algorithm此头文件是算法库的一部分。本篇介绍堆操作,最小/最大操作,比较操作,排列操作。
接口API
堆操作 | |
| 检查给定范围是否为一个最大堆 (函数模板) | |
| (C++11) | 查找能成为最大堆的最大子范围 (函数模板) |
| 从一个元素范围创建出一个最大堆 (函数模板) | |
| 将一个元素加入到一个最大堆 (函数模板) | |
| 从最大堆中移除最大元素 (函数模板) | |
| 将一个最大堆变成一个按升序排序的元素范围 (函数模板) | |
最小/最大操作 | |
| 返回各给定值中的较大者 (函数模板) | |
| 返回范围内的最大元素 (函数模板) | |
| 返回各给定值中的较小者 (函数模板) | |
| 返回范围内的最小元素 (函数模板) | |
| (C++11) | 返回两个元素的较小和较大者 (函数模板) |
| (C++11) | 返回范围内的最小元素和最大元素 (函数模板) |
比较操作 | |
| 确定两个元素集合是否是相同的 (函数模板) | |
| 当一个范围按字典顺序小于另一个范围时,返回 true (函数模板) | |
排列操作 | |
| (C++11) | 判断一个序列是否为另一个序列的排列 (函数模板) |
| 产生某个元素范围的按字典顺序的下一个较大的排列 (函数模板) | |
| 产生某个元素范围的按字典顺序的下一个较小的排列 (函数模板) | |
示例代码:
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <utility> // std::pair
#include <vector>
#include <array>
#include <cctype> // std::tolower
#include <string>
#include <ctime> // std::time
#include <cstdlib> // std::rand, std::srand
#include <random> // std::default_random_engine
#include <chrono> // std::chrono::system_clock
#include <iomanip>
bool myfn(int i, int j) { return i < j; }
struct myclass {
bool operator() (int i, int j) { return i < j; }
} myobj;
bool is_palindrome(const std::string& s)
{
return std::equal(s.cbegin(), s.cbegin() + s.size() / 2, s.crbegin());
}
void test_equal(const std::string& s)
{
std::cout << std::quoted(s)
<< (is_palindrome(s) ? " 是" : " 不是")
<< "回文\n";
}
// a case-insensitive comparison function:
bool mycomp(char c1, char c2)
{
return std::tolower(c1) < std::tolower(c2);
}
template<typename Os, typename V>
Os& operator<<(Os& os, const V& v)
{
os << "{ ";
for (const auto& e : v)
os << e << ' ';
return os << '}';
}
int main()
{
// make_heap example 从一个元素范围创建出一个最大堆
int myints[] = { 10,20,30,5,15 };
std::vector<int> v(myints, myints + 5);
std::make_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
std::cout << "initial max heap : " << v.front() << '\n';
// pop_heap example 从最大堆中移除最大元素
std::pop_heap(v.begin(), v.end()); v.pop_back();
std::cout << "max heap after pop : " << v.front() << '\n';
// push_heap example 将一个元素加入到一个最大堆
v.push_back(99); std::push_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
std::cout << "max heap after push: " << v.front() << '\n';
// sort_heap example 将一个最大堆变成一个按升序排序的元素范围
std::sort_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
std::cout << "final sorted range :";
for (unsigned i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
std::cout << ' ' << v[i];
std::cout << '\n';
// is_heap example 检查给定范围是否为一个最大堆
std::vector<int> foo{ 9,5,2,6,4,1,3,8,7 };
if (!std::is_heap(foo.begin(), foo.end()))
std::make_heap(foo.begin(), foo.end());
std::cout << "Popping out elements:";
while (!foo.empty()) {
std::pop_heap(foo.begin(), foo.end()); // moves largest element to back
std::cout << ' ' << foo.back(); // prints back
foo.pop_back(); // pops element out of container
}
std::cout << '\n';
// is_heap_until example 查找能成为最大堆的最大子范围
std::vector<int> foo2{ 2,6,9,3,8,4,5,1,7 };
std::sort(foo2.begin(), foo2.end());
std::reverse(foo2.begin(), foo2.end());
auto last = std::is_heap_until(foo2.begin(), foo2.end());
std::cout << "The " << (last - foo2.begin()) << " first elements are a valid heap:";
for (auto it = foo2.begin(); it != last; ++it)
std::cout << ' ' << *it;
std::cout << '\n';
// min example 返回各给定值中的较小者
std::cout << "min(1,2)==" << std::min(1, 2) << '\t';
std::cout << "min(2,1)==" << std::min(2, 1) << '\t';
std::cout << "min('a','z')==" << std::min('a', 'z') << '\t';
std::cout << "min(3.14,2.72)==" << std::min(3.14, 2.72) << '\n';
// max example 返回各给定值中的较大者
std::cout << "max(1,2)==" << std::max(1, 2) << '\t';
std::cout << "max(2,1)==" << std::max(2, 1) << '\t';
std::cout << "max('a','z')==" << std::max('a', 'z') << '\t';
std::cout << "max(3.14,2.73)==" << std::max(3.14, 2.73) << '\n';
// minmax example 返回两个元素的较小和较大者
auto result = std::minmax({ 1,2,3,4,5 });
std::cout << "minmax({1,2,3,4,5}): ";
std::cout << result.first << ' ' << result.second << '\n';
// min_element example 返回范围内的最小元素
// max_element example 返回范围内的最大元素
int myints2[] = { 3,7,2,5,6,4,9 };
// using default comparison:
std::cout << "The smallest element is " << *std::min_element(myints2, myints2 + 7) << '\n';
std::cout << "The largest element is " << *std::max_element(myints2, myints2 + 7) << '\n';
// using function myfn as comp:
std::cout << "The smallest element is " << *std::min_element(myints2, myints2 + 7, myfn) << '\n';
std::cout << "The largest element is " << *std::max_element(myints2, myints2 + 7, myfn) << '\n';
// using object myobj as comp:
std::cout << "The smallest element is " << *std::min_element(myints2, myints2 + 7, myobj) << '\n';
std::cout << "The largest element is " << *std::max_element(myints2, myints2 + 7, myobj) << '\n';
// minmax_element example 返回范围内的最小元素和最大元素
std::array<int, 7> foo3{ 3,7,2,9,5,8,6 };
auto result3 = std::minmax_element(foo3.begin(), foo3.end());
// print result:
std::cout << "min is " << *result3.first;
std::cout << ", at position " << (result3.first - foo3.begin()) << '\n';
std::cout << "max is " << *result3.second;
std::cout << ", at position " << (result3.second - foo3.begin()) << '\n';
// equal example 确定两个元素集合是否是相同的
test_equal("radar");
test_equal("hello");
// lexicographical_compare example 当一个范围按字典顺序小于另一个范围时,返回 true
char foo5[] = "Apple";
char bar5[] = "apartment";
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::cout << "Comparing foo and bar lexicographically (foo<bar):\n";
std::cout << "Using default comparison (operator<): ";
std::cout << std::lexicographical_compare(foo5, foo5 + 5, bar5, bar5 + 9);
std::cout << '\n';
std::cout << "Using mycomp as comparison object: ";
std::cout << std::lexicographical_compare(foo5, foo5 + 5, bar5, bar5 + 9, mycomp);
std::cout << '\n';
// is_permutation example 判断一个序列是否为另一个序列的排列
static auto v1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
static auto v2 = { 3, 5, 4, 1, 2 };
static auto v3 = { 3, 5, 4, 1, 1 };
std::cout << v2 << " 是 " << v1 << " 的排列:" << std::boolalpha
<< std::is_permutation(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin()) << '\n'
<< v3 << " 是 " << v1 << " 的排列:" << std::boolalpha
<< std::is_permutation(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v3.begin()) << '\n';
// next_permutation example 产生某个元素范围的按字典顺序的下一个较大的排列
int myints6[] = { 1,2,3 };
std::sort(myints6, myints6 + 3);
std::cout << "The 3! possible permutations with 3 elements:\n";
do {
std::cout << myints6[0] << ' ' << myints6[1] << ' ' << myints6[2] << '\n';
} while (std::next_permutation(myints6, myints6 + 3));
std::cout << "After loop: " << myints6[0] << ' ' << myints6[1] << ' ' << myints6[2] << '\n';
// prev_permutation example 产生某个元素范围的按字典顺序的下一个较小的排列
int myints7[] = { 1,2,3 };
std::sort(myints7, myints7 + 3);
std::reverse(myints7, myints7 + 3);
std::cout << "The 3! possible permutations with 3 elements:\n";
do {
std::cout << myints7[0] << ' ' << myints7[1] << ' ' << myints7[2] << '\n';
} while (std::prev_permutation(myints7, myints7 + 3));
std::cout << "After loop: " << myints7[0] << ' ' << myints7[1] << ' ' << myints7[2] << '\n';
std::cout << "hello world\n";
return 0;
}
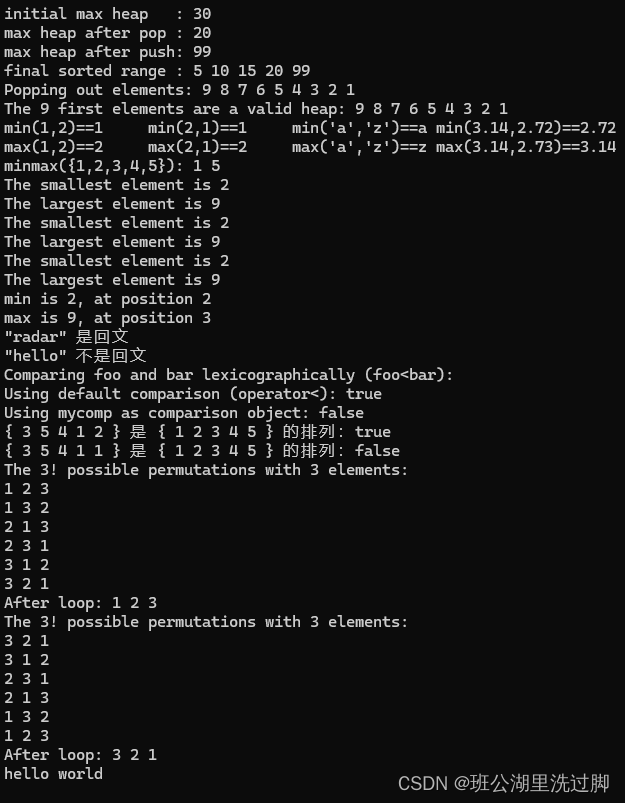
运行结果:
参考:






















 1334
1334

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








