一. 为什么要线程池
- 某类任务特别耗时,严重影响所在的线程处理其他任务
- 线程资源的开销与CPU核心之间的平衡
- 可以复用线程资源,充分利用系统资源,异步执行耗时任务
二.线程池
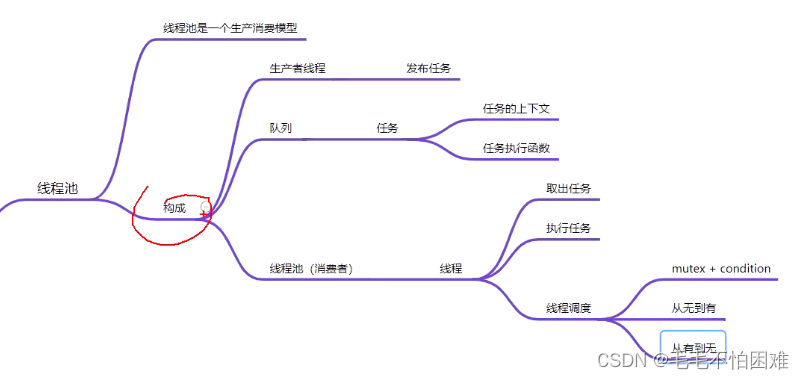
生产者消费者模型
构成:生产者线程(发布任务)
队列(任务:任务的上下文,任务执行函数)
线程池(消费者)线程池中的线程取出任务,执行任务,线程调度(mutex+condition)
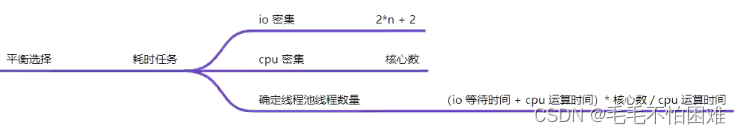
那么怎样确定线程池中的线程数量??
三. 实现线程池
// thread_pool_h
#ifndef THREAD_POOL_H
#define THREAD_POOL_H
typedef struct thread_pool_t thread_pool_t;
typedef void (*handler_pt)(void *);
thread_pool_t *thread_pool_create(int thrd_count, int quene_size);
int thread_pool_post(thread_pool_t *pool, handler_pt func, void *arg);
int thread_pool_destroy(thread_pool_t *pool);
int wait_all_done(thread_pool_t *pool);
#endif /* THREAD_POOL_H */
// thread_pool.c
#include "thread_pool.h"
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 封装任务 1.任务的上下文2.任务的回调函数
typedef struct task_t
{
handler_pt func;
void *arg;
} task_t;
// 任务的队列
typedef struct task_queue_t
{
uint32_t head;
uint32_t tail;
uint32_t count;
task_t *queue;
} task_queue_t;
// 线程池
struct thread_pool_t
{
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t condition;
pthread_t *threads;
task_queue_t task_queue;
int closed; // 线程池的运行状态,closed = 1为关闭状态
int started; // 当前运行的线程数量
int thrd_count;
int queue_size;
};
static void *thread_func(void *arg);
static void
thread_pool_free(thread_pool_t *pool)
{
if (pool == NULL || pool->started > 0)
return;
if (pool->threads)
{
free(pool->threads);
pool->threads = NULL;
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex));
pthread_mutex_destroy(&(pool->mutex));
pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->condition));
}
if (pool->task_queue.queue)
{
free(pool->task_queue.queue);
pool->task_queue.queue = NULL;
}
free(pool);
}
// 线程池的创建
thread_pool_t *
thread_pool_create(int thrd_count, int quene_size)
{
thread_pool_t *pool;
if (thrd_count <= 0 && quene_size <= 0)
return NULL;
pool = (thread_pool_t *)malloc(sizeof(struct thread_pool_t));
if (pool == NULL)
return NULL;
pool->thrd_count = 0; // 此时先传入0,因为后面开启线程不一定都能成功
pool->queue_size = quene_size;
pool->task_queue.head = 0;
pool->task_queue.tail = 0;
pool->task_queue.count = 0;
pool->started = pool->closed = 0;
pool->task_queue.queue = (task_t *)malloc(sizeof(struct task_t) * quene_size);
if (pool->task_queue.queue == NULL)
{
thread_pool_free(pool);
return NULL;
}
pool->threads = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * thrd_count);
if (pool->threads == NULL)
{
thread_pool_free(pool);
return NULL;
}
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < thrd_count; i++)
{
if (pthread_create(&(pool->threads[i]), NULL, thread_func, (void *)pool) != 0)
{
thread_pool_free(pool);
return NULL;
}
pool->thrd_count++;
pool->started++;
}
return pool;
}
// 向线程池添加任务
int thread_pool_post(thread_pool_t *pool, handler_pt func, void *arg)
{
if (pool == NULL || func == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
task_queue_t *task_queue = &(pool->task_queue);
// 加锁
if (pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex)) != 0)
{
return -2;
}
// 如果要关闭就把锁释放
if (pool->closed)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));
return -3;
}
// 队列满了,加不进去了
if (task_queue->count == pool->queue_size)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));
return -4;
}
task_queue->queue[task_queue->tail].func = func;
task_queue->queue[task_queue->tail].arg = arg;
task_queue->tail = (task_queue->tail + 1) % pool->queue_size;
task_queue->count++;
if (pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->condition)) != 0)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));
return -5;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));
return 0;
}
int wait_all_done(thread_pool_t *pool)
{
int i;
int ret = 0;
for (i = 0; i < pool->thrd_count; i++)
{
if (pthread_join(pool->threads[i], NULL) != 0)
{
ret = 1;
}
}
// printf("wait t tt t tt\n");
return ret;
}
// 销毁线程池
int thread_pool_destroy(thread_pool_t *pool)
{
if (pool == NULL)
return -1;
// 加锁
if (pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex)) != 0)
{
return -2;
}
if (pool->closed)
{
thread_pool_free(pool);
return -3;
}
pool->closed = 1;
if (pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->condition)) != 0 || pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex)) != 0)
{
thread_pool_free(pool);
return -4;
}
wait_all_done(pool);
thread_pool_free(pool);
return 0;
}
static void *
thread_func(void *arg)
{
thread_pool_t *pool = (thread_pool_t *)(arg);
task_queue_t *que;
task_t task;
while (1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex));
que = &pool->task_queue; // 取出任务队列
// 为什么要用while循环
// 1. 会有虚假唤醒问题
// 意思是生产者线程调用pthread_cond_signal后,可能唤醒好几个线程,
// 为了避免任务已经被取走,还需要再来检测一下while循环
// 2.信号
// 等
while (que->count == 0 && pool->closed == 0)
{
// 此处会先解锁
// 然后阻塞等
// 收到唤醒信号
// 再加锁
pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->condition), &(pool->mutex));
}
if (pool->closed == 1)
break;
task = que->queue[que->head]; // 取出任务
que->head = (que->head + 1) % pool->queue_size;
que->count--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));
(*(task.func))(task.arg); // 调用该任务的回调函数
}
pool->started--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));
pthread_exit(NULL);
return NULL;
}
// main.c
// 对线程池的测试
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "thread_pool.h"
pthread_mutex_t lock;
int nums = 0;
int done = 0;
void do_task(void *arg)
{
usleep(100000);
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
done++;
printf("正在执行第%d个任务\n", done);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
}
int main()
{
int threads = 8;
int queue_size = 128;
thread_pool_t *pool = thread_pool_create(threads, queue_size);
if (pool == NULL)
{
printf("thread pool create error!\n");
return 1;
}
while (thread_pool_post(pool, &do_task, NULL) == 0)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
nums++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
}
printf("一共添加了%d个任务\n",nums);
sleep(5); // 等待任务都执行完
thread_pool_destroy(pool);
return 0;
}






















 2844
2844

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








