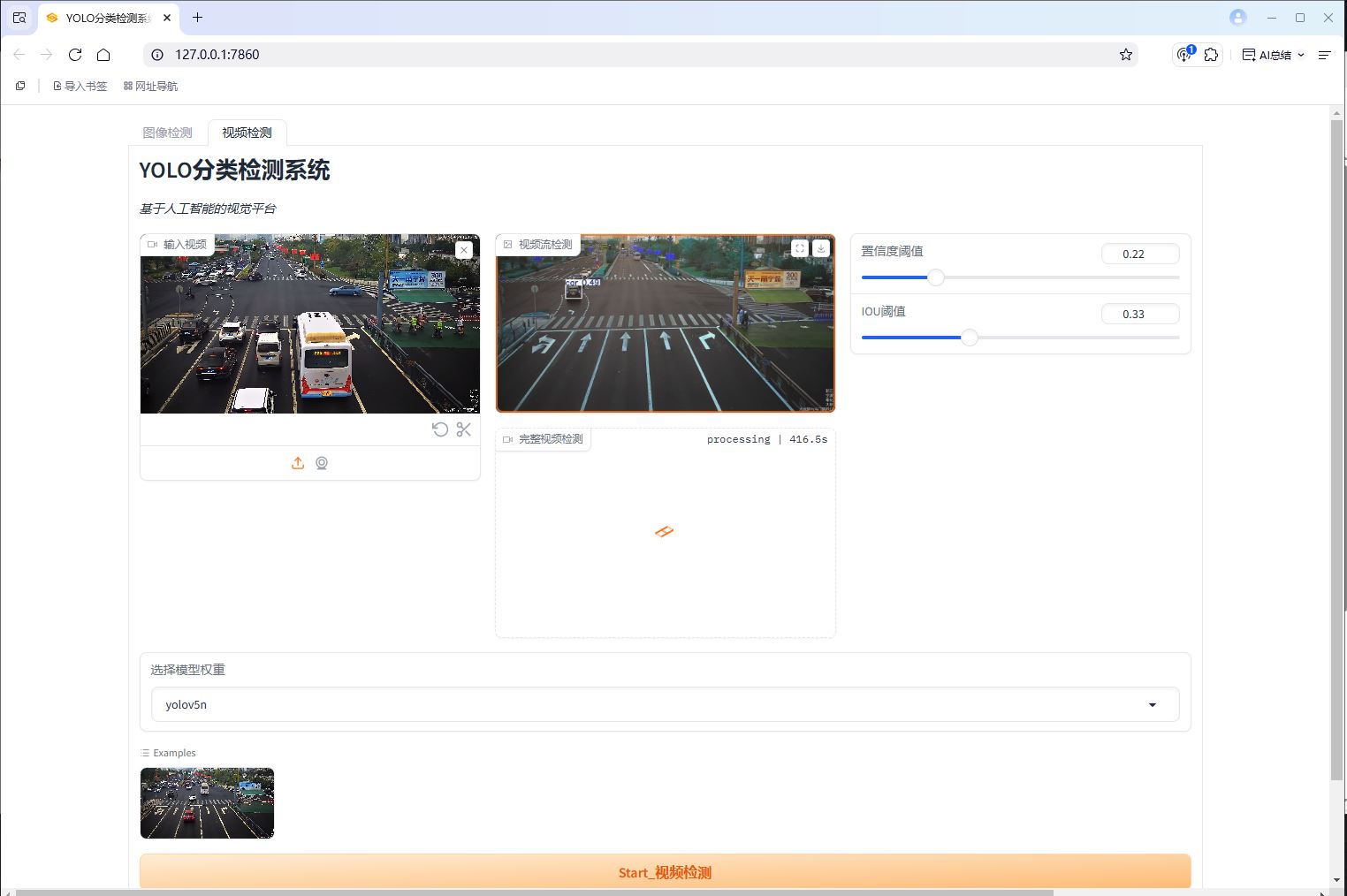
由于gradio平台自身限制以及我的电脑只支持CPU,实时检测时帧率较慢,但可以点击下载检测视频按钮,等待检测完成,查看检测后的文件,有兴趣的可以自己去优化,总之grdio平台相对来说还是差一些。注:生成的检测系统链接可分享,72小时有效

import threading
import gradio as gr
import torch
import cv2
import time
import tempfile
import os
import numpy as np
from datetime import datetime
from pathlib import Path
base_conf = 0.4
base_iou = 0.5
display_interval = 0.01
last_display_time = time.time()
weights_option = {"yolov5s": "yolov5s.pt",
"yolov5n": "yolov5n.pt"}
stop_event = threading.Event()
def load_weight(weight_name):
weight_path = weights_option[weight_name]
load_model = torch.hub.load(r'C:\\Users\Administrator\Desktop\yolov5-master\yolo1', 'custom', path=weight_path,
source='local')
return load_model
def model_dection(img, weight_name, conf, iou):
t = 70
y = 0
model = load_weight(weight_name)
model.conf = conf
model.iou = iou
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
results_prediction = model(img)
results = results_prediction.render()[0]
Frist_jpg_dection = results_prediction.pandas().xyxy[0]
results_opencv = cv2.cvtColor(results, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
count_class = Frist_jpg_dection['name'].value_counts()
for class_name, name_count in count_class.items():
y = y + t
text = f'{class_name} : {name_count}'
cv2.putText(results_opencv,
text,
(20, y),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
1,
(0, 0, 255),
2,
cv2.LINE_AA)
return results_opencv
def detect_objects(image, model, conf, iou):
if image is None:
return None
# 转换图像格式 (RGB -> BGR)
image_bgr = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# 使用模型进行预测
results = model(image_bgr)
# 渲染检测结果
rendered_img = results.render()[0]
# 转换回RGB格式供Gradio显示
return cv2.cvtColor(rendered_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
#############################################################
def save_image(image):
if image is None:
return "未捕获到有效图像"
try:
# 创建保存目录
os.makedirs("captured_frames", exist_ok=True)
# 生成带时间戳的文件名
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
filename = f"captured_frames/capture_{timestamp}.jpg"
# 转换图像格式并保存
image_bgr = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
cv2.imwrite(filename, image_bgr)
return f"图像已保存为: {filename}"
except Exception as e:
return f"保存失败: {str(e)}"
def capture_and_save(image, weight_name, conf, iou):
if image is None:
return None
# 加载模型
model = load_weight(weight_name)
if model is None:
return None
# 设置参数
model.conf = conf
model.iou = iou
# 检测对象
detected_img = detect_objects(image, model, conf, iou)
# 保存图像
save_status = save_image(detected_img if detected_img is not None else image)
print(save_status) # 打印保存状态到控制台
return detected_img if detected_img is not None else image
##########################################################
def realtime_detection(image, model, conf_thres):
if model is None or image is None:
return None
# 设置置信度阈值
model.conf = conf_thres
return detect_objects(image, model)
def video_pred(video_file, weight_name, conf, iou):
stop_event.clear()
model = load_weight(weight_name)
model.conf = conf
model.iou = iou
video = cv2.VideoCapture(video_file)
# 获取视频属性
fps = video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
width = int(video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
height = int(video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
frame_contorl = max(1, int(fps // 60))
frame_count = 0
temp_dir = tempfile.mkdtemp()
output_path = str(Path(temp_dir) / "output.mp4")
# 设置视频编码器和创建VideoWriter对象
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v')
out_video = cv2.VideoWriter(output_path, fourcc, fps, (width, height))
while True:
start_time = time.time()
ret, frame = video.read()
if not ret:
break
else:
img = frame
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
with torch.no_grad():
results_prediction = model(img)
results = results_prediction.render()[0]
result_frame = cv2.cvtColor(results, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
out_video.write(result_frame)
video.release()
out_video.release()
while not os.path.exists(output_path) or os.path.getsize(output_path) == 0:
time.sleep(0.1)
return output_path
def clear_video():
stop_event.set()
return None, None
def video_frame(video_file, weight_name, conf, iou):
# 初始化模型
t=50
model = load_weight(weight_name)
model.conf = conf
model.iou = iou
# 打开视频文件
video = cv2.VideoCapture(video_file)
while True:
y = 0
ret, frame = video.read()
if not ret:
break
# 转换颜色空间
img = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 进行预测
with torch.no_grad():
results_prediction = model(img)
results = results_prediction.render()[0]
# 转换回BGR并yield给Gradio
First_message = results_prediction.pandas().xyxy[0]
count_class = First_message['name'].value_counts()
result_frame = cv2.cvtColor(results, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
for class_name, name_count in count_class.items():
y = y + t
text = f'{class_name} : {name_count}'
cv2.putText(result_frame,
text,
(20, y),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
2,
(0, 0, 255),
4,
cv2.LINE_AA)
yield result_frame
video.release()
def video_save(video_file, weight_name, conf, iou):
t=30
model = load_weight(weight_name)
model.conf = conf
model.iou = iou
video = cv2.VideoCapture(video_file)
# 获取视频属性
fps = video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
width = int(video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
height = int(video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
# 创建临时文件保存输出视频
temp_dir = tempfile.mkdtemp()
output_path = os.path.join(temp_dir, "output.mp4")
# 设置视频编码器和创建VideoWriter对象
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID')
# fourcc = cv2.VideoCapture_fourcc(*'mp4v'))
out_video = cv2.VideoWriter(output_path, fourcc, fps, (width, height))
while True:
y=0
ret, frame = video.read()
if not ret:
break
else:
img = frame
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
with torch.no_grad():
results_prediction = model(img)
results = results_prediction.render()[0]
result_frame = cv2.cvtColor(results, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
First_message = results_prediction.pandas().xyxy[0]
count_class = First_message['name'].value_counts()
for class_name, name_count in count_class.items():
y = y + t
text = f'{class_name} : {name_count}'
cv2.putText(result_frame,
text,
(20, y),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
1,
(0, 0, 255),
2,
cv2.LINE_AA)
out_video.write(result_frame)
video.release()
out_video.release()
while not os.path.exists(output_path) or os.path.getsize(output_path) == 0:
time.sleep(0.1)
return output_path
with gr.Blocks(title="YOLO分类检测系统") as demo:
with gr.Tab("图像检测"):
gr.Markdown("""# YOLO分类检测系统
*基于人工智能的视觉平台*""")
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column(scale=6):
input_img = gr.Image(sources=["upload"])
with gr.Column(scale=6):
output_img = gr.Image(label="检测图像")
with gr.Column():
conf_slider = gr.Slider(label="conf_set",
minimum=0,
maximum=1,
value=base_conf)
iou_slider = gr.Slider(label="iou_set",
minimum=0,
maximum=1,
value=base_iou)
with gr.Row():
weight_dropdown = gr.Dropdown(
choices=list(weights_option.keys()),
value="yolov5n",
label="选择模型权重"
)
gr.Examples([
[r"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\yolov5-master\datasets\coco1281\images\train2017\000000000025.jpg", base_conf, base_iou],
], inputs=input_img, outputs=output_img)
button = gr.Button(value="Start_目标检测",
min_width=1,
variant="primary")
button.click(fn=model_dection,
inputs=[input_img,
weight_dropdown,
conf_slider,
iou_slider],
outputs=output_img)
with gr.Tab("视频检测"):
gr.Markdown("""# YOLO分类检测系统
*基于人工智能的视觉平台*""")
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column(scale=6):
input_video = gr.Video(label="输入视频")
with gr.Column(scale=6):
output_img = gr.Image(label="视频流检测")
output_video = gr.Video(label="完整视频检测")
with gr.Column(scale=6):
video_conf = gr.Slider(minimum=0,
maximum=1,
value=0.4,
label="置信度阈值")
video_iou = gr.Slider(minimum=0,
maximum=1,
value=0.5,
label="IOU阈值")
with gr.Row():
weight_dropdown = gr.Dropdown(
choices=list(weights_option.keys()),
value="yolov5n",
label="选择模型权重"
)
gr.Examples([
[r"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\yolov5-master\traffic.mp4", base_conf, base_iou]
], inputs=input_video,
outputs=output_img)
button1 = gr.Button(
value="Start_视频检测",
min_width=1,
variant="primary")
button1.click(
fn=video_frame,
inputs=[input_video,
weight_dropdown,
video_conf,
video_iou], # 明确指定每个输入
outputs=output_img
)
button2 = gr.Button(
value="下载完成检测视频",
min_width=1,
variant="primary")
button2.click(
fn=video_save,
inputs=[input_video,
weight_dropdown,
video_conf,
video_iou], # 明确指定每个输入
outputs=output_video
)
demo.launch( share=True)





















 633
633

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








