一、EL 表达式概述
EL(Express Lanuage)表达式可以嵌入在jsp页面内部,减少jsp脚本的编写,EL 出现的目的是要替代jsp页面中脚本的编写。
EL有3个作用。二、EL从域中取出数据
EL最重要的作用。在我们以后使用EL的过程中占有率达到90%以上。
EL最主要的作用是获得四大域中的数据,格式${EL表达式}
jsp脚本:<%=request.getAttribute(name)%>
EL获得pageContext域中的值:${pageScope.key};
EL获得request域中的值:${requestScope.key};
EL获得session域中的值:${sessionScope.key};
EL获得application域中的值:${applicationScope.key};
EL从四个域(全域)中获得某个值${key};
---同样是依次从pageContext域,request域,session域,application域中获取属性,在某个域中获取后将不在向后寻找
1)获得普通字符串
2)获得User对象的值
3)获得List<User>的值
创建一个jsp,演示EL的表达式:<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-16"
pageEncoding="UTF-16"%>
<%@ page import="com.ken.domain.User"%>
<%@ page import="java.util.*"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-16">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 模拟域中的数据 -->
<%
//存储字符串
request.setAttribute("company", "百度");
//存储一个对象
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("zhangsan");
user.setPassword("123");
session.setAttribute("user", user);
//存储一个集合
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>();
User user1 = new User();
user1.setId(1);
user1.setName("zhangsan");
user1.setPassword("123");
list.add(user1);
User user2 = new User();
user2.setId(1);
user2.setName("zhangsan");
user2.setPassword("123");
list.add(user2);
application.setAttribute("list", list);
%>
<!-- 脚本取出域中的值 -->
<%=request.getAttribute("company")%>
<%
User sessionUser = (User) session.getAttribute("user");
out.write(sessionUser.getName());
%>
<!-- 使用EL表达式获得域中的值 -->
${requestScope.company }
${sessionScope.user.name }
${applicationScope.list[1].name }
<!-- 使用EL表达式 全域查找 -->
${company }
${user.name }
${list[1].name }
</body>
</html>三、EL的内置对象11个
很少用。EL的内置对象的出现就是为了接收客户端的请求数据。
pageScope,requestScope,sessionScope,applicationScope ---- 获取JSP中域中的数据
param------相当于request.getParameter() - 接收参数
paramValues------相当于request.getParameterValues() - 接收参数
header,headerValues------相当于request.getHeader(name) - 获取请求头信息
initParam------相当于this.getServletContext().getInitParameter(name) - 获取全局初始化参数
cookie------相当于request.getCookies()---cookie.getName()---cookie.getValue() - WEB开发中cookie
pageContext -WEB开发中的pageContext.
pageContext获得其他八大对象
案例:
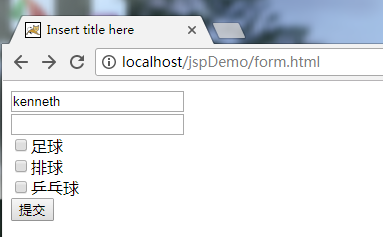
创建form.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/jspDemo/form.jsp" method="post">
<input type="text" name="username"><br>
<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="zq">足球<br>
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="pq">排球<br>
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="ppq">乒乓球<br>
<input type="submit" value="提交"><br>
</form>
</body>
</html><%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-16"
pageEncoding="UTF-16"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-16">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 获得表单的参数 -->
<%
//request.getParameter("username");
//
%>
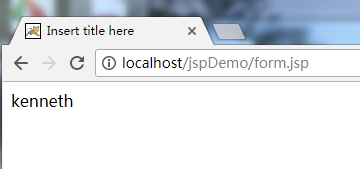
<!-- 使用el获得参数 -->
${param.username }<!-- 相当于request.getParameter("username"); -->
</body>
</html>
重定向的时候,客户端需要再次访问服务端,所以需要拼url地址,所以需要web应用的名称,所以需要contextPath。
所以,${pageContext.request.contextPath}重要。这个表达式可以写在字符串中。
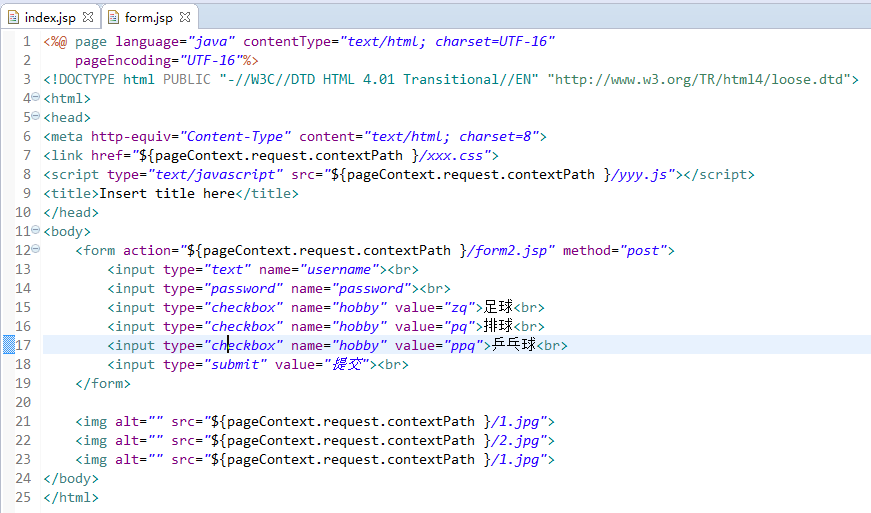
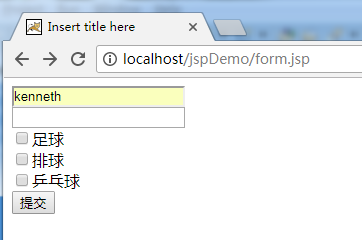
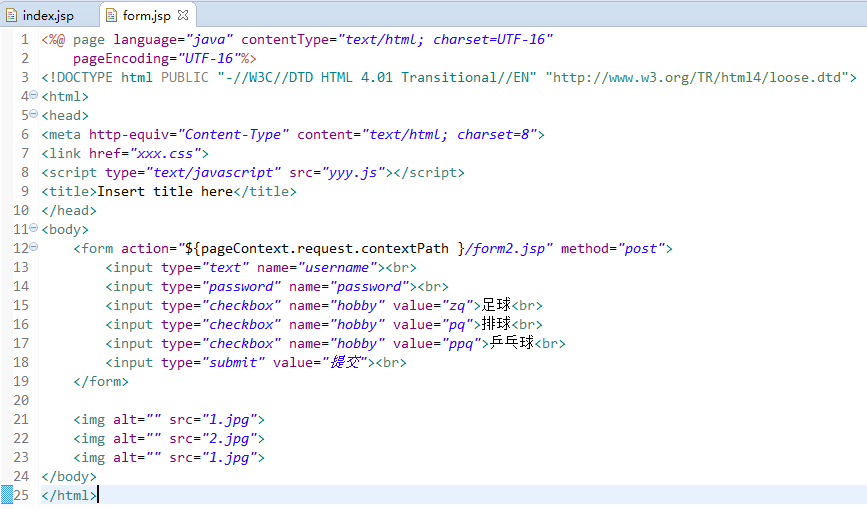
创建form.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-16"
pageEncoding="UTF-16"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-16">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/form2.jsp" method="post">
<input type="text" name="username"><br>
<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="zq">足球<br>
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="pq">排球<br>
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="ppq">乒乓球<br>
<input type="submit" value="提交"><br>
</form>
</body>
</html><%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-16"
pageEncoding="UTF-16"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-16">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 获得表单的参数 -->
<%
//request.getParameter("username");
//
%>
<!-- 使用el获得参数 -->
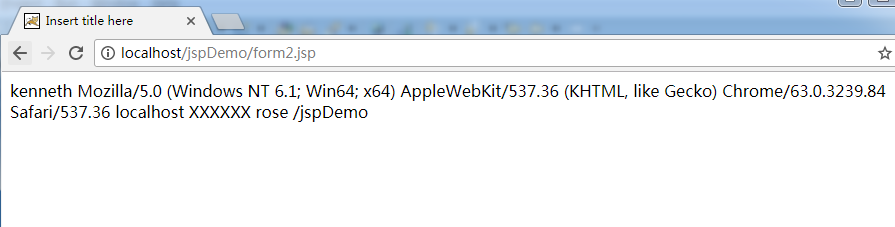
${param.username }
<!-- 相当于request.getParameter("username"); -->
${header["User-Agent"] }
${header.host }
${initParam.aaa }
${cookie.name.value }
<!-- 通过EL表达式获得request对象 -->
${pageContext.request.contextPath }
</body>
</html>
扩展知识点:
客户端访问这个jsp。首先,这个jsp的内容以字符串的形式返回给客户端,然后,客户端进行解析。解析到<link href="xxx.css">的时候,客户端就又去服务器拿xxx.css。然后,又去拿yyy.js, 再拿1.jpg, 再拿2.jpg。第二个1.jpg不会拿了,因为一般的客户端都有缓存图片的能力。客户端会把1.jpg缓存到本地,第二次需要的时候,就不访问服务器了,直接从缓存中拿。
我们刚才获取资源的地址叫做客户端地址。客户端地址都需要把web应用的名称写上。
四、EL执行表达式
例如:
${1+1}
${empty user}
${user==null?true:false}
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-16"
pageEncoding="UTF-16"%>
<%@ page import="com.ken.domain.User"%>
<%@ page import="java.util.*"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-16">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 模拟域中的数据 -->
<%
//存储字符串
request.setAttribute("company", "百度");
//存储一个对象
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("zhangsan");
user.setPassword("123");
session.setAttribute("user", user);
//存储一个集合
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>();
User user1 = new User();
user1.setId(1);
user1.setName("zhangsan");
user1.setPassword("123");
list.add(user1);
User user2 = new User();
user2.setId(1);
user2.setName("zhangsan");
user2.setPassword("123");
list.add(user2);
application.setAttribute("list", list);
%>
<!-- 脚本取出域中的值 -->
<%=request.getAttribute("company")%>
<%
User sessionUser = (User) session.getAttribute("user");
out.write(sessionUser.getName());
%>
<!-- 使用EL表达式获得域中的值 -->
${requestScope.company } ${sessionScope.user.name }
${applicationScope.list[1].name }
<!-- 使用EL表达式 全域查找 -->
${company } ${user.name } ${list[1].name }
<!-- el可以执行表达式运算 -->
${1+1 }
${1==1?true:false }
</body>
</html>







 本文详细介绍了EL表达式的功能和用途,包括如何从不同域中获取数据、内置对象的应用及执行表达式运算等内容。
本文详细介绍了EL表达式的功能和用途,包括如何从不同域中获取数据、内置对象的应用及执行表达式运算等内容。
















 966
966

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








