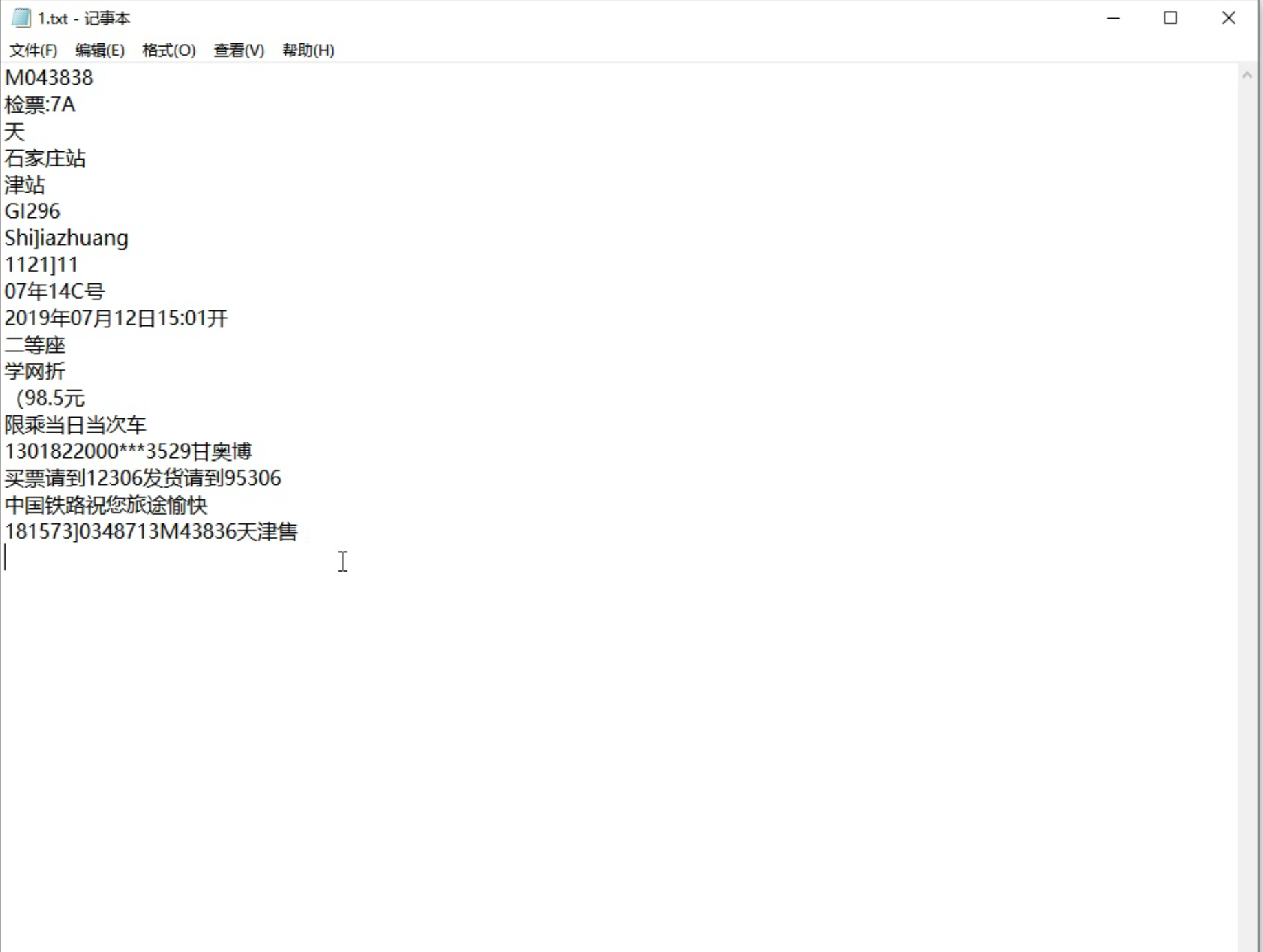
1.图片识别
识别结果输出TXT文档
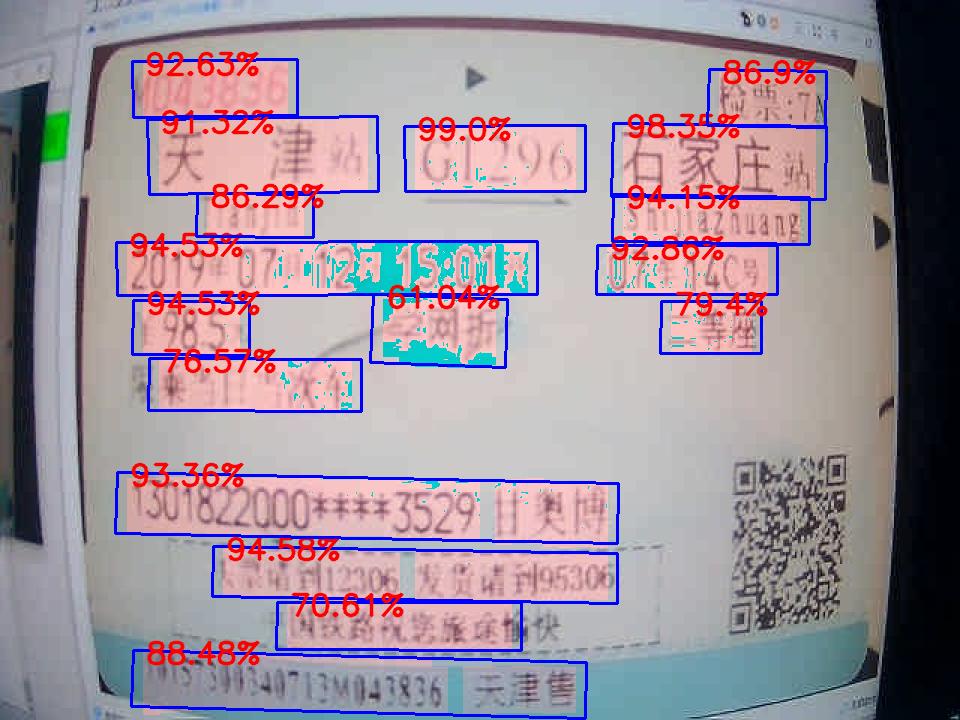
2.实时识别
3.视频展示
手把手带你构建OCR网络&火车票识别(完整源码)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
4.CRNN+CTC文本识别网络构建
首先CNN提取图像卷积特征
然后LSTM进一步提取图像卷积特征中的序列特征
参考该博客引入CTC解决训练时字符无法对齐的问题
一般情况下对一张图像中的文字进行识别需要以下步骤:
定位文稿中的图片,表格,文字区域,区分文字段落(版面分析)
进行文本行识别(识别)
使用NLP相关算法对文字识别结果进行矫正(后处理)
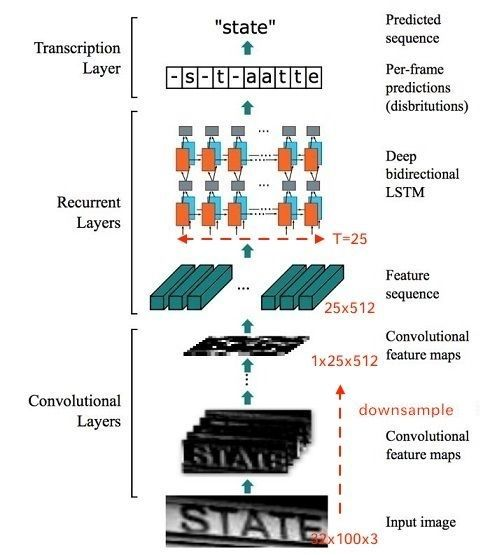
整个CRNN网络可以分为三个部分:
假设输入图像大小为 ,注意提及图像都是 形式。
Convlutional Layers
这里的卷积层就是一个普通的CNN网络,用于提取输入图像的Convolutional feature maps,即将大小为 的图像转换为 大小的卷积特征矩阵,网络细节请参考本文给出的实现代码。
Recurrent Layers
这里的循环网络层是一个深层双向LSTM网络,在卷积特征的基础上继续提取文字序列特征。
在CRNN中显然使用了第二种stack形深层双向结构。
由于CNN输出的Feature map是大小,所以对于RNN最大时间长度 (即有25个时间输入)。
Transcription Layers
将RNN输出做softmax后,为字符输出。
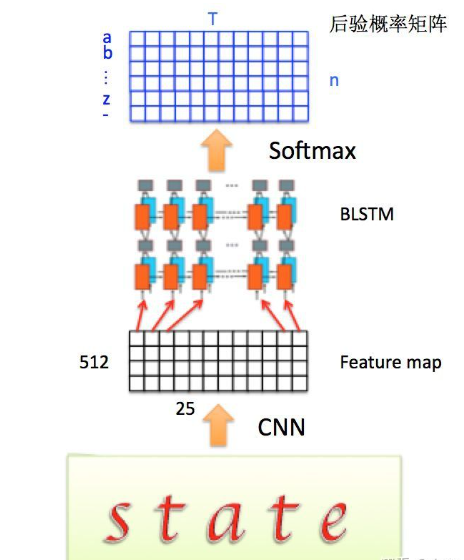
对于Recurrent Layers,如果使用常见的Softmax cross-entropy loss,则每一列输出都需要对应一个字符元素。那么训练时候每张样本图片都需要标记出每个字符在图片中的位置,再通过CNN感受野对齐到Feature map的每一列获取该列输出对应的Label才能进行训练,如图9。
在实际情况中,标记这种对齐样本非常困难(除了标记字符,还要标记每个字符的位置),工作量非常大。另外,由于每张样本的字符数量不同,字体样式不同,字体大小不同,导致每列输出并不一定能与每个字符一一对应。
整个CRNN的流程如图。先通过CNN提取文本图片的Feature map,然后将每一个channel作为 的时间序列输入到LSTM中。
详细教程参考:
一文读懂CRNN+CTC文字识别 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
5.代码实现
import cv2
from math import *
import numpy as np
from detect.ctpn_predict import get_det_boxes
from recognize.crnn_recognizer import PytorchOcr
recognizer = PytorchOcr()
def dis(image):
cv2.imshow('image', image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
def sort_box(box):
"""
对box进行排序
"""
box = sorted(box, key=lambda x: sum([x[1], x[3], x[5], x[7]]))
return box
def dumpRotateImage(img, degree, pt1, pt2, pt3, pt4):
height, width = img.shape[:2]
heightNew = int(width * fabs(sin(radians(degree))) + height * fabs(cos(radians(degree))))
widthNew = int(height * fabs(sin(radians(degree))) + width * fabs(cos(radians(degree))))
matRotation = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((width // 2, height // 2), degree, 1)
matRotation[0, 2] += (widthNew - width) // 2
matRotation[1, 2] += (heightNew - height) // 2
imgRotation = cv2.warpAffine(img, matRotation, (widthNew, heightNew), borderValue=(255, 255, 255))
pt1 = list(pt1)
pt3 = list(pt3)
[[pt1[0]], [pt1[1]]] = np.dot(matRotation, np.array([[pt1[0]], [pt1[1]], [1]]))
[[pt3[0]], [pt3[1]]] = np.dot(matRotation, np.array([[pt3[0]], [pt3[1]], [1]]))
ydim, xdim = imgRotation.shape[:2]
imgOut = imgRotation[max(1, int(pt1[1])): min(ydim - 1, int(pt3[1])),
max(1, int(pt1[0])): min(xdim - 1, int(pt3[0]))]
return imgOut
def charRec(img, text_recs, adjust=False):
"""
加载OCR模型,进行字符识别
"""
results = {}
xDim, yDim = img.shape[1], img.shape[0]
for index, rec in enumerate(text_recs):
xlength = int((rec[6] - rec[0]) * 0.1)
ylength = int((rec[7] - rec[1]) * 0.2)
if adjust:
pt1 = (max(1, rec[0] - xlength), max(1, rec[1] - ylength))
pt2 = (rec[2], rec[3])
pt3 = (min(rec[6] + xlength, xDim - 2), min(yDim - 2, rec[7] + ylength))
pt4 = (rec[4], rec[5])
else:
pt1 = (max(1, rec[0]), max(1, rec[1]))
pt2 = (rec[2], rec[3])
pt3 = (min(rec[6], xDim - 2), min(yDim - 2, rec[7]))
pt4 = (rec[4], rec[5])
degree = degrees(atan2(pt2[1] - pt1[1], pt2[0] - pt1[0])) # 图像倾斜角度
partImg = dumpRotateImage(img, degree, pt1, pt2, pt3, pt4)
# dis(partImg)
if partImg.shape[0] < 1 or partImg.shape[1] < 1 or partImg.shape[0] > partImg.shape[1]: # 过滤异常图片
continue
text = recognizer.recognize(partImg)
if len(text) > 0:
results[index] = [rec]
results[index].append(text) # 识别文字
return results
def ocr(image):
# detect
text_recs, img_framed, image = get_det_boxes(image)
text_recs = sort_box(text_recs)
result = charRec(image, text_recs)
return result, img_framed
6.系统整合
参考博客《Python原创OCR算法&轻量部署&火车票识别[源码&非PaddleOCR&技术原理&部署教程]》
7.参考文献:
-
Shi, B., Bai, X., & Yao, C. (2016). An end-to-end trainable neural network for image-based sequence recognition and its application to scene text recognition. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 39(11), 2298-2304.↩︎
-
Fedor Borisyuk, Albert Gordo, and Viswanath Sivakumar. Rosetta: Large scale system for text detection and recognition in images. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pages 71–79. ACM, 2018.↩︎
-
Gao, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, J., & Lu, H. (2017). Reading scene text with attention convolutional sequence modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:1709.04303.↩︎
-
Shi, B., Wang, X., Lyu, P., Yao, C., & Bai, X. (2016). Robust scene text recognition with automatic rectification. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 4168-4176).↩︎
-
Baoguang Shi, Mingkun Yang, XingGang Wang, Pengyuan Lyu, Xiang Bai, and Cong Yao. Aster: An attentional scene text recognizer with flexible rectification. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 31(11):855–868, 2018.↩︎
-
Star-Net Max Jaderberg, Karen Simonyan, Andrew Zisserman, et al. Spatial transformer networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems, pages 2017–2025, 2015.↩︎
-
Lee C Y , Osindero S . Recursive Recurrent Nets with Attention Modeling for OCR in the Wild[C]// IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2016.↩︎
-
Li, H., Wang, P., Shen, C., & Zhang, G. (2019, July). Show, attend and read: A simple and strong baseline for irregular text recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 33, No. 01, pp. 8610-8617).↩︎
-
P. Lyu, C. Yao, W. Wu, S. Yan, and X. Bai. Multi-oriented scene text detection via corner localization and region segmentation. In Proc. CVPR, pages 7553–7563, 2018.↩︎
-
Liao, M., Zhang, J., Wan, Z., Xie, F., Liang, J., Lyu, P., … & Bai, X. (2019, July). Scene text recognition from two-dimensional perspective. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 33, No. 01, pp. 8714-8721).↩︎
-
Yu, D., Li, X., Zhang, C., Liu, T., Han, J., Liu, J., & Ding, E. (2020). Towards accurate scene text recognition with semantic reasoning networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 12113-12122).↩︎
-
Sheng, F., Chen, Z., & Xu, B. (2019, September). NRTR: A no-recurrence sequence-to-sequence model for scene text recognition. In 2019 International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR) (pp. 781-786). IEEE.↩︎
-
Yang, L., Wang, P., Li, H., Li, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2020). A holistic representation guided attention network for scene text recognition. Neurocomputing, 414, 67-75.↩︎
-
Wang, Y., Xie, H., Fang, S., Wang, J., Zhu, S., & Zhang, Y. (2021). From two to one: A new scene text recognizer with visual language modeling network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 14194-14203).↩︎
-
Li, H., Wang, P., Shen, C., & Zhang, G. (2019, July). Show, attend and read: A simple and strong baseline for irregular text recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 33, No. 01, pp. 8610-8617).↩︎
-
Canjie, L., Yuanzhi, Z., & Lianwen, J. (2020). Yongpan Wang2Learn to Augment: Joint Data Augmentation and Network Optimization for Text Recognition.↩︎






















 1970
1970











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








