S变换
S变换采用高斯窗函数且窗宽与频率的倒数成正比,免去了窗函数的选择和改善了窗宽固定的缺陷,并且时频表示中各频率分量的相位谱与原始信号保持直接的联系,S变换具有良好的时频特性,适合用S变换对信号的一些时频与特征进行提取。
可以看出S变换不同于短时傅里叶变换之处在于高斯窗的高度和宽度随频率变化,这样就克服了短时傅里叶变化窗口高度和宽度固定的缺陷。S变化的离散变现形式:
S变换的结果
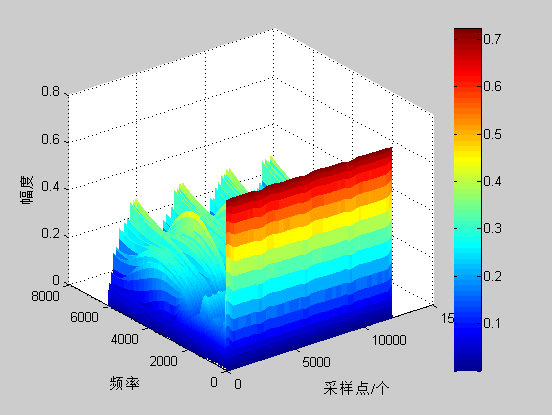
S变换的结果是一个二维矩阵,列对应采样点时间,行对应频率值,矩阵元素是一个复数,可以从这个元素里面获取幅值和相位信息。需要说明的是此时的频率值需要根据采样频率和采样数进行转化才能和实际的频率对应,转换方式与离散傅里叶转化方式相同,每个点的实际频率是(fs/N)*n,fs为采样频率,N为采样数,n为第n个点的序号。S变化的结果可以用三维立体图、二维等高线以及灰度图等直观表示,或者截取某一剖面用二维曲线表示。
S变化提取特征
国内现阶段在电能质量监测和评价方面根据S变化判断电压突降、突升、谐波以及震荡等电能扰动类型。通过s变化对不同电压扰动进行时频域特征提取很流行,合理选择分类器进行训练分类,最后对电压扰动进行检测与判断。下面就以一组电力信号为例,进行S变换特征提取以及结果简要分析。
给定一个电力信号序列,对该序列进行S变换分析,获取一个二维矩阵。首先用三维图画出各个分量,如下所示:
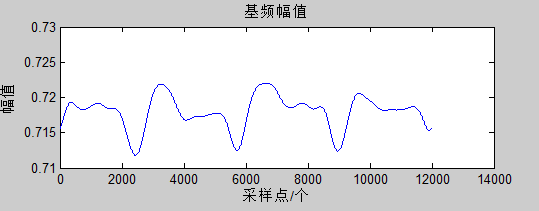
由于电流序列的基频是60Hz,如果对该信号进行谐波分析,就需要对谐波含量进行提取,从上图可以看出信号中含有较大的直流成分。由于谐波中大多是奇次谐波,偶次谐波通常只会发生在电路谐振的条件下。下面就从二维矩阵中抽取一行采样点与幅值信息,给出频率为60Hz(基波)时的幅值曲线。
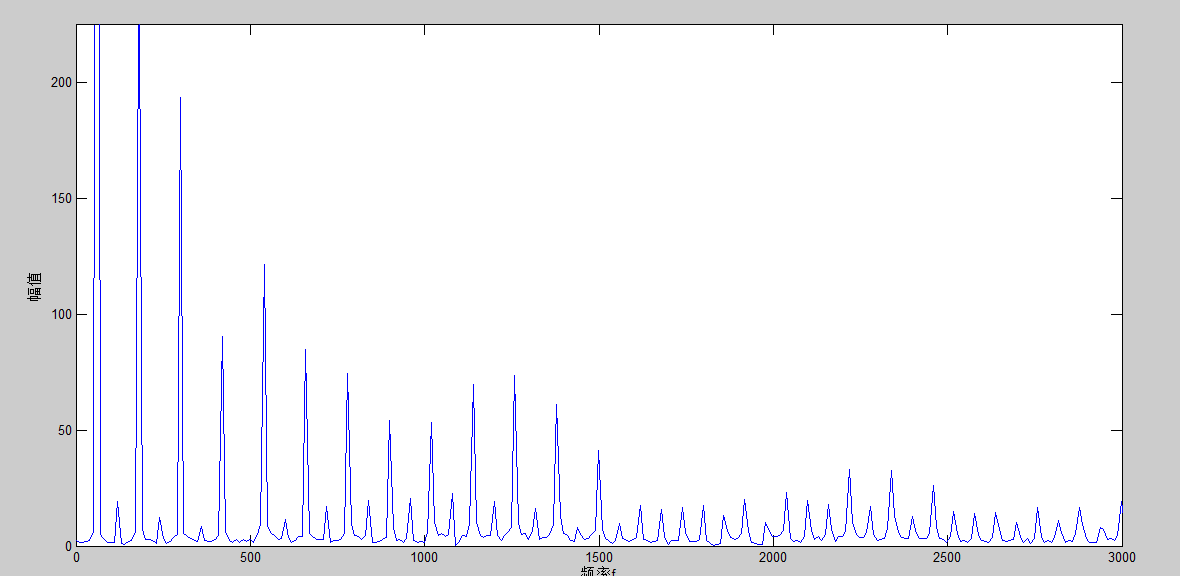
再根据二维矩阵获取该序列信号的频谱图:
通过以上图可以得知该信号中的谐波分量的大致分布。接下来可以根据实际情况选择S变化的形态域、频域、时频域特征作为样本特征,选择合适的分类器进行训练。
下面给出一段开源的S变换仿真代码:
function [st,t,f] = st(timeseries,minfreq,maxfreq,samplingrate,freqsamplingrate)
% Returns the Stockwell Transform of the timeseries.
% Code by Robert Glenn Stockwell.
% DO NOT DISTRIBUTE
% BETA TEST ONLY
% Reference is "Localization of the Complex Spectrum: The S Transform"
% from IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 44., number 4, April 1996, pages 998-1001.
%
%-------Inputs Needed------------------------------------------------
%
% *****All frequencies in (cycles/(time unit))!******
% "timeseries" - vector of data to be transformed
%-------Optional Inputs ------------------------------------------------
%
%"minfreq" is the minimum frequency in the ST result(Default=0)
%"maxfreq" is the maximum frequency in the ST result (Default=Nyquist)
%"samplingrate" is the time interval between samples (Default=1)
%"freqsamplingrate" is the frequency-sampling interval you desire in the ST result (Default=1)
%Passing a negative number will give the default ex. [s,t,f] = st(data,-1,-1,2,2)
%-------Outputs Returned------------------------------------------------
%
% st -a complex matrix containing the Stockwell transform.
% The rows of STOutput are the frequencies and the
% columns are the time values ie each column is
% the "local spectrum" for that point in time
% t - a vector containing the sampled times
% f - a vector containing the sampled frequencies
%--------Additional details-----------------------
% % There are several parameters immediately below that
% the user may change. They are:
%[verbose] if true prints out informational messages throughout the function.
%[removeedge] if true, removes a least squares fit parabola
% and puts a 5% hanning taper on the edges of the time series.
% This is usually a good idea.
%[analytic_signal] if the timeseries is real-valued
% this takes the analytic signal and STs it.
% This is almost always a good idea.
%[factor] the width factor of the localizing gaussian
% ie, a sinusoid of period 10 seconds has a
% gaussian window of width factor*10 seconds.
% I usually use factor=1, but sometimes factor = 3
% to get better frequency resolution.
% Copyright (c) by Bob Stockwell
% $Revision: 1.2 $ $Date: 1997/07/08 $
% This is the








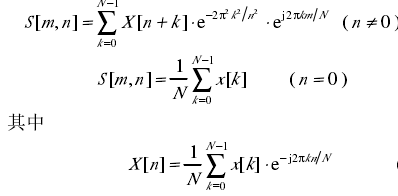
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1694
1694

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








