
✅ 博主简介:擅长数据搜集与处理、建模仿真、程序设计、仿真代码、论文写作与指导,毕业论文、期刊论文经验交流。
✅ 具体问题可以私信或扫描文章底部二维码。
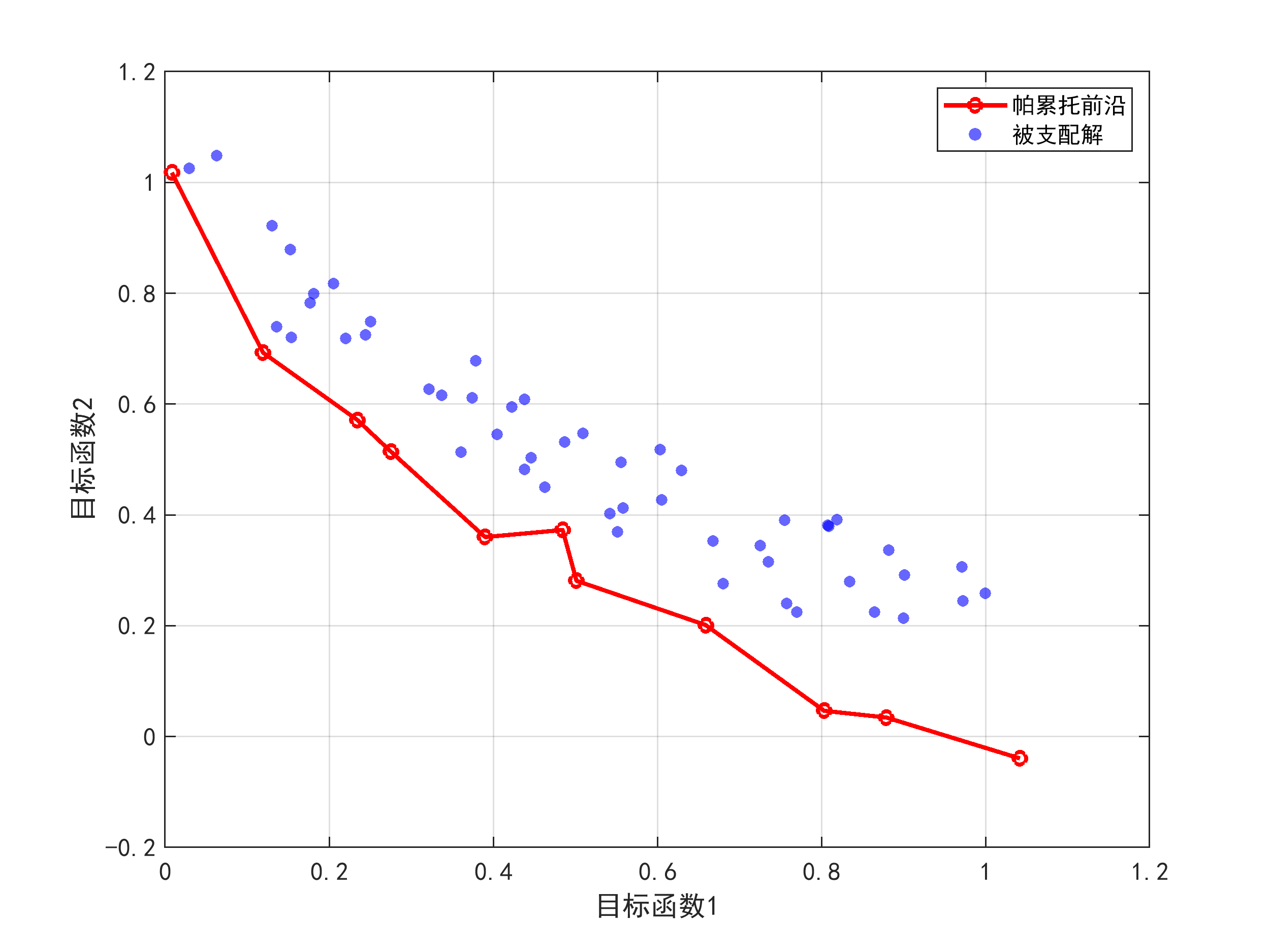
1) 针对高维全局优化问题中生物地理学优化算法易陷入局部最优、收敛速度慢的不足,提出一种融合正弦余弦算法和动态混合变异的对偶BBO变体(SCBBO)。该算法首先采用拉丁超立方抽样初始化种群,确保解空间均匀覆盖;其次,在迁移算子中嵌入改进的正弦余弦更新公式,引入非线性递减参数和惯性权重,增强高维环境下的勘探能力;然后,设计动态混合变异算子,结合拉普拉斯变异的大步长探索和高斯变异的精细开发,根据迭代进度自适应调整变异概率,平衡全局与局部搜索;最后,集成对偶学习策略,为每个个体生成对称解,通过比较选择更优者,提升收敛精度。理论分析通过构造数列收敛模型证明算法以概率1全局收敛。在CEC2013高维测试集上的实验表明,SCBBO在1000维至10000维问题上均保持稳定性能,显著优于对比算法。
(2) 为解决复杂多峰优化问题中BBO算法开发能力弱、参数敏感的问题,提出一种基于混合迁移算子和反馈差分进化机制的BBO变体(HFBBO)。该算法引入榜样学习法,在迁移过程中禁止劣解覆盖优解,保留精英信息;混合迁移算子通过随机切换全局迁移(向最优个体学习)和局部迁移(向邻域个体学习),实现搜索模式动态调整;反馈差分进化机制替代传统变异,根据种群多样性指标自动选择差分变异策略(如DE/rand/1或DE/best/2),避免早熟收敛。算法收敛性通过Markov链模型证明,复杂度分析显示其与标准BBO相当。在CEC2014和CEC2017测试集的广泛实验中,HFBBO在多数函数上获得最优结果,Friedman检验排名第一,显示出强大鲁棒性。
(3) 面向现实工程中的约束优化问题,将改进的Oracle惩罚函数法与BBO算法结合,处理等式和不等式约束。该方法将约束违反度转化为自适应惩罚项,动态调整惩罚系数,确保搜索朝向可行域;同时,针对混合变量问题,设计通用离散化处理模块,将离散变量映射为连续编码,优化后再逆映射回原始空间。基于此,开发SCBBO-CH和HFBBO-CH两种算法,应用于CEC2020现实约束优化测试集的57个问题,涵盖机械设计、资源分配等领域。实验结果表明,所提算法在近半数问题上达到理论最优解,且求解效率高于传统罚函数法,验证了其在复杂约束处理中的有效性。
import numpy as np
import math
def latin_hypercube_sampling(num, dim, bounds):
samples = np.zeros((num, dim))
for i in range(dim):
segment = (bounds[1] - bounds[0]) / num
samples[:, i] = np.array([bounds[0] + (j + np.random.rand()) * segment for j in range(num)])
np.random.shuffle(samples[:, i])
return samples
class SCBBO:
def __init__(self, num_species, dim, bounds, objective):
self.population = latin_hypercube_sampling(num_species, dim, bounds)
self.fitness = np.array([objective(ind) for ind in self.population])
self.bounds = bounds
self.dim = dim
self.best_idx = np.argmin(self.fitness)
self.best_solution = self.population[self.best_idx].copy()
self.best_fitness = self.fitness[self.best_idx]
def migration(self, migration_rates):
new_pop = self.population.copy()
for i in range(len(self.population)):
if np.random.rand() < migration_rates[i]:
j = np.random.randint(len(self.population))
for k in range(self.dim):
if np.random.rand() < 0.5:
new_pop[i][k] = self.population[j][k]
return new_pop
def sca_update(self, iteration, max_iter):
a = 2 - iteration * (2 / max_iter)
new_pop = self.population.copy()
for i in range(len(self.population)):
r1 = a * (1 - iteration / max_iter)
r2 = 2 * math.pi * np.random.rand()
r3 = 2 * np.random.rand()
r4 = np.random.rand()
if r4 < 0.5:
new_pop[i] += r1 * math.sin(r2) * abs(r3 * self.best_solution - self.population[i])
else:
new_pop[i] += r1 * math.cos(r2) * abs(r3 * self.best_solution - self.population[i])
return new_pop
def dynamic_mutation(self, iteration, max_iter):
mutated = self.population.copy()
mutation_prob = 0.1 * (1 - iteration / max_iter)
for i in range(len(self.population)):
if np.random.rand() < mutation_prob:
if np.random.rand() < 0.5:
mutated[i] += np.random.laplace(0, 1, self.dim) * 0.5
else:
mutated[i] += np.random.normal(0, 1, self.dim) * 0.2
return mutated
def dual_learning(self):
dual_pop = -self.population.copy()
return np.clip(dual_pop, self.bounds[0], self.bounds[1])
def optimize(self, max_iter, objective):
for iter in range(max_iter):
migration_rates = 1 - (self.fitness - np.min(self.fitness)) / (np.max(self.fitness) - np.min(self.fitness) + 1e-8)
self.population = self.migration(migration_rates)
self.population = self.sca_update(iter, max_iter)
self.population = self.dynamic_mutation(iter, max_iter)
dual_pop = self.dual_learning()
combined_pop = np.vstack([self.population, dual_pop])
combined_fitness = np.array([objective(ind) for ind in combined_pop])
best_combined_idx = np.argsort(combined_fitness)[:len(self.population)]
self.population = combined_pop[best_combined_idx]
self.fitness = combined_fitness[best_combined_idx]
self.best_idx = np.argmin(self.fitness)
if self.fitness[self.best_idx] < self.best_fitness:
self.best_fitness = self.fitness[self.best_idx]
self.best_solution = self.population[self.best_idx].copy()
return self.best_solution, self.best_fitness
def ackley_function(x):
return -20 * np.exp(-0.2 * np.sqrt(np.mean(x ** 2))) - np.exp(np.mean(np.cos(2 * math.pi * x))) + 20 + math.e
scbbo = SCBBO(50, 10, [-32, 32], ackley_function)
best_sol, best_fit = scbbo.optimize(100, ackley_function)
print(f"Best Solution: {best_sol}, Best Fitness: {best_fit}")
如有问题,可以直接沟通
👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇





















 6706
6706

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










