本文主要针对Map中的Hashmap和LinkedHashMap学习和总结
特点:
1、map<key,value>中不允许重复的key,如果key一样,则会把相同的覆盖,也是把最后一个相同的key添加到map中。
2、Hashmap存储是无序的
3、LinkedHashMap存储是按照添加的顺序存储。1、hashmap实例
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("张", "a");
//这个元素将不会添加到map中;被map.put("王", "b")覆盖
map.put("王", "1");
map.put("王", "b");
map.put("李", "c");
map.put("赵", "d");
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "---" + entry.getValue());
}运行结果:没有把map.put(“王”, “1”);添加到map中,并且 无序。
张---a
赵---d
王---b
李---c分析put源码:
public V put(K key, V value)
{
// 如果 key 为 null,调用 putForNullKey 方法进行处理
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
// 根据 key 的 keyCode 计算 Hash 值
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
// 搜索指定 hash 值在对应 table 中的索引
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
// 如果 i 索引处的 Entry 不为 null,通过循环不断遍历 e 元素的下一个元素
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
{
Object k;
// 找到指定 key 与需要放入的 key 相等(hash 值相同
// 通过 equals 比较放回 true)
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key
|| key.equals(k)))
{
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
// 如果 i 索引处的 Entry 为 null,表明此处还没有 Entry
modCount++;
// 将 key、value 添加到 i 索引处
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
} 1、当执行put代码时,其实是根据key运算产生一个hashcode值,根据这个产生的hashcode值,系统决它的存储位置,value也是跟着key的值存储,也是就它的存储位置是由key决定的,无value无关。
2、 数组的特点是:寻址容易,插入和删除困难;
链表的特点是:寻址困难,插入和删除容易。
对于集合理想的操作是:既要查找容易,又想插入和删除容易。。Hashmap实际上是一个数组和链表的结合体(在数据结构中,一般称之为“链表散列“),
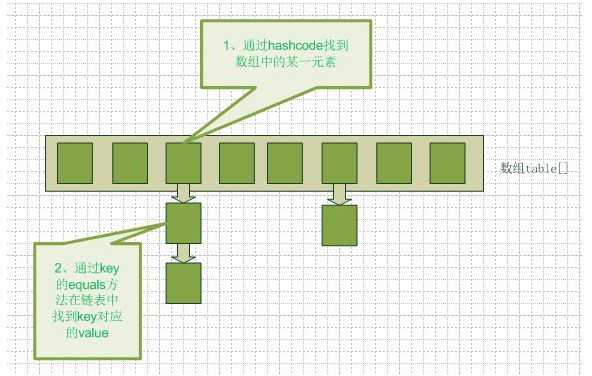
3、hash()代码:根据key值返回的一个int值。
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}2、LinkedHashMap实例
LinkedHashMap<String, String> linkHap = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
linkHap.put("张", "a");
linkHap.put("王", "b");
linkHap.put("李", "c");
linkHap.put("赵", "d");
for (Entry entry : linkHap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "---" + entry.getValue());
}运行结果:按照添加的顺序打印出来
张---a
王---b
李---c
赵---d分析:
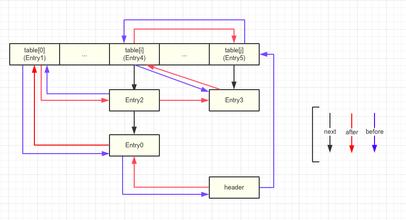
1、LinkedHashMap,它继承与HashMap、底层使用哈希表与双向链表来保存所有元素。其基本操作与父类HashMap相似,它通过重写父类相关的方法,来实现自己的链接列表特性。
这样用双向链表记录hash表前后的位置,实现LinkedHashMap的有序
2、源代码:
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}3、Map.Entry,在遍历map时用到的Map.Entry是一个带泛型参数的接口,它表示map中的一个实体
interface Entry<K,V> {
K getKey();
V getValue();
V setValue(V value);
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
}4、对map的遍历
1增强for循环,比较常用。
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("张", "a");
map.put("王", "b");
map.put("李", "c");
map.put("赵", "d");
//Map.Entry得到map中的实体;
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "---" + entry.getValue());
}2、用迭代器遍历:提供一种方法访问一个容器(container)对象中的各个元素。Iterator源码如下:
public interface Iterator<E> {
//判断是否还有更多元素;
boolean hasNext();
E next();
default void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("remove");
}
}使用iterator进行遍历
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("张", "a");
map.put("王", "b");
map.put("李", "c");
map.put("赵", "d");
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (entries.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, String> entry = entries.next();
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey() + ", Value = " + entry.getValue());
} 运行结果:
Key = 张, Value = a
Key = 赵, Value = d
Key = 王, Value = b
Key = 李, Value = c






















 1227
1227











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








