刚开始接触java的时候免不了对多线程技术总是怀抱着好奇心,总想弄明白多线程好在哪里。甚至于认为使用多线程效率就比单线程要高。但事实真的如此吗?下面我们做一些测试
测试1-单线程执行效率
public static void main(String[] args) {
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 总数据条数
int dataSize = 5000;
System.out.println("开启1个线程...");
// 创建一个线程池
ExecutorService pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
for (int i = 0; i <dataSize ; i++) {
//放到线程池中,线程异步执行
pool.execute(new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//模拟业务处理数据的时间
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
//当调用shutdown()方法后,并且所有提交的任务完成后,isTerminated()返回为true;
pool.shutdown();
while (true) {
if (pool.isTerminated()) {//所有的子线程都结束了
break;
}
}
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("总共花费了===========" + (end - start) / 1000 + "." + (end - start) % 1000 + "s");
}
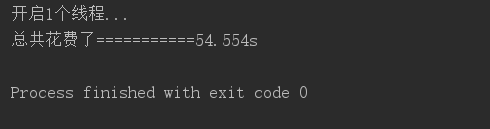
结果:
测试2-多线程执行效率(5个线程异步执行)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 总数据条数
int dataSize = 5000;
// 每1000条数据开启一条线程
int threadSize = 1000;
// 线程数
int threadNum = dataSize / threadSize;
System.out.println("开启" + threadNum + "个线程...");
ExecutorService pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadNum, threadNum, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());
// 分割成多个线程执行
for (int i = 0; i < dataSize; i++) {
//放到线程池中,线程异步执行
pool.execute(new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//模拟业务处理数据的时间
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
pool.shutdown();
while (true) {
if (pool.isTerminated()) {
break;
}
}
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("总共花费了===========" + (end - start) / 1000 + "." + (end - start) % 1000 + "s");
}
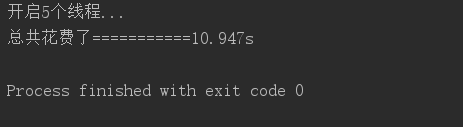
结果:
测试3-多线程执行效率(50个线程异步执行)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 总数据条数
int dataSize = 5000;
// 每100条数据开启一条线程
int threadSize = 100;
// 线程数
int threadNum = dataSize / threadSize;
System.out.println("开启" + threadNum + "个线程...");
ExecutorService pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadNum, threadNum, 0L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());
// 分割成多个线程执行
for (int i = 0; i < dataSize; i++) {
//放到线程池中,线程异步执行
pool.execute(new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//模拟业务处理数据的时间
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
pool.shutdown();
while (true) {
if (pool.isTerminated()) {
break;
}
}
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("总共花费了===========" + (end - start) / 1000 + "." + (end - start) % 1000 + "s");
}
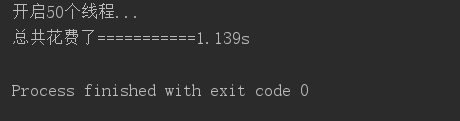
结果:
测试4-多线程执行效率(500个线程异步执行)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 总数据条数
int dataSize = 5000;
// 每10条数据开启一条线程
int threadSize = 10;
// 线程数
int threadNum = dataSize / threadSize;
System.out.println("开启" + threadNum + "个线程...");
ExecutorService pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadNum, threadNum, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());
// 分割成多个线程执行
for (int i = 0; i < dataSize; i++) {
//放到线程池中,线程异步执行
pool.execute(new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//模拟业务处理数据的时间
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
pool.shutdown();
while (true) {
if (pool.isTerminated()) {
break;
}
}
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("总共花费了===========" + (end - start) / 1000 + "." + (end - start) % 1000 + "s");
}
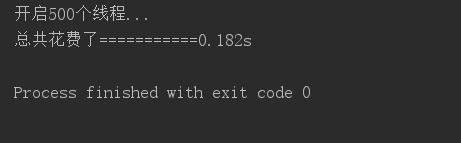
结果:
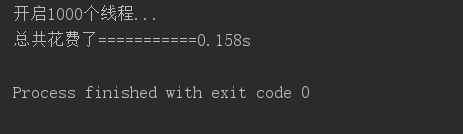
测试5-多线程执行效率(1000个线程异步执行)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 总数据条数
int dataSize = 5000;
// 每5条数据开启一条线程
int threadSize = 5;
// 线程数
int threadNum = dataSize / threadSize;
System.out.println("开启" + threadNum + "个线程...");
ExecutorService pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadNum, threadNum, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());
// 分割成多个线程执行
for (int i = 0; i < threadNum; i++) {
//放到线程池中,线程异步执行
pool.execute(new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//模拟业务处理数据的时间
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
pool.shutdown();
while (true) {
if (pool.isTerminated()) {
break;
}
}
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("总共花费了===========" + (end - start) / 1000 + "." + (end - start) % 1000 + "s");
}
结果:
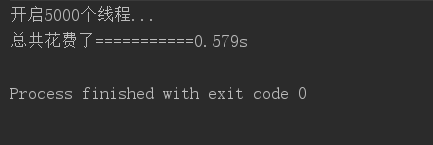
测试6-多线程执行效率(5000个线程异步执行)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 总数据条数
int dataSize = 5000;
// 每1条数据开启一条线程
int threadSize = 1;
// 线程数
int threadNum = dataSize / threadSize;
System.out.println("开启" + threadNum + "个线程...");
ExecutorService pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadNum, threadNum, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());
// 分割成多个线程执行
for (int i = 0; i < threadNum; i++) {
//放到线程池中,线程异步执行
pool.execute(new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//模拟业务处理数据的时间
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
pool.shutdown();
while (true) {
if (pool.isTerminated()) {
break;
}
}
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("总共花费了===========" + (end - start) / 1000 + "." + (end - start) % 1000 + "s");
}
结果:
数据分析
1个线程---------------54.554s
5个线程---------------10.947s
50个线程--------------1.139s
500个线程-------------0.182s
1000个线程-----------0.158s
5000个线程-----------0.579s
总结:
多线程的确可以提高并发任务处理效率,特别是初期线程数慢慢提高的时候。但随着线程数大幅的提高效率却降低了。在我本地测试的线程数到达5000个的时候明显效率还不如500个~。这是因为每台计算机都有其性能瓶颈,开多少线程效率最高, 和线程的任务利用何种部件,以及这些部件的独立/共享状态相关。至于能运行多少个线程与你运行的程序有关,你可以用以下代码在自己电脑上测试可以开到多少个线程(谨慎使用)。
private static Object object = new Object();
private static int count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(;;){
new Thread(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
synchronized(object){
count += 1;
System.err.println("New thread #"+count);
}
for(;;){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e){
System.err.println(e);
}
}
}
}).start();
}
}
我用jdk1.8 + windows10 + 4核CPU + 8G内存 最多到 172020 的时候就死机了~






















 4234
4234











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








