heap block 引发的思考
问题背景:
Implicit Free Lists
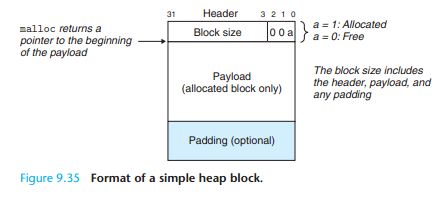
Any practical allocator needs some data structure that allows it to distinguish block boundaries and to distinguish between allocated and free blocks. Most allocators embed this information in the blocks themselves. One simple approach is shown in Figure 9.35.
malloc函数第一次申请出的是payload区域顶端的内存区域,返回的指针指向该处。
在payload之前还有一个header的区域,这个区域记录了block size,这里作者有点误导,由于是8byte align
于是在只有最底位(图中的a,用来记录block是否已经allocated还是free)
首先要理解malloc中block size的原理
这个问题要能搞定,填对,不然下面的demo看了没用。。。
这是在32bit的机器上
对于上面那个题目的题解:
This problem touches on some core ideas such as alignment requirements, minimum block sizes, and header encodings. The general approach for determining the block size is to round the sum of the requested payload and the header size to the nearest multiple of the alignment requirement (in this case 8 bytes). For
example, the block size for the malloc(1) request is 4 + 1 = 5 rounded up to 8. The block size for the malloc(13)request is 13 + 4 = 17 rounded up to 24.
Request Block size (decimal bytes) Block header (hex)
malloc(1) 8 0x9
malloc(5) 16 0x11
malloc(12) 16 0x11
malloc(13) 24 0x19
64bit的机器的malloc采用的是16byte对齐的!
在linux 64bit的 Ubuntu上做测试:
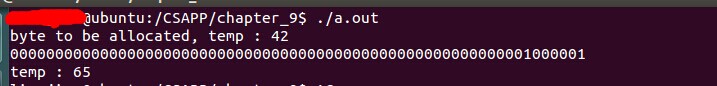
malloc(42)
这里申请 42byte的空间,malloc返回的连续内存空间是 64byte的
42 byte,由于开始有8byte的block size 区域,
42+8 = 50;
由于16byte对齐,于是对齐到64byte
至于最后的temp == 65 ,那是因为最后一位是用来提示该内存区域是否allocated。由于该bit 位等于1,于是,是allocated
上述测试代码:
/***********************************************************
code writer : EOF
code date : 2014.07.27
e-mail:jasonleaster@gmail.com
code purpose:
Find out what beyond the payload location. :)
************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MACHINE_ADDRESS_LENGTH 64
void print_dec2bin(int dec_number)
//Just a simple function which translate decimal number into binary numebr
{
int temp = 0;
int to_be_print = 0;
int array[MACHINE_ADDRESS_LENGTH];
for(temp = 0;temp < MACHINE_ADDRESS_LENGTH; temp++)
{
array[MACHINE_ADDRESS_LENGTH-temp-1] = dec_number%2;
dec_number >>=1;
}
for(temp = 0;temp < MACHINE_ADDRESS_LENGTH; temp++)
{
printf("%d",array[temp]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
int *ptr = NULL;
int temp = 42;//how many bytes to be allocated
printf("byte to be allocated, temp : %d\n",temp);
ptr = (int *)malloc(temp);
if(ptr == NULL)
{
printf("malloc failed\n");
return 0;
}
else
{
*ptr = 2014;//just write some data into payload location.
}
temp = *(ptr - 2);//You may never forget that this code must be run on 64-bits machine, and ptr point to 'int'!!!Attention!!
// otherwise you have to change 'ptr-2' into 'ptr-1'
print_dec2bin(temp);
printf("temp : %d\n",temp);
free(ptr);
return 0;
}
再三提示那个ptr-2!
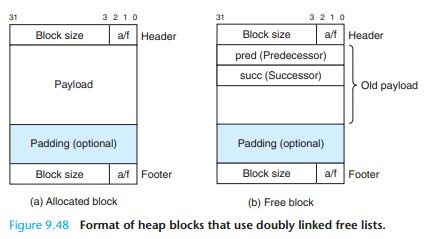
如果多次malloc,除了最后一个block之外,每个block前后都有记录block的block size段,最后一个只有header blocksize
ubuntu2@ubuntu:~$ ./a.out
ptr_void:0x185f010
foo_void:0x185f030
ptr_void header size:32
ptr_void foot size:32
foo_void header size:32
foo_void foot size:135104
最后的size是不是blocksize,印证最后的block是没有foot block size记录块的!
测试demo:
/************************************************************************
code writer : EOF
code date : 2014.07.28
e-mail: jasonleaster@gmail.com
code purpose :
test the block-size of each memory block which was allocated by
library function -- malloc().
If there are something wrong with my code, please touch me by e-mail
or send me a message to my blog in CSDN. Thank you.
*************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MACHINE_BITS 64 //the bits of this machine
#define BYTE 8 //one byte == eight bits
#define ALLOCATED_OR_NOT(bp) ((unsigned long)(bp) & 0x1)
//@bp : block pointer which point into the start location of this block
#define GET_VALUE_LONG(ptr) (*((long*)(ptr)))
//get the value of the location where ptr point to.
#define BLOCK_SIZE(bp) ((GET_VALUE_LONG(bp))&(~0x7))
//get the block size
int main()
{
void* ptr_void = malloc(sizeof(int));//allocate the first block.
printf("ptr_void:%p\n",ptr_void);
void* foo_void = malloc(sizeof(int));//allocate the second block.
printf("foo_void:%p\n",foo_void);
long block_size = BLOCK_SIZE((char*)ptr_void-(MACHINE_BITS/BYTE));//get the first block's header-block-size
printf("ptr_void header size:%ld\n",block_size);
printf("ptr_void foot size:%ld\n",BLOCK_SIZE((char*)ptr_void+block_size-(MACHINE_BITS/BYTE)));
//print out the foot-block-size
block_size = BLOCK_SIZE((char*)foo_void-(MACHINE_BITS/BYTE));
printf("foo_void header size:%ld\n",block_size);
printf("foo_void foot size:%ld\n",BLOCK_SIZE((char*)foo_void+block_size-(MACHINE_BITS/BYTE)));
free(ptr_void);
free(foo_void);
return 0;
}



























 2156
2156

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








