本文转自http://blog.csdn.net/luoweifu/article/details/49382969
上一篇文章带你玩转Visual Studio——带你跳出坑爹的Runtime Library坑帮我们理解了Windows中的各种类型C/C++运行时库及它的来龙去脉,这是C++开发中特别容易误入歧途的一个地方,我们对它进行了总结和归纳。本篇文章我们将继续讲解C++开发中容易混淆的另一个概念——多字节字符集与Unicode字符集。
多字节字符与宽字节字符
char与wchar_t
我们知道C++基本数据类型中表示字符的有两种:char、wchar_t。
char叫多字节字符,一个char占一个字节,之所以叫多字节字符是因为它表示一个字时可能是一个字节也可能是多个字节。一个英文字符(如’s’)用一个char(一个字节)表示,一个中文汉字(如’中’)用3个char(三个字节)表示,看下面的例子。
void TestChar()
{
char ch1 = 's'; // 正确
cout << "ch1:" << ch1 << endl;
char ch2 = '中'; // 错误,一个char不能完整存放一个汉字信息
cout << "ch2:" << ch2 << endl;
char str[4] = "中"; //前三个字节存放汉字'中',最后一个字节存放字符串结束符\0
cout << "str:" << str << endl;
//char str2[2] = "国"; // 错误:'str2' : array bounds overflow
//cout << str2 << endl;
}
结点如下:
ch1:s
ch2:
str:中
wchar_t被称为宽字符,一个wchar_t占2个字节。之所以叫宽字符是因为所有的字都要用两个字节(即一个wchar_t)来表示,不管是英文还是中文。看下面的例子:
void TestWchar_t()
{
wcout.imbue(locale("chs")); // 将wcout的本地化语言设置为中文
wchar_t wch1 = L's'; // 正确
wcout << "wch1:" << wch1 << endl;
wchar_t wch2 = L'中'; // 正确,一个汉字用一个wchar_t表示
wcout << "wch2:" << wch2 << endl;
wchar_t wstr[2] = L"中"; // 前两个字节(前一个wchar_t)存放汉字'中',最后两个字节(后一个wchar_t)存放字符串结束符\0
wcout << "wstr:" << wstr << endl;
wchar_t wstr2[3] = L"中国";
wcout << "wstr2:" << wstr2 << endl;
}
结果如下:
ch1:s
ch2:中
str:中
str2:中国
说明:
1. 用常量字符给wchar_t变量赋值时,前面要加L。如: wchar_t wch2 = L’中’;
2. 用常量字符串给wchar_t数组赋值时,前面要加L。如: wchar_t wstr2[3] = L”中国”;
3. 如果不加L,对于英文可以正常,但对于非英文(如中文)会出错。
string与wstring
字符数组可以表示一个字符串,但它是一个定长的字符串,我们在使用之前必须知道这个数组的长度。为方便字符串的操作,STL为我们定义好了字符串的类string和wstring。大家对string肯定不陌生,但wstring可能就用的少了。
string是普通的多字节版本,是基于char的,对char数组进行的一种封装。
wstring是Unicode版本,是基于wchar_t的,对wchar_t数组进行的一种封装。
string 与 wstring的相关转换:
以下的两个方法是跨平台的,可在Windows下使用,也可在Linux下使用。
<code class="language-C++ hljs cpp has-numbering" style="display: block; padding: 0px; background-color: transparent; color: inherit; box-sizing: border-box; font-family: 'Source Code Pro', monospace;font-size:undefined; white-space: pre; border-top-left-radius: 0px; border-top-right-radius: 0px; border-bottom-right-radius: 0px; border-bottom-left-radius: 0px; word-wrap: normal; background-position: initial initial; background-repeat: initial initial;"><span class="hljs-preprocessor" style="color: rgb(68, 68, 68); box-sizing: border-box;">#include <cstdlib></span>
<span class="hljs-preprocessor" style="color: rgb(68, 68, 68); box-sizing: border-box;">#include <string.h></span>
<span class="hljs-preprocessor" style="color: rgb(68, 68, 68); box-sizing: border-box;">#include <string></span>
<span class="hljs-comment" style="color: rgb(136, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">// wstring => string</span>
<span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">std</span>::<span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">string</span> WString2String(<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">const</span> <span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">std</span>::wstring& ws)
{
<span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">std</span>::<span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">string</span> strLocale = setlocale(LC_ALL, <span class="hljs-string" style="color: rgb(0, 136, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">""</span>);
<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">const</span> <span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">wchar_t</span>* wchSrc = ws.c_str();
size_t nDestSize = wcstombs(NULL, wchSrc, <span class="hljs-number" style="color: rgb(0, 102, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">0</span>) + <span class="hljs-number" style="color: rgb(0, 102, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">1</span>;
<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">char</span> *chDest = <span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">new</span> <span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">char</span>[nDestSize];
<span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">memset</span>(chDest,<span class="hljs-number" style="color: rgb(0, 102, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">0</span>,nDestSize);
wcstombs(chDest,wchSrc,nDestSize);
<span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">std</span>::<span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">string</span> strResult = chDest;
<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">delete</span> []chDest;
setlocale(LC_ALL, strLocale.c_str());
<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">return</span> strResult;
}
<span class="hljs-comment" style="color: rgb(136, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">// string => wstring</span>
<span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">std</span>::wstring String2WString(<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">const</span> <span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">std</span>::<span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">string</span>& s)
{
<span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">std</span>::<span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">string</span> strLocale = setlocale(LC_ALL, <span class="hljs-string" style="color: rgb(0, 136, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">""</span>);
<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">const</span> <span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">char</span>* chSrc = s.c_str();
size_t nDestSize = mbstowcs(NULL, chSrc, <span class="hljs-number" style="color: rgb(0, 102, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">0</span>) + <span class="hljs-number" style="color: rgb(0, 102, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">1</span>;
<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">wchar_t</span>* wchDest = <span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">new</span> <span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">wchar_t</span>[nDestSize];
wmemset(wchDest, <span class="hljs-number" style="color: rgb(0, 102, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">0</span>, nDestSize);
mbstowcs(wchDest,chSrc,nDestSize);
<span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">std</span>::wstring wstrResult = wchDest;
<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">delete</span> []wchDest;
setlocale(LC_ALL, strLocale.c_str());
<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">return</span> wstrResult;
}</code><ul class="pre-numbering" style="box-sizing: border-box; position: absolute; width: 50px; background-color: rgb(238, 238, 238); top: 0px; left: 0px; margin: 0px; padding: 6px 0px 40px; border-right-width: 1px; border-right-style: solid; border-right-color: rgb(221, 221, 221); list-style: none; text-align: right;"><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">1</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">2</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">3</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">4</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">5</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">6</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">7</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">8</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">9</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">10</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">11</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">12</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">13</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">14</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">15</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">16</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">17</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">18</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">19</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">20</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">21</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">22</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">23</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">24</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">25</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">26</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">27</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">28</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">29</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">30</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">31</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">32</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">33</li></ul>
字符集(Charcater Set)与字符编码(Encoding)
字符集(Charcater Set或Charset):是一个系统支持的所有抽象字符的集合,也就是一系列字符的集合。字符是各种文字和符号的总称,包括各国家文字、标点符号、图形符号、数字等。常见的字符集有:ASCII字符集、GB2312字符集(主要用于处理中文汉字)、GBK字符集(主要用于处理中文汉字)、Unicode字符集等。
字符编码(Character Encoding):是一套法则,使用该法则能够对自然语言的字符的一个字符集(如字母表或音节表),与计算机能识别的二进制数字进行配对。即它能在符号集合与数字系统之间建立对应关系,是信息处理的一项基本技术。通常人们用符号集合(一般情况下就是文字)来表达信息,而计算机的信息处理系统则是以二进制的数字来存储和处理信息的。字符编码就是将符号转换为计算机能识别的二进制编码。
一般一个字符集等同于一个编码方式,ANSI体系(ANSI是一种字符代码,为使计算机支持更多语言,通常使用 0x80~0xFF 范围的 2 个字节来表示 1 个字符)的字符集如ASCII、ISO 8859-1、GB2312、GBK等等都是如此。一般我们说一种编码都是针对某一特定的字符集。
一个字符集上也可以有多种编码方式,例如UCS字符集(也是Unicode使用的字符集)上有UTF-8、UTF-16、UTF-32等编码方式。
从计算机字符编码的发展历史角度来看,大概经历了三个阶段:
第一个阶段:ASCII字符集和ASCII编码。
计算机刚开始只支持英语(即拉丁字符),其它语言不能够在计算机上存储和显示。ASCII用一个字节(Byte)的7位(bit)表示一个字符,第一位置0。后来为了表示更多的欧洲常用字符又对ASCII进行了扩展,又有了EASCII,EASCII用8位表示一个字符,使它能多表示128个字符,支持了部分西欧字符。
第二个阶段:ANSI编码(本地化)
为使计算机支持更多语言,通常使用 0x80~0xFF 范围的 2 个字节来表示 1 个字符。比如:汉字 ‘中’ 在中文操作系统中,使用 [0xD6,0xD0] 这两个字节存储。
不同的国家和地区制定了不同的标准,由此产生了 GB2312, BIG5, JIS 等各自的编码标准。这些使用 2 个字节来代表一个字符的各种汉字延伸编码方式,称为 ANSI 编码。在简体中文系统下,ANSI 编码代表 GB2312 编码,在日文操作系统下,ANSI 编码代表 JIS 编码。
不同 ANSI 编码之间互不兼容,当信息在国际间交流时,无法将属于两种语言的文字,存储在同一段 ANSI 编码的文本中。
第三个阶段:UNICODE(国际化)
为了使国际间信息交流更加方便,国际组织制定了 UNICODE 字符集,为各种语言中的每一个字符设定了统一并且唯一的数字编号,以满足跨语言、跨平台进行文本转换、处理的要求。UNICODE 常见的有三种编码方式:UTF-8(1个字节表示)、UTF-16((2个字节表示))、UTF-32(4个字节表示)。
我们可以用一个树状图来表示由ASCII发展而来的各个字符集和编码的分支:
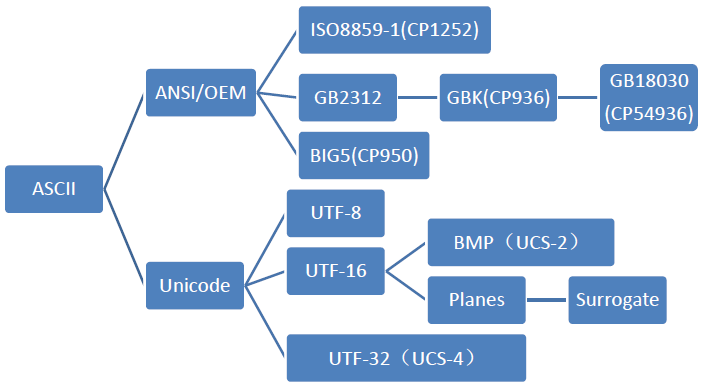
图 1: 各种类型的编译
如果要更详细地了解字符集和字符编码请参考:
字符集和字符编码(Charset & Encoding)
工程里多字节与宽字符的配制
右键你的工程名->Properties,设置如下:
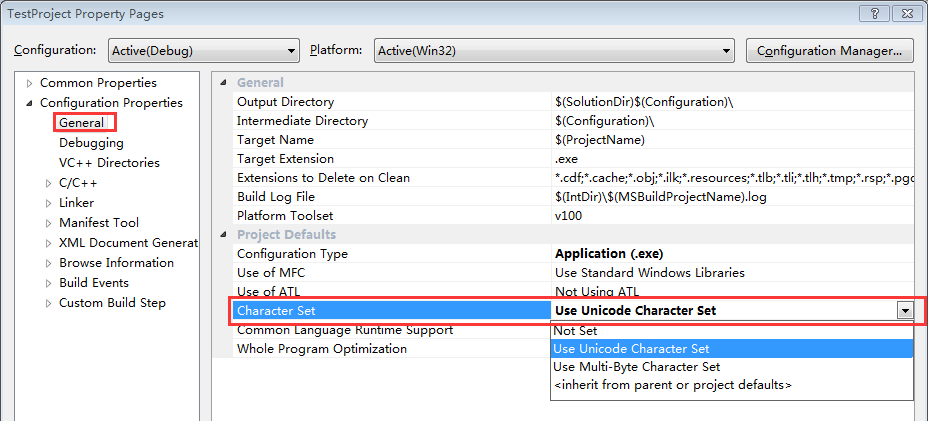
图 2: Character Set
- 当设置为Use Unicode Character Set时,会有预编译宏:_UNICODE、UNICODE
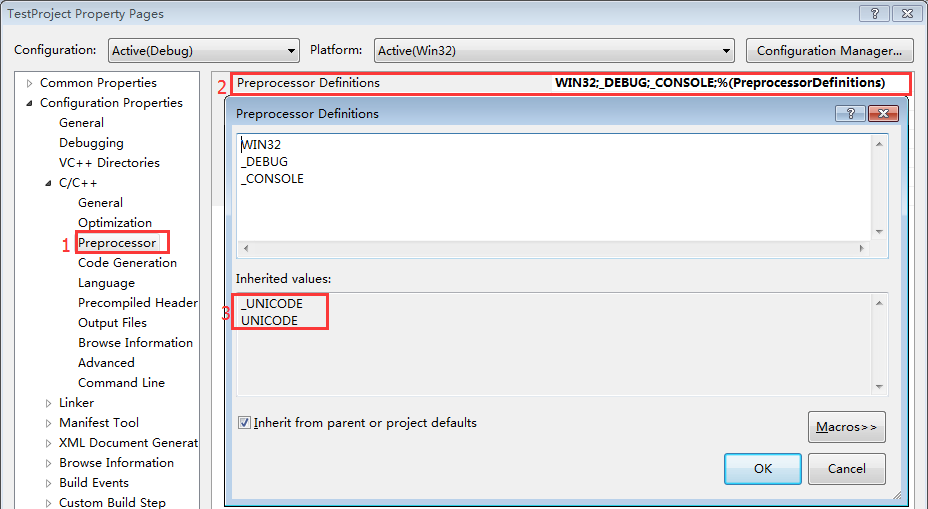
图 3: Unicode
- 当设置为Use Multi-Byte Character Set时,会有预编译宏:_MBCS
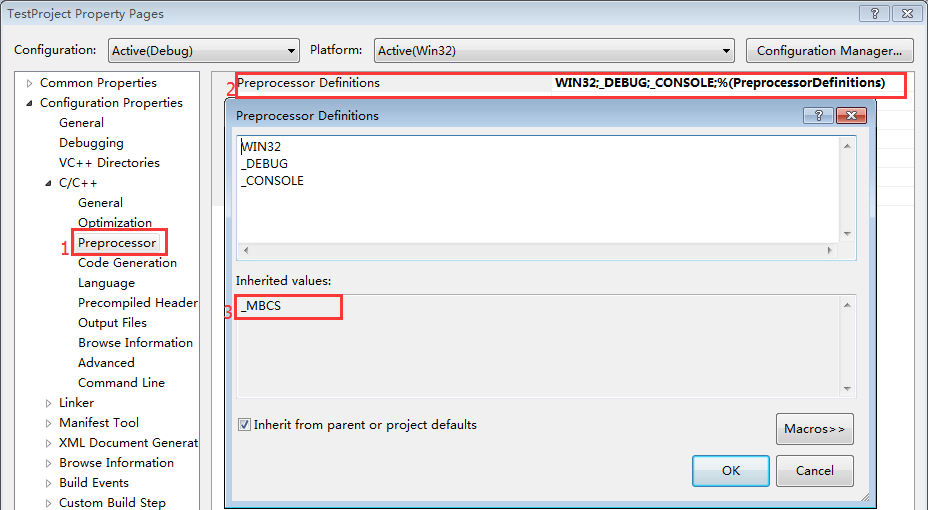
图 4: Multi-Byte
Unicode Character Set与Multi-Byte Character Set有什么区别呢?
Unicode Character Set和Multi-Byte Character Set这两个设置有什么区别呢?我们来看一个例子:
有一个程序需要用MessageBox弹出提示框:
<code class="language-C++ hljs lasso has-numbering" style="display: block; padding: 0px; background-color: transparent; color: inherit; box-sizing: border-box; font-family: 'Source Code Pro', monospace;font-size:undefined; white-space: pre; border-top-left-radius: 0px; border-top-right-radius: 0px; border-bottom-right-radius: 0px; border-bottom-left-radius: 0px; word-wrap: normal; background-position: initial initial; background-repeat: initial initial;"><span class="hljs-variable" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">#include</span> <span class="hljs-string" style="color: rgb(0, 136, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">"windows.h"</span>
<span class="hljs-literal" style="color: rgb(0, 102, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">void</span> TestMessageBox()
{
<span class="hljs-tag" style="color: rgb(0, 102, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">::MessageBox</span>(<span class="hljs-built_in" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); box-sizing: border-box;">NULL</span>, <span class="hljs-string" style="color: rgb(0, 136, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">"这是一个测试程序!"</span>, <span class="hljs-string" style="color: rgb(0, 136, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">"Title"</span>, MB_OK);
}</code><ul class="pre-numbering" style="box-sizing: border-box; position: absolute; width: 50px; background-color: rgb(238, 238, 238); top: 0px; left: 0px; margin: 0px; padding: 6px 0px 40px; border-right-width: 1px; border-right-style: solid; border-right-color: rgb(221, 221, 221); list-style: none; text-align: right;"><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">1</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">2</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">3</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">4</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">5</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">6</li></ul>
上面这个Demo非常简单不用多说了吧!我们将Character Set设置为Multi-Byte Character Set时,可以正常编译和运行。但当我们设置为Unicode Character Set,则会有以下编译错误:
error C2664: ‘MessageBoxW’ : cannot convert parameter 2 from ‘const char [18]’ to ‘LPCWSTR’
这是因为MessageBox有两个版本,一个MessageBoxW针对Unicode版的,一个是MessageBoxA针对Multi-Byte的,它们通过不同宏进行隔开,预设不同的宏会使用不同的版本。我们使用了Use Unicode Character Set就预设了_UNICODE、UNICODE宏,所以编译时就会使用MessageBoxW,这时我们传入多字节常量字符串肯定会有问题,而应该传入宽符的字符串,即将”Title”改为L”Title”就可以了,”这是一个测试程序!”也一样。
<code class="hljs bash has-numbering" style="display: block; padding: 0px; background-color: transparent; color: inherit; box-sizing: border-box; font-family: 'Source Code Pro', monospace;font-size:undefined; white-space: pre; border-top-left-radius: 0px; border-top-right-radius: 0px; border-bottom-right-radius: 0px; border-bottom-left-radius: 0px; word-wrap: normal; background-position: initial initial; background-repeat: initial initial;">WINUSERAPI
int
WINAPI
MessageBoxA(
__<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">in</span>_opt HWND hWnd,
__<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">in</span>_opt LPCSTR lpText,
__<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">in</span>_opt LPCSTR lpCaption,
__<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">in</span> UINT uType);
WINUSERAPI
int
WINAPI
MessageBoxW(
__<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">in</span>_opt HWND hWnd,
__<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">in</span>_opt LPCWSTR lpText,
__<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">in</span>_opt LPCWSTR lpCaption,
__<span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">in</span> UINT uType);
<span class="hljs-comment" style="color: rgb(136, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">#ifdef UNICODE</span>
<span class="hljs-comment" style="color: rgb(136, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">#define MessageBox MessageBoxW</span>
<span class="hljs-comment" style="color: rgb(136, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">#else</span>
<span class="hljs-comment" style="color: rgb(136, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">#define MessageBox MessageBoxA</span>
<span class="hljs-comment" style="color: rgb(136, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">#endif // !UNICODE</span></code><ul class="pre-numbering" style="box-sizing: border-box; position: absolute; width: 50px; background-color: rgb(238, 238, 238); top: 0px; left: 0px; margin: 0px; padding: 6px 0px 40px; border-right-width: 1px; border-right-style: solid; border-right-color: rgb(221, 221, 221); list-style: none; text-align: right;"><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">1</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">2</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">3</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">4</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">5</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">6</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">7</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">8</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">9</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">10</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">11</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">12</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">13</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">14</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">15</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">16</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">17</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">18</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">19</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">20</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">21</li></ul>
上面的Multi-Byte Character Set一般是指ANSI(多字节)字符集,关于ANSI请参考第二小节字符集(Charcater Set)与字符编码(Encoding)。而Unicode Character Set就是Unicode字符集,一般是指UTF-16编码的Unicode。也就是说每个字符编码为两个字节,两个字节可以表示65535个字符,65535个字符可以表示世界上大部分的语言。
一般推荐使用Unicode的方式,因为它可以适应各个国家语言,在进行软件国际时将会非常便得。除非在对存储要求非常高的时候,或要兼容C的代码时,我们才会使用多字节的方式 。
理解_T()、_Text()宏即L”“
上一小节对MessageBox的调用中除了使用L”Title”外,还可以使用_T(“Title”)和_TEXT(“Title”)。而且你会发现在MFC和Win32程序中会更多地使用_T和_TEXT,那_T、_TEXT和L之间有什么区别呢?
通过第一小节多字节字符与宽字节字符我们知道表示多字节字符(char)串常量时用一般的双引号括起来就可以了,如”String test”;而表示宽字节字符(wchar_t)串常量时要在引号前加L,如L”String test”。
查看tchar.h头文件的定义我们知道_T和_TEXT的功能是一样的,是一个预定义的宏。
<code class="hljs cs has-numbering" style="display: block; padding: 0px; background-color: transparent; color: inherit; box-sizing: border-box; font-family: 'Source Code Pro', monospace;font-size:undefined; white-space: pre; border-top-left-radius: 0px; border-top-right-radius: 0px; border-bottom-right-radius: 0px; border-bottom-left-radius: 0px; word-wrap: normal; background-position: initial initial; background-repeat: initial initial;"><span class="hljs-preprocessor" style="color: rgb(68, 68, 68); box-sizing: border-box;">#<span class="hljs-keyword" style="box-sizing: border-box;">define</span> _T(x) __T(x)</span>
<span class="hljs-preprocessor" style="color: rgb(68, 68, 68); box-sizing: border-box;">#<span class="hljs-keyword" style="box-sizing: border-box;">define</span> _TEXT(x) __T(x)</span></code><ul class="pre-numbering" style="box-sizing: border-box; position: absolute; width: 50px; background-color: rgb(238, 238, 238); top: 0px; left: 0px; margin: 0px; padding: 6px 0px 40px; border-right-width: 1px; border-right-style: solid; border-right-color: rgb(221, 221, 221); list-style: none; text-align: right;"><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">1</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">2</li></ul>
我们再看看__T(x)的定义,发现它有两个:
<code class="hljs r has-numbering" style="display: block; padding: 0px; background-color: transparent; color: inherit; box-sizing: border-box; font-family: 'Source Code Pro', monospace;font-size:undefined; white-space: pre; border-top-left-radius: 0px; border-top-right-radius: 0px; border-bottom-right-radius: 0px; border-bottom-left-radius: 0px; word-wrap: normal; background-position: initial initial; background-repeat: initial initial;"><span class="hljs-comment" style="color: rgb(136, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">#ifdef _UNICODE</span>
// <span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">...</span> 省略其它代码
<span class="hljs-comment" style="color: rgb(136, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">#define __T(x) L ## x</span>
// <span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">...</span> 省略其它代码
<span class="hljs-comment" style="color: rgb(136, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">#else /* ndef _UNICODE */</span>
// <span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">...</span> 省略其它代码
<span class="hljs-comment" style="color: rgb(136, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">#define __T(x) x</span>
// <span class="hljs-keyword" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 136); box-sizing: border-box;">...</span> 省略其它代码
<span class="hljs-comment" style="color: rgb(136, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box;">#endif /* _UNICODE */</span></code><ul class="pre-numbering" style="box-sizing: border-box; position: absolute; width: 50px; background-color: rgb(238, 238, 238); top: 0px; left: 0px; margin: 0px; padding: 6px 0px 40px; border-right-width: 1px; border-right-style: solid; border-right-color: rgb(221, 221, 221); list-style: none; text-align: right;"><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">1</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">2</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">3</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">4</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">5</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">6</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">7</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">8</li><li style="box-sizing: border-box; padding: 0px 5px;">9</li></ul>
这下明白了吗?当我们的工程的Character Set设置为Use Unicode Character Set时_T和_TEXT就会在常量字符串前面加L,否则(即Use Multi-Byte Character Set时)就会以一般的字符串处理。
Dword、LPSTR、LPWSTR、LPCSTR、LPCWSTR、LPTSTR、LPCTSTR
VC++中还有一些常用的宏你也许会范糊涂,如Dword、LPSTR、LPWSTR、LPCSTR、LPCWSTR、LPTSTR、LPCTSTR。这里我们统一总结一下:
常见的宏:
| 类型 | MBCS | UNICODE |
|---|
| WCHAR | wchar_t | wchar_t |
| LPSTR | char* | char* |
| LPCSTR | const char* | const char* |
| LPWSTR | wchar_t* | wchar_t* |
| LPCWSTR | const wchar_t* | const wchar_t* |
| TCHAR | char | wchar_t |
| LPTSTR | TCHAR*(或char*) | TCHAR* (或wchar_t*) |
| LPCTSTR | const TCHAR* | const TCHAR* |
相互转换方法:
LPWSTR->LPTSTR: W2T();
LPTSTR->LPWSTR: T2W();
LPCWSTR->LPCSTR: W2CT();
LPCSTR->LPCWSTR: T2CW();
ANSI->UNICODE: A2W();
UNICODE->ANSI: W2A();
字符串函数:
还有一些字符串的操作函数,它们也有一 一对应关系:
| MBCS | UNICODE |
|---|
| strlen(); | wcslen(); |
| strcpy(); | wcscpy(); |
| strcmp(); | wcscmp(); |
| strcat(); | wcscat(); |
| strchr(); | wcschr(); |
| … | … |
通过这些函数和宏的命名你也许就发现了一些霍规律,一般带有前缀w(或后缀W)的都是用于宽字符的,而不带前缀w(或带有后缀A)的一般是用于多字节字符的。
理解CString产生的原因与工作的机理
CString:动态的TCHAR数组,是对TCHAR数组的一种封闭。它是一个完全独立的类,封装了“+”等操作符和字符串操作方法,换句话说就是CString是对TCHAR操作的方法的集合。它的作用是方便WIN32程序和MFC程序进行字符串的处理和类型的转换。
关于CString更详细的用法请参考:
CString与string、char*的区别和转换
CString的常见用法
参考文章:
字符集和字符编码(Charset & Encoding)
字符,字节和编码
《windows核心编程系列》二谈谈ANSI和Unicode字符集
Dword、LPSTR、LPWSTR、LPCSTR、LPCWSTR、LPTSTR、LPCTSTR
上一篇回顾:
带你玩转Visual Studio——带你跳出坑爹的Runtime Library坑
下一篇要讲述的内容:
带你玩转Visual Studio——带你解读__cdecl、__fastcall、__stdcall三种调用约定


























 2794
2794

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








