ServletContext对象
WEB容器在启动时,它会为每个WEB应用程序都创建一个对应的ServletContext对象,它代表当前web应用。
ServletContext对象被包含在ServletConfig对象中,开发人员在编写servlet时,可以通过ServletConfig.getServletContext方法获得对ServletContext对象的引用。
由于一个WEB应用中的所有Servlet共享同一个ServletContext对象,因此Servlet对象之间可以通过ServletContext对象来实现通讯。ServletContext对象通常也被称之为context域对象。
得到servletContext对象的方式:
package servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/*
* servletContext示例
*/
public class ServletDemo6 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//得到servletContext的方式1
ServletContext context = this.getServletConfig().getServletContext();
//得到servletContext的方式2
context = this.getServletContext();
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
}
}
ServletContext应用
- 多个Servlet通过ServletContext对象实现数据共享。
示例代码:
package servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/*
* ServletContext的应用
* 所有Servlet共享同一个ServletContext
* ServletContex对象通常被称为context域对象
*
*/
public class ServletDemo7 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String data = "aaaa";
this.getServletContext().setAttribute("data",data);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
}
}
package servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/*
* servletContext域:
* 1.这是一个容器
* 2.servletContext域这句话说明了这个容器作用范围,也就应用程序范围
*
*/
//通过servletContext实现ServletDemo7和servletDemo8的数据交换
public class ServletDemo8 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String value = (String) this.getServletContext().getAttribute("data");
System.out.println(value);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
}
}
先访问ServletDemo7然后访问ServletDemo8,发现在命令行输出了:aaaa。
- 获取WEB应用的初始化参数。
示例代码:
package servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
//获取web应用的初始化参数
/*
* <!-- 获取web应用的初始化参数 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>data</param-name>
<param-value>xxx</param-value>
</context-param>
*/
public class ServletDemo9 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String value = this.getServletContext().getInitParameter("data");
System.out.println(value);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
}
}
在应用程序的web.xml中增加以下内容:
<!-- 获取web应用的初始化参数 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>data</param-name>
<param-value>xxx</param-value>
</context-param>
访问ServletDemo9,发现命令行输出了:xxx。
- 实现Servlet的转发。
- 示例代码:
package servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
//通过servletContext实现请求转发、
public class ServletDemo10 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String data = "aaaaaa";
//把数据带给1.jsp
this.getServletContext().setAttribute("data", data);
RequestDispatcher rd = this.getServletContext().getRequestDispatcher("/1.jsp"); //得到转发到的对象(得到转发到1.jsp的对象)
rd.forward(request, response);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
}
}
1.jsp的文件内容如下:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>My JSP '1.jsp' starting page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>
<font color="red">
<%
String data = (String)application.getAttribute("data");
out.write(data);
%>
</font>
</h1>
</body>
</html>
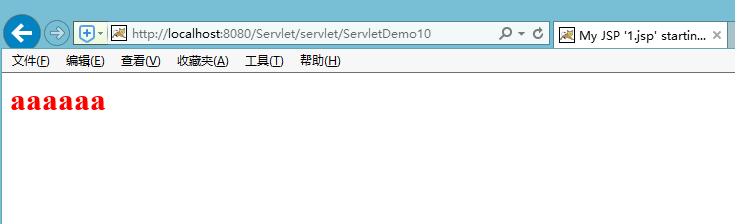
访问ServletDemo10,可以在浏览器看到如下结果:
- 利用ServletContext对象读取资源文件。
示例代码:
package servlet;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class ServletDemo11 extends HttpServlet {
//通过ServletContext去读取资源文件(db.properties)
//读取资源文件(模板代码)
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
test1();
System.out.println("---------------");
test2();
System.out.println("---------------");
test3();
System.out.println("---------------");
test4();
System.out.println("---------------");
test5();
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
//读取/src下面的db.properties文件
private void test1() throws IOException {
InputStream in = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/WEB-INF/classes/db.properties");//把资源文件作为流返回
Properties props = new Properties(); //map
props.load(in);
String url = props.getProperty("url");
String username = props.getProperty("username");
String password = props.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(url);
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
}
//读取/src/servlet下面的db.properties文件
private void test2() throws IOException {
InputStream in = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/WEB-INF/classes/servlet/db.properties");//把资源文件作为流返回
Properties props = new Properties(); //map
props.load(in);
String url = props.getProperty("url");
String username = props.getProperty("username");
String password = props.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(url);
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
}
//读取/WebRoot下面的db.properties文件
private void test3() throws IOException {
InputStream in = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/db.properties");//把资源文件作为流返回
Properties props = new Properties(); //map
props.load(in);
String url = props.getProperty("url");
String username = props.getProperty("username");
String password = props.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(url);
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
}
//读取资源文件需要注意的问题(不要采用传统方式,要采用ServletContext)
//传统方式采用相对路径去读取资源文件
private void test4() throws IOException {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("classes/db.properties");//把资源文件作为流返回,相对路径,相对于java虚拟机,就是Tomcat的启动目录D:\Tomcat\apache-tomcat-6.0.20\bin
//在D:\Tomcat\apache-tomcat-6.0.20\bin目录下创建一个classes文件,里面放入db.properties文件。
Properties props = new Properties(); //map
props.load(in);
String url = props.getProperty("url");
String username = props.getProperty("username");
String password = props.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(url);
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
}
//传统方式用绝对路径去读取资源文件
private void test5() throws IOException{
String path = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/db.properties");//返回资源文件的绝对路径
//好处:可以截取到资源文件的名称
String filename = path.substring(path.lastIndexOf("\\")+1);
System.out.println("当前读取到的资源名称是:"+filename);
//之后用传统方式
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(path);//把资源文件作为流返回
Properties props = new Properties(); //map
props.load(in);
String url = props.getProperty("url");
String username = props.getProperty("username");
String password = props.getProperty("password");
System.out.println("当前读取到的资源数据是:");
System.out.println(url);
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
}
}






















 889
889

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








