When a user creates a file or directory under Linux or UNIX, she makes it with default permissions. In most cases, the system defaults may be open or relaxed for file sharing purposes. For example, if a text file has 666 permissions, it grants read and write permission to everyone. Similarly, a directory with 777 permissions grants read, write, and execute permission to everyone.
What is Umask and find the default umask value?
The user file-creation mode mask (umask) is used to determine the file permission for newly created files. It can be used to control the default file permission for new files. It is a four-digit octal number. A umask can be set or expressed using:
- Symbolic values
- Octal values
Use the umask command to set default file permissions on Linux and Unix-like machines.
Finding the current shell’s umask value
The umask command without any arguments will display the current value of the shell’s umask. For example:
umask
Procedure to set up default umask on Linux
You can set up umask in /etc/bashrc or /etc/profile file for all users. By default most Linux distro set it to 0022 (022) or 0002 (002). Edit the ~/.bashrc file in your HOME directory to override the system defaults:
On all modern Linux distro it is better to create or edit the /etc/profile.d/set-umask-for-all-users.sh file to override the system defaults for ALL USERS:
vi /etc/profile.d/set-umask-for-all-users.sh
OR edit your personal ~/.bashrc or ~/.bash_profile file:
vi ~/.bashrc
Append/modify the following line to set up a new umask on Linux:
umask 022
Save and close the file when using vim/vi as a text editor by pressing the ESC+x. Changes will take effect after next login. All UNIX users can override the system umask defaults in their /etc/profile file, ~/.profile (Korn / Bourne shell) ~/.cshrc file (C shells), ~/.bash_profile (Bash shell) or ~/.login file (defines the user’s environment at login).
Explain octal umask mode 022 and 002
As I said earlier, if the default settings are not changed, files are created with the access mode 666 and directories with 777. In this example:
- The default umask 002 used for normal user. With this mask default directory permissions are 775 and default file permissions are 664.
- The default umask for the root user is 022 result into default directory permissions are 755 and default file permissions are 644.
- For directories, the base permissions are (rwxrwxrwx) 0777 and for files they are 0666 (rw-rw-rw).
In short,
- A umask of 022 allows only you to write data, but anyone can read data.
- A umask of 077 is good for a completely private system. No other user can read or write your data if umask is set to 077.
- A umask of 002 is good when you share data with other users in the same group. Members of your group can create and modify data files; those outside your group can read data file, but cannot modify it. Set your umask to 007 to completely exclude users who are not group members.
But, how do I calculate umask value under Linux?
The octal umasks are calculated via the bitwise AND of the unary complement of the argument using bitwise NOT. The octal notations are as follows:
-
-
-
- Octal value : Permission
- 0 : read, write and execute
- 1 : read and write
- 2 : read and execute
- 3 : read only
- 4 : write and execute
- 5 : write only
- 6 : execute only
- 7 : no permissions
-
-
Now, you can use above table to calculate file permission. For example, if umask is set to 077, the permission can be calculated as follows:
| Bit | Targeted at | File permission |
| 0 | Owner | read, write and execute |
| 7 | Group | No permissions |
| 7 | Others | No permissions |
umask examples
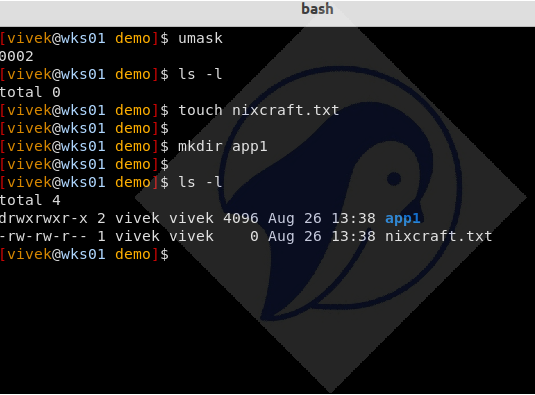
The following example explains how the umask affects the permissions of files and directories on Linux and Unix-like systems. First, note down the default umask permissions for both files and directories in the current shell using the ls command:
umask
ls -l
touch nixcraft.txt
mkdir app1
ls -l
Let us see what happens if you set umask to 0:
umask 0
ls -l
touch cyberciti.biz.txt
mkdir myapp1
ls -l
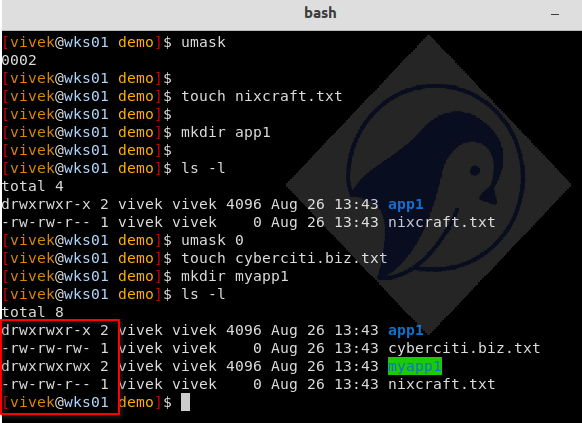
The cyberciti.biz.txt file permissions for other changes from read to read and write. The myapp1 directory permissions for other changes from read and execute to read, write, and execute.
Next, set the umask 077 type the following umask command at shell prompt:
umask 077
Make a new directory using the mkdir command and a new file using the touch command as follows:
mkdir dir1
touch file
Use the ls command to list file details including permissions:
ls -ld dir1 file
Here is what I see when the umask is set to 077:
drwx------ 2 vivek vivek 4096 2011-03-04 02:05 dir1 -rw------- 1 vivek vivek 0 2011-03-04 02:05 file
Task: Calculating The Final Permission For FILES
You can simply subtract the umask from the base permissions to determine the final permission for file as follows:
666 – 022 = 644
- File base permissions : 666
- umask value : 022
- subtract to get permissions of new file (666-022) : 644 (rw-r–r–)
Task: Calculating The Final Permission For DIRECTORIES
You can simply subtract the umask from the base permissions to determine the final permission for directory as follows:
777 – 022 = 755
- Directory base permissions : 777
- umask value : 022
- Subtract to get permissions of new directory (777-022) : 755 (rwxr-xr-x)
How Do I Set umask Using Symbolic Values?
The following symbolic values are used:
- r : read
- w : write
- x : execute
- u : User ownership (user who owns the file)
- g : group ownership (the permissions granted to other users who are members of the file’s group)
- o : other ownership (the permissions granted to users that are in neither of the two preceding categories)
The following command will set umask to 077 i.e. a umask set to u=rwx,g=,o= will result in new files having the modes -rw-------, and new directories having the modes drwx------:
umask u=rwx,g=,o=
mkdir dir2
touch file2
ls -ld dir2 file2
Sample umask Values and File Creation Permissions
| If umask value set to | User permission | Group permission | Others permission |
| 000 | all | all | all |
| 007 | all | all | none |
| 027 | all | read / execute | none |
all = read, write and executable file permission
Limitations of the umask
- The umask command can restricts permissions.
- The umask command cannot grant extra permissions beyond what is specified by the program that creates the file or directory. If you need to make permission changes to existing file use the chmod command.
umask and level of security
The umask command be used for setting different security levels as follows:
| umask value | Security level | Effective permission (directory) |
| 022 | Permissive | 755 |
| 026 | Moderate | 751 |
| 027 | Moderate | 750 |
| 077 | Severe | 700 |
Summing up
For more information about the umask read the man page of bash or ksh or tcsh shell using the man command or help command:
man bash
help umask
man chmod




















 7178
7178

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








