n"
)
while True:
filename = record_audio(pya, default_speakers)
thread = threading.Thread(target=whisper_audio, args=(filename, model))
thread.start()
main()
实时转写WebSocket服务器模式
在最新Google Bard的帮助下,从同步多线程单机版变成了异步WebSocket服务器版本,Unity可以链接并监听实时转写的数据了(写这篇文章时是冬季,ChatGPT实测已经开始休眠状态了)
import asyncio
import os
import wave
import tempfile
import torch
import pyaudiowpatch as pyaudio
from faster_whisper import WhisperModel as whisper
import websockets
import json
# Audio buffer time
AUDIO_BUFFER = 5
# Dictionary to store WebSocket connections
clients = {}
# handle client
async def handle_client(websocket):
client_id = id(websocket) # Using the WebSocket object's ID as a unique identifier
print(f"Client connected from {websocket.remote_address} with ID {client_id}")
clients[client_id] = websocket
try:
# print(f"Client connected from {websocket.remote_address}")
# Wait for messages from the client
async for message in websocket:
print(f"Received message from client {client_id}: {message}")
# Process the message (you can replace this with your logic)
response = f"Server received: {message}"
# Send a response back to the client
await websocket.send(response)
print(f"Sent response to client {client_id}: {response}")
except websockets.exceptions.ConnectionClosedError:
print(f"Connection with {websocket.remote_address} closed.")
finally:
# Remove the WebSocket connection when the client disconnects
del clients[client_id]
# Send a message to all connected clients
async def send_all_clients(message):
if clients==None or clients=={}:
print("No clients connected.")
return
for client_id, websocket in clients.items():
try:
await websocket.send(message)
print(f"Sent message to client {client_id}: {message}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error sending message to client {client_id}: {e}")
# Send a message to a specific client identified by client_id
async def send_message(client_id, message):
if client_id in clients:
websocket = clients[client_id]
await websocket.send(message)
print(f"Sent message to client {client_id}: {message}")
else:
print(f"Client with ID {client_id} not found.")
# Start the server
async def main_server():
server = await websockets.serve(handle_client, "localhost", 8765)
print("WebSocket server started. Listening on ws://localhost:8765")
await server.wait_closed()
#This function records audio using the PyAudio library and saves it as a temporary WAV file.
#Use pyaudio PyAudio instance creates an audio stream and writes audio data in real-time to a WAV file by specifying the callback function callback.
#Due to the use of the asyncio library, it is no longer necessary to use time. sleep() to block execution, but instead to use asyncio. sleep() to wait asynchronously.
#Finally, the function returns the file name of the saved WAV file.
async def record_audio(p, device):
"""Record audio from output device and save to temporary WAV file."""
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(suffix=".wav", delete=False) as f:
filename = f.name
wave_file = wave.open(filename, "wb")
wave_file.setnchannels(device["maxInputChannels"])
wave_file.setsampwidth(pyaudio.get_sample_size(pyaudio.paInt16))
wave_file.setframerate(int(device["defaultSampleRate"]))
def callback(in_data, frame_count, time_info, status):
"""Write frames and return PA flag"""
wave_file.writeframes(in_data)
return (in_data, pyaudio.paContinue)
stream = p.open(
format=pyaudio.paInt16,
channels=device["maxInputChannels"],
rate=int(device["defaultSampleRate"]),
frames_per_buffer=pyaudio.get_sample_size(pyaudio.paInt16),
input=True,
input_device_index=device["index"],
stream_callback=callback,
)
await asyncio.sleep(AUDIO_BUFFER)
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
wave_file.close()
# print(f"{filename} saved.")
return filename
# SegmentData class
class SegmentData:
def __init__(self, start, end,text):
# 实例属性
self.start = start
self.end = end
self.text = text
def __dict__(self):
return {"start": self.start, "end": self.end, "text": self.text}
def convert_to_unity_data(data): # 参数 data 为字典列表
unity_data = []
for item in data:
segment_data = SegmentData(item["start"], item["end"], item["text"])
unity_data.append(segment_data)
return unity_data
# This function transcribes the recorded audio using the Whisper model and outputs the transcription result.
async def whisper_audio(filename, model):
"""Transcribe audio buffer and display."""
segments, info = model.transcribe(filename, beam_size=5, language="zh", vad_filter=True, vad_parameters=dict(min_silence_duration_ms=1000))
os.remove(filename)
# print(f"{filename} removed.")
if segments:
segments_dict_list = [{"start": segment.start, "end": segment.end, "text": segment.text.strip()} for segment in segments]
json_transcriptions=json.dumps(segments_dict_list)
print(f"Transcription: {json_transcriptions}")
try:
await send_all_clients(json_transcriptions)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error sending message: {e}")
# Start recording audio using PyAudio and concurrently run the whisper_audio function for audio transcription using asyncio.gather.
async def main():
"""Load model record audio and transcribe from default output device."""
print("Loading model...")
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print(f"Using {device} device.")
model = whisper("large-v3", device=device, local_files_only=True,compute_type="int8_float16")
print("Model loaded.")
with pyaudio.PyAudio() as pya:
# Get microphone device information (assuming you want to select the first microphone device)
microphone_index = 0
microphone_info = pya.get_device_info_by_index(microphone_index)
while True:
filename = await record_audio(pya, microphone_info)
await asyncio.gather(whisper_audio(filename, model))
async def appmain():
await asyncio.gather(main(), main_server()) # Gather coroutines here
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(appmain()) # Pass the main coroutine to asyncio.run()
参考
faster-whisper
MyloBishop/transper
Google Bard
基于faster_whisper的实时语音识别
基于faster whisper实现实时语音识别项目语音转文本python编程实现







 本文介绍了如何在本地搭建环境,安装Faster-Whisper模型,并通过实时转写脚本和WebSocket服务器实现音频的实时识别和转写。作者分享了从BaiduAPI切换到本地解决方案的过程,包括测试代码、音频处理和WebSocket服务的整合示例。
本文介绍了如何在本地搭建环境,安装Faster-Whisper模型,并通过实时转写脚本和WebSocket服务器实现音频的实时识别和转写。作者分享了从BaiduAPI切换到本地解决方案的过程,包括测试代码、音频处理和WebSocket服务的整合示例。
















 379
379

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








