第七章 不太遥远的经典问题
7.1 寿司吧问题
这个问题的灵感来自Kenneth Reek提出的问题[9]。 想象一下有5个座位的寿司吧。 如果您在空座位时到达,您可以立即就座。 但是如果你在所有5个座位都已满的时候到达,这意味着他们所有人都在一起用餐,你必须等待整个派对离开后,你才能坐下。
思考:为进入和离开寿司吧的客户编写代码,以执行这些要求。
7.1.1 寿司吧提示
以下是我使用的变量:
eating和waiting记录坐在寿司吧和在寿司吧等待的线程数量。 互斥锁可以保护两个计数器。must_wait表示该吧已经坐满,而且即将到来的客户必须在block上阻塞。
7.1.2 寿司吧不正确方案
这是一个不正确的解决方案,Reek用来说明这个问题的一个难点。
思考:这个解决方案有什么问题?
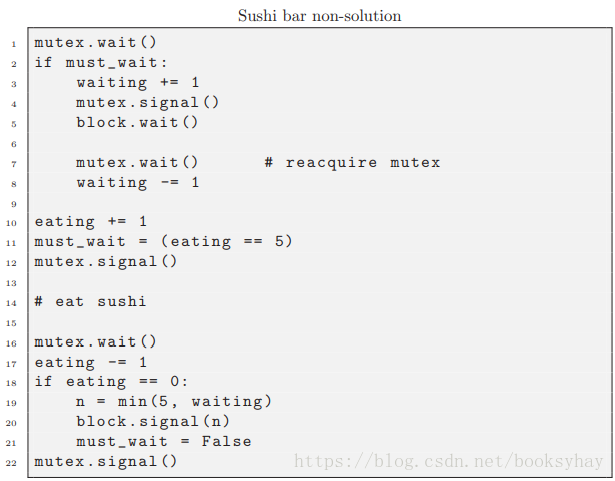
7.1.3 寿司吧非解决方案
问题出在第7行。如果顾客在酒吧满员时到达,他必须在等待时放弃互斥锁,以便其他顾客可以离开。 当最后一个顾客离开时,她发出block信号,这至少会唤醒一些等待的顾客,并且清除must_wait。
但是当顾客醒来时,他们必须恢复互斥,这意味着他们必须与进来的新线程竞争。 如果新线程先到达并获得互斥锁,则可以在等待线程之前占用所有席位。 这不仅仅是一个不公正的问题; 超过5个线程可能同时处于临界区,这违反了同步约束。
Reek为这个问题提供了两种解决方案,它们将在接下来的两节中介绍。
思考:看看你是否能提出两种不同的正确方案!
提示:两种解决方案都不使用其他任何变量。
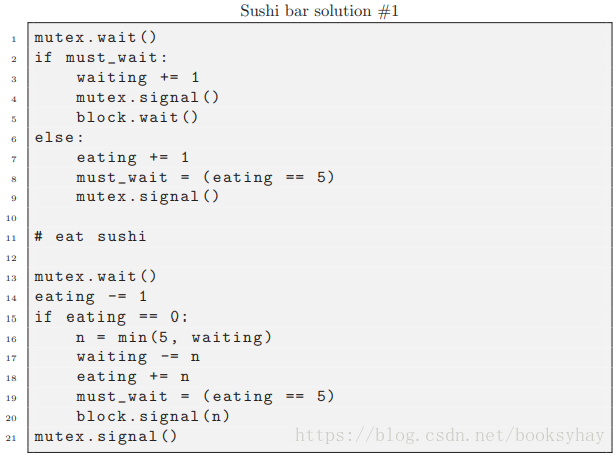
7.1.4 寿司吧解决方案-1#
等待的顾客必须重新获取互斥锁的唯一原因是要更新eating和waiting的状态,因此解决这个问题的一种方法是让拥有互斥锁的已经离开的顾客进行更新。
当最后一个离开的顾客释放互斥锁时,eating已经更新,因此新到达的顾客会看到正确的状态并在必要时阻止。 Reek称这种模式为“我会为你做的”,因为离开的线程正在做的工作在逻辑上似乎属于等待的线程。
这种方法的缺点是,有点难于确认状态是否被正确更新。
7.1.5 寿司吧解决方案-2#
Reek的替代方案是基于违反直觉的观念,即我们可以将互斥锁从一个线程转移到另一个线程! 换句话说,一个线程可以获取一个锁,然后另一个线程可以释放它。 只要两个线程都知道锁已被传送,就没有任何问题。
如果酒吧中的客户少于5个且没有人在等待,则进入的客户只会增加eating并释放互斥锁。 第五个客户设置must_wait为真。
如果must_wait已经置位,则进入的顾客要阻塞,直到酒吧里的最后一个客户清除must_wait并发出block信号。 可以理解,发送信号的线程放弃互斥锁,等待的线程接收它。 但请记住,这是程序员理解的不变量,并在注释中记录,但不是由信号量的语义强制执行。 我们应该把它做对。
当等待线程恢复时,我们知道它具有互斥锁。 如果有其他线程在等待,它会发出block信号,再次将互斥锁传递给等待的线程。 此过程继续执行,每个线程都将互斥锁传递到下一个,直到没有更多的空位或者没有更多等待线程。 在任何一种情况下,最后一个线程释放互斥锁并坐下。
Reek称这种模式为“传递接力棒”,因为互斥体正在从一个线程传递到下一个线程,就像接力赛中的接力棒一样。 这个解决方案的一个好处是很容易确认eating和waiting的更新是一致的。 缺点是很难确认互斥锁是否正确使用。























 4516
4516











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








