Regularized Linear Regression and Bias v.s. Variance
实现正则化线性回归模型,并且学习不同方差、偏差下的模型特性。
已有脚本:
ex5.m-Octave / MATLAB的引导脚本
ex5data1.mat-数据集
featureNormalize.m-归一化函数
fmincg.m-函数最小化例程(类似于fminunc)
plotFit.m-绘制多项式t
trainLinearReg.m-使用成本函数训练线性回归
编写脚本:
linearRegCostFunction.m-正则化线性回归损失函数
learningCurve.m-生成学习曲线
polyFeatures.m-将数据映射到多项式特征空间
validationCurve.m-生成交叉验证曲线
1、Regularized Linear Regression 正则化线性回归
1.1 Visualizing the dataset:
数据集分为三部分:
- 训练集:X,y
- 交叉验证集:Xval,yval
- 测试集:Xtest,ytest
1.2 & 1.3 Regularized linear regression cost function: & Regularized linear regression gradient:
线性回归的损失函数(不要和logistic回归的损失函数记混了):

线性回归的梯度计算公式:
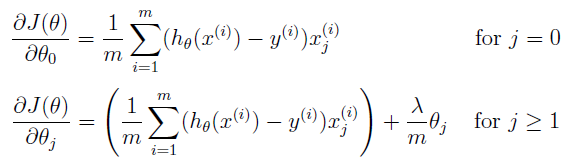
linearRegCostFunction.m:
function [J, grad] = linearRegCostFunction(X, y, theta, lambda)
%LINEARREGCOSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for regularized linear
%regression with multiple variables
% [J, grad] = LINEARREGCOSTFUNCTION(X, y, theta, lambda) computes the
% cost of using theta as the parameter for linear regression to fit the
% data points in X and y. Returns the cost in J and the gradient in grad% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost and gradient of regularized linear
% regression for a particular choice of theta.
%
% You should set J to the cost and grad to the gradient.
%
h = X * theta;
J = ((h-y)'*(h-y))/(2*m) + lambda*(theta(2:end,:)'*theta(2:end,:))/(2*m); %注意正则项是从j=1开始,而不是从j=0开始的
grad = ((h-y)'*X)/m + lambda*(theta')/m;% =========================================================================
grad = grad(:);
end
注意:正则项是从第二项开始的,也就是下标为 j = 1 而不是 j = 0.如果正则项同样把第一项也算上,这个部分的损失函数相差不大,但是到后面的计算则会有较大的偏差。
2 Bias-variance: 偏差-方差
由于没有足够代表所有数据的特征的数据会导致模型有高偏差,也就是会使模型欠拟合;但是过多的特征又会使模型具有高方差,也就是趋于过拟合状态。
2.1 Learing curves:
学习曲线是检测学习算法的重要方式,其主要绘制了训练偏差和交叉验证偏差。
注意两个误差都是不包括正则项的;

learningCurve.m:
function [error_train, error_val] = ...
learningCurve(X, y, Xval, yval, lambda)
%LEARNINGCURVE Generates the train and cross validation set errors needed
%to plot a learning curve
% [error_train, error_val] = ...
% LEARNINGCURVE(X, y, Xval, yval, lambda) returns the train and
% cross validation set errors for a learning curve. In particular,
% it returns two vectors of the same length - error_train and
% error_val. Then, error_train(i) contains the training error for
% i examples (and similarly for error_val(i)).
%
% In this function, you will compute the train and test errors for
% dataset sizes from 1 up to m. In practice, when working with larger
% datasets, you might want to do this in larger intervals.
%% Number of training examples
m = size(X, 1);% You need to return these values correctly
error_train = zeros(m, 1);
error_val = zeros(m, 1);% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Fill in this function to return training errors in
% error_train and the cross validation errors in error_val.
% i.e., error_train(i) and
% error_val(i) should give you the errors
% obtained after training on i examples.
%
% Note: You should evaluate the training error on the first i training
% examples (i.e., X(1:i, :) and y(1:i)).
%
% For the cross-validation error, you should instead evaluate on
% the _entire_ cross validation set (Xval and yval).
%
% Note: If you are using your cost function (linearRegCostFunction)
% to compute the training and cross validation error, you should
% call the function with the lambda argument set to 0.
% Do note that you will still need to use lambda when running
% the training to obtain the theta parameters.
%
% Hint: You can loop over the examples with the following:
%
% for i = 1:m
% % Compute train/cross validation errors using training examples
% % X(1:i, :) and y(1:i), storing the result in
% % error_train(i) and error_val(i)
% ....
%
% end
%% ---------------------- Sample Solution ----------------------
for i =1:m
X_temple = X(1:i,:);
y_temple = y(1:i);
theta = trainLinearReg(X_temple, y_temple, lambda);
error_train(i,1) = ((X_temple*theta-y_temple)'*(X_temple*theta-y_temple)) / (2*m);
error_val(i,1) = ((Xval*theta-yval)'*(Xval*theta-yval)) / (2*size(yval,1));
end
% -------------------------------------------------------------% =========================================================================
end
3 Polynomial regression:
polyFeatures.m:
function [X_poly] = polyFeatures(X, p)
%POLYFEATURES Maps X (1D vector) into the p-th power
% [X_poly] = POLYFEATURES(X, p) takes a data matrix X (size m x 1) and
% maps each example into its polynomial features where
% X_poly(i, :) = [X(i) X(i).^2 X(i).^3 ... X(i).^p];
%
% You need to return the following variables correctly.
X_poly = zeros(numel(X), p);% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Given a vector X, return a matrix X_poly where the p-th
% column of X contains the values of X to the p-th power.
%
%
for i = 1:p
X_poly(:,i) = power(X,i);
end% =========================================================================
end
3.3 Selecting λ using a cross validation set:
validationCurve.m:
function [lambda_vec, error_train, error_val] = ...
validationCurve(X, y, Xval, yval)
%VALIDATIONCURVE Generate the train and validation errors needed to
%plot a validation curve that we can use to select lambda
% [lambda_vec, error_train, error_val] = ...
% VALIDATIONCURVE(X, y, Xval, yval) returns the train
% and validation errors (in error_train, error_val)
% for different values of lambda. You are given the training set (X,
% y) and validation set (Xval, yval).
%% Selected values of lambda (you should not change this)
lambda_vec = [0 0.001 0.003 0.01 0.03 0.1 0.3 1 3 10]';% You need to return these variables correctly.
error_train = zeros(length(lambda_vec), 1);
error_val = zeros(length(lambda_vec), 1);% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Fill in this function to return training errors in
% error_train and the validation errors in error_val. The
% vector lambda_vec contains the different lambda parameters
% to use for each calculation of the errors, i.e,
% error_train(i), and error_val(i) should give
% you the errors obtained after training with
% lambda = lambda_vec(i)
%
% Note: You can loop over lambda_vec with the following:
%
% for i = 1:length(lambda_vec)
% lambda = lambda_vec(i);
% % Compute train / val errors when training linear
% % regression with regularization parameter lambda
% % You should store the result in error_train(i)
% % and error_val(i)
% ....
%
% end
%
%
for i = 1:length(lambda_vec)
lambda = lambda_vec(i);
theta = trainLinearReg(X, y, lambda);
error_train(i) = linearRegCostFunction(X, y, theta, 0);
error_val(i) = linearRegCostFunction(Xval, yval, theta, 0);
end
% =========================================================================end
选作部分:
3.2 Computing test set error:
%% ===== Comuting test set error ==========
lambda = 3;
theta = trainLinearReg([ones(size(X_poly,1),1) X_poly], y, lambda);
[J, grad] = linearRegCostFunction([ones(size(X_poly_test,1),1) X_poly_test],...
ytest, theta, lambda);
fprintf('Cost J is ', J);
fprintf('grad is ', grad);
可是不知道为什么J = 13.20715,期望值是 J = 3.8599 ???
希望知道的大佬不吝赐教
























 311
311











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








