概述
在这篇博客中我主要讲解最短路径算法中的Floyd算法,这是针对多源最短路径的一个经典算法。对于单源最短路径算法请详见我的另一篇博客:最短路径算法(上)——迪杰斯特拉(Dijikstra)算法
弗洛伊德(Floyd)算法是解决任意两点间的最短路径的一种算法,可以正确处理有向图或有向图或负权(但不可存在负权回路)的最短路径问题,同时也被用于计算有向图的传递闭包。
算法思想与过程
(一)算法思想:
Floyd算法是一个经典的动态规划算法。用通俗的语言来描述的话,首先我们的目标是寻找从点i到点j的最短路径。从动态规划的角度看问题,我们需要为这个目标重新做一个诠释(这个诠释正是动态规划最富创造力的精华所在)。
从任意节点i到任意节点j的最短路径不外乎2种可能,一是直接从i到j,二是从i经过若干个节点k到j。所以,我们假设Dis(i,j)为节点u到节点v的最短路径的距离,对于每一个节点k,我们检查Dis(i,k) + Dis(k,j) < Dis(i,j)是否成立,如果成立,证明从i到k再到j的路径比i直接到j的路径短,我们便设置Dis(i,j) = Dis(i,k) + Dis(k,j),这样一来,当我们遍历完所有节点k,Dis(i,j)中记录的便是i到j的最短路径的距离。
(二)算法过程
1)首先把初始化距离dist数组为图的邻接矩阵,路径数组path初始化为-1。其中对于邻接矩阵中的数首先初始化为正无穷,如果两个顶点存在边则初始化为权重
2)对于每一对顶点 u 和 v,看看是否存在一个顶点 w 使得从 u 到 w 再到 v 比己知的路径更短。如果是就更新它。
状态转移方程为
如果 dist[i][k]+dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]
则dist[i][j] = dist[i][k]+dist[k][j]
//Floyd算法(多源最短路径算法)
bool Floyd(){
for(int k = 1 ; k < this->Nv+1 ; k++){ //k代表中间顶点
for(int i = 1 ; i < this->Nv+1 ; i++){//i代表起始顶点
for(int j = 1 ; j < this->Nv+1 ; j++){//j代表终点
if(this->dist[i][k] + this->dist[k][j] < this->dist[i][j]){
this->dist[i][j] = this->dist[i][k] + this->dist[k][j];
if(i == j && this->dist[i][j] < 0){//发现了负值圈
return false;
}
this->path[i][j] = k;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
例子
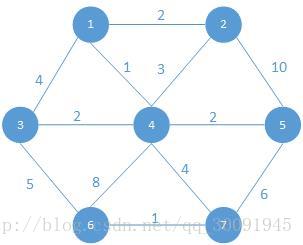
我们用如下图结构来演示Floyd算法:
全部代码为:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 65535;
class Graph{
private:
int** G; // 邻接矩阵
int** dist; // 距离数组
int** path; // 路径数组
int Nv; // 顶点数
public:
//构造函数
Graph(int nv, int ne){
this->Nv = nv;
G = new int*[nv+1];
dist = new int*[nv+1];
path = new int*[nv+1];
for(int i = 0 ; i < nv+1 ; i++){
G[i] = new int[nv+1];
dist[i] = new int[nv+1];
path[i] = new int[nv+1];
memset(path[i],-1,sizeof(path[0][0])*(nv+1));
for(int j = 0 ; j < nv+1 ; j++){
this->G[i][j] = this->dist[i][j] = MAX;
}
this->G[i][i] = this->dist[i][i] = 0;
}
cout<<“请输入边与权重:”<<endl;
for(int i = 0 ; i < ne ; i++){
int v1,v2,weight;
cin>>v1>>v2>>weight;
this->G[v1][v2] = this->G[v2][v1] = weight;
this->dist[v1][v2] = this->dist[v2][v1] = weight;
}
}
//Floyd算法(多源最短路径算法)
bool Floyd(){
for(int k = 1 ; k < this->Nv+1 ; k++){ //k代表中间顶点
for(int i = 1 ; i < this->Nv+1 ; i++){//i代表起始顶点
for(int j = 1 ; j < this->Nv+1 ; j++){//j代表终点
if(this->dist[i][k] + this->dist[k][j] < this->dist[i][j]){
this->dist[i][j] = this->dist[i][k] + this->dist[k][j];
if(i == j && this->dist[i][j] < 0){//发现了负值圈
return false;
}
this->path[i][j] = k;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
// 分治法寻找start到end最短路径的中间结点
void Find(queue<int> &q ,int start,int end){
int mid = this->path[start][end];
if(mid == -1){
return;
}
Find(q,start,mid);
q.push(mid);
Find(q,mid,end);
}
//打印start顶点到end顶点的路径
void Print_Path(int start,int end){
queue<int> queue;
queue.push(start);
this->Find(queue,start,end);
queue.push(end);
cout<<queue.front();
queue.pop();
while(!queue.empty()){
cout<<"->"<<queue.front();
queue.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
}
void Print_Floyd(){
int i,j,k;
for(int i = 1 ; i < this->Nv+1 ; i++){
for(int j = 1 ; j < this->Nv+1 ; j++){
cout<<this->path[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<" length path"<<endl;
for(i = 1 ; i < this->Nv+1 ; i++){
for(j = i+1 ; j < this->Nv+1 ; j++){
cout<<i<<"->"<<j<<" ";
cout<<this->dist[i][j]<<" ";
this->Print_Path(i,j);
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
};
int main()
{
cout<<“请输入顶点数与边长数:”<<endl;
int nv,ne;
cin>>nv>>ne;
Graph graph(nv,ne);
if(graph.Floyd()){
cout<<“各个顶点的最短路径为:”<<endl;
graph.Print_Floyd();
}
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
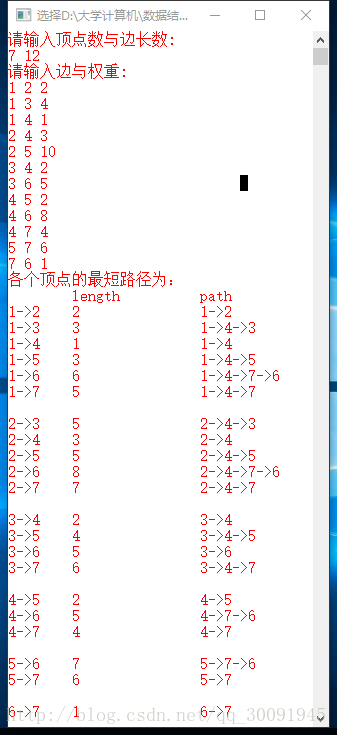
截图如下:
</div>
<link href="https://csdnimg.cn/release/phoenix/mdeditor/markdown_views-e9f16cbbc2.css" rel="stylesheet">
</div>





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








