关于文件系统操作的几个常用类和使用
流结构和文件的二进制和字符读写
文件监控类FileSystemWatcher的使用
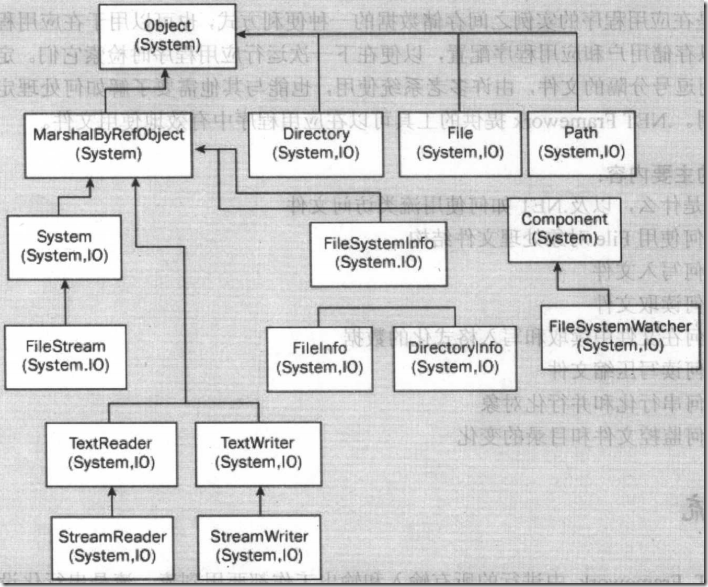
首先先看一张C#常用与文件操作有关的类图
所有的这些类都在System.IO的命名空间中,所以一下的所有代码,使用时都要先添加
using System.IO;
另外在这部分程序中出现异常均为IOException
开始介绍一下文件和目录的操作。
文件使用FileInfo类或File类。区别是FileInfo有生成一个实例,而File类只是一个静态类。如果对文件只需要进行一次性操作,使用File类会更好。下面代码展示FileInfo类的使用,File类使用类似。更多的方法可以直接转到FileInfo的类定义中查看。
1: static void Main(string[] args)
2: {
3: FileInfo test;
4: try
5: {
6: test = new FileInfo(@"D:/test.txt");
7: if (!test.Exists)//文件是否存在
8: {
9: test.Create();//创建文件
10: }
11: //第二个参数表示是否允许覆盖现有文件。
12: //test.CopyTo(@"E:/test.txt",false);
13: Console.WriteLine("目录名: {0}", test.DirectoryName);
14: Console.WriteLine("文件名: {0}", test.Name);
15: Console.WriteLine("文件大小为{0}字节", test.Length);
16: //test.Delete();删除文件
17: //test.MoveTo(@"D:/1.txt");移动/重命名
18: }
19: catch (IOException e)
20: {
21: Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
22: }
23: Console.ReadKey();
24: }
对于目录的操作也是类似的分为了DirectoryInfo和Directory两个类。
所能实现的方法可以直接参考定义,都不难理解。但是定义中没有提供整个目录的复制功能。需要自己递归实现,具体看以下代码
1: static void CopyDirectory(DirectoryInfo source, DirectoryInfo destination)
2: {
3: try
4: {
5: if (!destination.Exists)
6: {
7: destination.Create();
8: }
9:
10: FileInfo[] files = source.GetFiles();
11: foreach (FileInfo file in files)
12: {
13: file.CopyTo(destination.FullName + file.Name);
14: }
15:
16: DirectoryInfo[] directorys = source.GetDirectories();
17: foreach (DirectoryInfo directory in directorys)
18: {
19: //构建目标子目录的绝对地址,目标目录地址+文件夹名
20: string newDirName = Path.Combine(destination.FullName,directory.Name);
21: //复制子目录
22: CopyDirectory(directory, new DirectoryInfo(newDirName));
23: }
24: }
25: catch (IOException e)
26: {
27: Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
28: }
29:
30: }
31: static void Main(string[] args)
32: {
33: try
34: {
35: DirectoryInfo test = new DirectoryInfo(@"D:/test");
36: if (!test.Exists)
37: {
38: test.Create();
39: }
40: CopyDirectory(test, new DirectoryInfo(@"E:/test"));
41:
42: }
43: catch (IOException e)
44: {
45: Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
46: }
47: Console.ReadKey();
48: }
49:
以上介绍的都是文件和目录级别的操作下面介绍文件的读写。
文件的读写分为两种模式,一种是按二进制方式读写,另一种按文本方式读写。分别用于一般二进制文件和文本文件。
在给代码前有两个知识点需要提一下。
一个是我们的硬盘磁盘都是以线性方式保存数据,所以我们就可以构建一个流结构来对文件进行读写。通过流结构,让数据流向文件,或者是让文件内容流向变量。
另一个是文件指针。就是一个指向我们将要操作的位置。比如我们文件指针位于文件的第10个字节,我们的读写操作都是从文件指针的位置即第10个字节开始。相当于我们编辑文件时能看到的光标。可以用Seek()方法进行操作。
首先我们先看如何读写二进制文件,使用FileStream类。下面代码实现向image.ima写入boot.bin。注意这里是写入,不是插入,假设我们boot.bin的文件大小为N个字节,那么读写完后image.imz原来开头的N个字节的内容就被修改掉了,而第N+1及之后的内容不变。
1: static void Main(string[] args)
2: {
3: FileStream source = null;
4: FileStream destination = null;
5: try
6: {
7: source = new FileStream(@"D:/boot.bin", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
8: destination = new FileStream(@"D:/image.imz", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Write);
9: byte[] buffer = new byte[215];
10: int count = 0;
11: count = source.Read(buffer, 0, 215);
12: while (count != 0)
13: {
14: destination.Write(buffer, 0, count);
15: count = source.Read(buffer, 0, 215);
16: }
17: Console.WriteLine("OK");
18: }
19: catch (IOException e)
20: {
21: Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
22: }
23: finally
24: {
25: if (source != null)
26: {
27: source.Close();
28: }
29: if (destination != null)
30: {
31: destination.Close();
32: }
33: }
34: Console.ReadKey();
35: }
1: static void Main(string[] args)
2: {
3: FileStream file = null;
4: StreamWriter sw = null;
5: StreamReader sr = null;
6: string[][] table = new string[3][];
7: table[0] = new string[3] { "11", "22", "33" };
8: table[1] = new string[3] { "44", "55", "66" };
9: table[2] = new string[3] { "77", "88", "99" };
10: try
11: {
12: file = new FileStream(@"D:/test.txt", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.ReadWrite);
13:
14: sw = new StreamWriter(file);
15: foreach (string[] i in table)
16: {
17: foreach (string str in i)
18: {
19: Console.Write("{0} ",str);
20: sw.Write("{0} ",str);
21: }
22: Console.WriteLine();
23: sw.WriteLine();
24: }
25: sw.Flush();//把缓存区内容输出
26: Console.WriteLine("write");
27:
28: file.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);//把文件指针移到文件头
29: sr = new StreamReader(file);
30: string strline = sr.ReadLine();
31: while (strline != null)
32: {
33: string[] strElement = strline.Split(' ');
34: foreach (string element in strElement)
35: {
36: Console.Write("{0} ", element);
37: }
38: Console.WriteLine();
39:
40: strline = sr.ReadLine();
41: }
42: Console.WriteLine("read");
43: }
44: catch (IOException e)
45: {
46: Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
47: }
48: finally
49: {
50: if (sw != null)
51: {
52: sw.Close();
53: }
54: if (sr != null)
55: {
56: sr.Close();
57: }
58: if (file != null)
59: {
60: file.Close();
61: }
62: }
63: Console.ReadKey();
64: }
最后介绍一个文件监控实例,利用FileSystemWatcher可以监控文件的修改,删除,创建,重命名等事件。只要添加相应的事件处理函数,就可以在方式相应事件时执行函数。
下面的代码监控了文件的删除事件,其他的事件可以仿照删除时间处理函数进行处理
1: static void Main(string[] args)
2: {
3: FileSystemWatcher watcher = new FileSystemWatcher(@"D:/","1.txt");
4: watcher.Deleted += OnDelete;
5: watcher.EnableRaisingEvents = true;
6:
7: Console.ReadKey();
8:
9: }
10: static void OnDelete(object sender, FileSystemEventArgs e)
11: {
12: Console.WriteLine("{0} had been deleted!", e.FullPath);
13: }
关于文件处理的类,还有很多方法和属性没办法讲解,都可以参考类的定义来使用。






















 1559
1559

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








