1. 简介
Android Priority Job Queue是一款专门为Android平台编写,实现了Job Queue的后台任务队列类库,能够轻松的在后台执行定时任务,提高用户体验和应用的稳定性。
github地址:https://github.com/path/android-priority-jobqueue
2. 背景
几乎所有的应用程序都存在后台线程工作。这些“背景任务”需要保持应用程序响应性和鲁棒性,特别是在不利的情况下(如有限的网络连接)。在安卓应用中,有几种方法来实现后台工作:
1) 异步任务:
使用异步任务是最简单的方法,但它与activity生命周期紧密耦合。如果Activity生命周期发生了改变,比如用户旋转了它的屏幕,那么Activity重新加载,那么后台任务可能会被停止。
2) 使用service:
使用服务可以很好地处理界面逻辑,但是,随着事物的增加,可能需要一个线程池来安排队列请求道磁盘中,而且需要考虑任务的优先级和并发时的并发问题
作业队列提供了一个很好的框架来完成上述所有的工作。当确定了你的后台任务的工作时,将它们作为Job添加到你jobmanager实例。Job Manage会照顾优先级,持久性,负载平衡,延迟,网络控制,分组等,它还提供了一个很好的生命周期,为工作提供一个更好的,一致的用户体验。
3. 使用(基于android studio)
1.添加依赖
compile 'com.birbit:android-priority-jobqueue:1.3.5'
- 1
- 1
2.创建Application并配置JobManager
public class AppApplication extends Application {
private JobManager jobManager;
public static AppApplication instance;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
configureJobManager();
}
public AppApplication(){
instance=this;
}
public JobManager getJobManager() {
return jobManager;
}
public static AppApplication getInstance() {
return instance;
}
private void configureJobManager() {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration.Builder(this)
.customLogger(new CustomLogger() {
private static final String TAG = "JOBS";
@Override
public boolean isDebugEnabled() {
return true;
}
@Override
public void d(String text, Object... args) {
Log.d(TAG, String.format(text, args));
}
@Override
public void e(Throwable t, String text, Object... args) {
Log.e(TAG, String.format(text, args), t);
}
@Override
public void e(String text, Object... args) {
Log.e(TAG, String.format(text, args));
}
})
.minConsumerCount(1)//always keep at least one consumer alive
.maxConsumerCount(3)//up to 3 consumers at a time
.loadFactor(3)//3 jobs per consumer
.consumerKeepAlive(120)//wait 2 minute
.build();
jobManager = new JobManager(this, configuration);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
3.创建Job任务
public class MJob extends Job {
public static final int PRIORITY = 1;
private String text;
public MJob(String text) {
// This job requires network connectivity,
// and should be persisted in case the application exits before job is completed.
super(new Params(Integer.parseInt(text)).requireNetwork().persist());
this.text = text;
Log.i("job",text+" goin");
}
@Override
public void onAdded() {
// Job has been saved to disk.
// This is a good place to dispatch a UI event to indicate the job will eventually run.
// In this example, it would be good to update the UI with the newly posted tweet.
Log.i("job",text+" Onadded");
}
@Override
public void onRun() throws Throwable {
// Job logic goes here. In this example, the network call to post to Twitter is done here.
// All work done here should be synchronous, a job is removed from the queue once
// onRun() finishes.
Log.i("job",text+" onRun");
}
@Override
protected RetryConstraint shouldReRunOnThrowable(Throwable throwable, int runCount,
int maxRunCount) {
// An error occurred in onRun.
// Return value determines whether this job should retry or cancel. You can further
// specify a backoff strategy or change the job's priority. You can also apply the
// delay to the whole group to preserve jobs' running order.
return RetryConstraint.createExponentialBackoff(runCount, 1000);
}
@Override
protected void onCancel() {
}
}
任务调用执行Job时会依次执行onAdded(),onRun().
4.MainActivity
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private JobManager jobManager;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
jobManager = AppApplication.getInstance().getJobManager();
Button btn_start = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_start);
btn_start.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
jobManager.addJobInBackground(new MJob("1"));
jobManager.addJobInBackground(new MJob("2"));
jobManager.addJobInBackground(new MJob("3"));
jobManager.addJobInBackground(new MJob(""));
jobManager.addJobInBackground(new MJob(""));
jobManager.addJobInBackground(new MJob(""));
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
4.执行结果
初始化所有的job
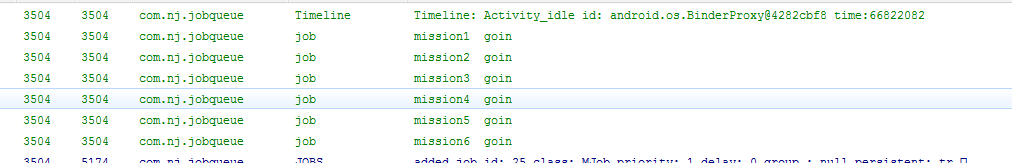
执行前三个Job的Onadd()方法,同时执行Job1的OnRun()方法。
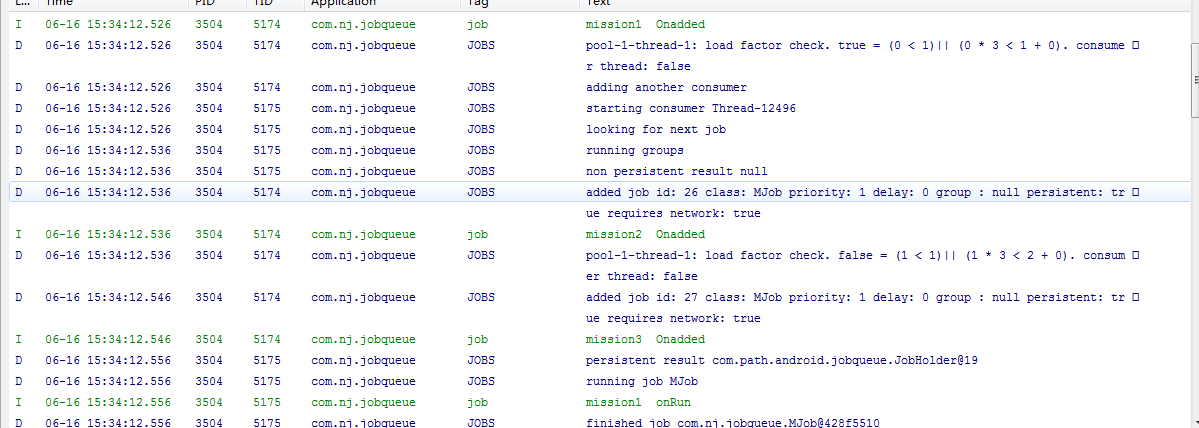
在执行完一个onAdd()方法后接着会调用队列中的第一个的OnAdd()方法。
5.分析
从Log中可以看到这个框架有一套自己的调度算法:

事实上,感觉这套框架其实跟Java的线程池差不多,都是来安排队列任务的优先级,调度方案,不过这套框架使用比较简单。
推荐一个Android的线程池博客:http://www.xuanyusong.com/archives/2439






















 201
201

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








