本程序实现彩色立方体的绘制。主要包括立方体顶点位置、顶点颜色的定义,着色语言的编写,以及深度缓冲的应用等。
参考视频:【2.4.2 VS-OpenGL之彩色立方体2】 https://b23.tv/VCx93GB
【2.4.1 VS-OpenGL 彩色立方体】 https://b23.tv/jQX6KKU
参考网站Tutorial 4 : A Colored Cube (opengl-tutorial.org)
主程序.cpp:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <GL/glew.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtx/transform.hpp>
#include <common/shader.hpp>
using namespace glm;
// A cube has 6 faces with 2 triangles each, so this makes 6*2=12 triangles, and 12*3 vertices
static const GLfloat g_vertex_buffer_data[] = {
-1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f, // triangle 1 : begin
-1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // triangle 1 : end
1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f, // triangle 2 : begin
-1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f, // triangle 2 : end
1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f
};
// One color for each vertex.They were generated randomly.
static const GLfloat g_color_buffer_data[] = {
0.583f, 0.771f, 0.014f,
0.609f, 0.115f, 0.436f,
0.327f, 0.483f, 0.844f,
0.822f, 0.569f, 0.201f,
0.435f, 0.602f, 0.223f,
0.310f, 0.747f, 0.185f,
0.597f, 0.770f, 0.761f,
0.559f, 0.436f, 0.730f,
0.359f, 0.583f, 0.152f,
0.483f, 0.596f, 0.789f,
0.559f, 0.861f, 0.639f,
0.195f, 0.548f, 0.859f,
0.014f, 0.184f, 0.576f,
0.771f, 0.328f, 0.970f,
0.406f, 0.615f, 0.116f,
0.676f, 0.977f, 0.133f,
0.971f, 0.572f, 0.833f,
0.140f, 0.616f, 0.489f,
0.997f, 0.513f, 0.064f,
0.945f, 0.719f, 0.592f,
0.543f, 0.021f, 0.978f,
0.279f, 0.317f, 0.505f,
0.167f, 0.620f, 0.077f,
0.347f, 0.857f, 0.137f,
0.055f, 0.953f, 0.042f,
0.714f, 0.505f, 0.345f,
0.783f, 0.290f, 0.734f,
0.722f, 0.645f, 0.174f,
0.302f, 0.455f, 0.848f,
0.225f, 0.587f, 0.040f,
0.517f, 0.713f, 0.338f,
0.053f, 0.959f, 0.120f,
0.393f, 0.621f, 0.362f,
0.673f, 0.211f, 0.457f,
0.820f, 0.883f, 0.371f,
0.982f, 0.099f, 0.879f
};
int main() {
// Initialise GLFW
glewExperimental = true; // Needed for core profile
if (!glfwInit())
{
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize GLFW\n");
return -1;
}
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_SAMPLES, 4); // 4x antialiasing
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3); // We want OpenGL 3.3
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE); // To make MacOS happy; should not be needed
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
// Open a window and create its OpenGL context
GLFWwindow* window; // (In the accompanying source code, this variable is global for simplicity)
window = glfwCreateWindow(1024, 768, "Tutorial 01", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open GLFW window. If you have an Intel GPU, they are not 3.3 compatible. Try the 2.1 version of the tutorials.\n");
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window); // Initialize GLEW
glewExperimental = true; // Needed in core profile
if (glewInit() != GLEW_OK) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize GLEW\n");
return -1;
}
// Projection matrix : 45° Field of View, 4:3 ratio, display range : 0.1 unit <-> 100 units
glm::mat4 Projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(45.0f), (float)4 / (float)3, 0.1f, 100.0f);
// Or, for an ortho camera :
//glm::mat4 Projection = glm::ortho(-10.0f,10.0f,-10.0f,10.0f,0.0f,100.0f); // In world coordinates
// Camera matrix
glm::mat4 View = glm::lookAt(
glm::vec3(4, 3, -3), // Camera is at (4,3,-3), in World Space
glm::vec3(0, 0, 0), // and looks at the origin
glm::vec3(0, 1, 0) // Head is up (set to 0,-1,0 to look upside-down)
);
// Model matrix : an identity matrix (model will be at the origin)
glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
// Our ModelViewProjection : multiplication of our 3 matrices
glm::mat4 mvp = Projection * View * Model; // Remember, matrix multiplication is the other way around
GLuint VertexArrayID;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID);
glBindVertexArray(VertexArrayID);
// This will identify our vertex buffer
GLuint vertexbuffer;
glGenBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer);// Generate 1 buffer, put the resulting identifier in vertexbuffer
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer); // The following commands will talk about our 'vertexbuffer' buffer
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(g_vertex_buffer_data), g_vertex_buffer_data, GL_STATIC_DRAW); // Give our vertices to OpenGL.
GLuint colorbuffer;
glGenBuffers(1, &colorbuffer);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, colorbuffer);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(g_color_buffer_data), g_color_buffer_data, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// Create and compile our GLSL program from the shaders
GLuint programID = LoadShaders("SimpleVertexShader.vertexshader", "SimpleFragmentShader.fragmentshader");
GLuint MatrixID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "MVP");
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_STICKY_KEYS, GL_TRUE);
do {
// Clear the screen. It's not mentioned before Tutorial 02, but it can cause flickering, so it's there nonetheless.
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);// Enable depth test
glDepthFunc(GL_LESS);// Accept fragment if it closer to the camera than the former one
glUseProgram(programID);// Use our shader
// 1st attribute buffer : vertices
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer);
glVertexAttribPointer(
0, // attribute 0. No particular reason for 0, but must match the layout in the shader.
3, // size
GL_FLOAT, // type
GL_FALSE, // normalized?
0, // stride
(void*)0 // array buffer offset
);
// 2nd attribute buffer : colors
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, colorbuffer);
glVertexAttribPointer(
1, // attribute. No particular reason for 1, but must match the layout in the shader.
3, // size
GL_FLOAT, // type
GL_FALSE, // normalized?
0, // stride
(void*)0 // array buffer offset
);
glUniformMatrix4fv(MatrixID, 1, GL_FALSE, &mvp[0][0]);// Send our transformation to the currently bound shader, in the "MVP" uniform
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 3*12); // Starting from vertex 0; 3 vertices total -> 1 triangle
glDisableVertexAttribArray(0);
glDisableVertexAttribArray(1);
glfwSwapBuffers(window);// Swap buffers
glfwPollEvents();
} // Check if the ESC key was pressed or the window was closed
while (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) != GLFW_PRESS &&
glfwWindowShouldClose(window) == 0);
}
顶点着色器SimpleVertexShader.vertexshader 文件中GLSL代码为:
#version 330 core
layout(location = 0) in vec3 vertexPosition_modelspace;
layout(location = 1) in vec3 vertexColor;
uniform mat4 MVP;
out vec3 fragmentColor;
void main(){
gl_Position = MVP * vec4(vertexPosition_modelspace,1);
fragmentColor = vertexColor;
}片段着色器SimpleFragmentShader.fragmentshader 文件中代码:
#version 330 core
in vec3 fragmentColor;
out vec3 Color;
void main(){
Color=fragmentColor;
}
shader.hpp 文件中的代码同博客<1.2.2 Visual Studio OpenGL着色器语言文件读取>,链接为:Visual Studio OpenGL着色器语言文件读取-CSDN博客
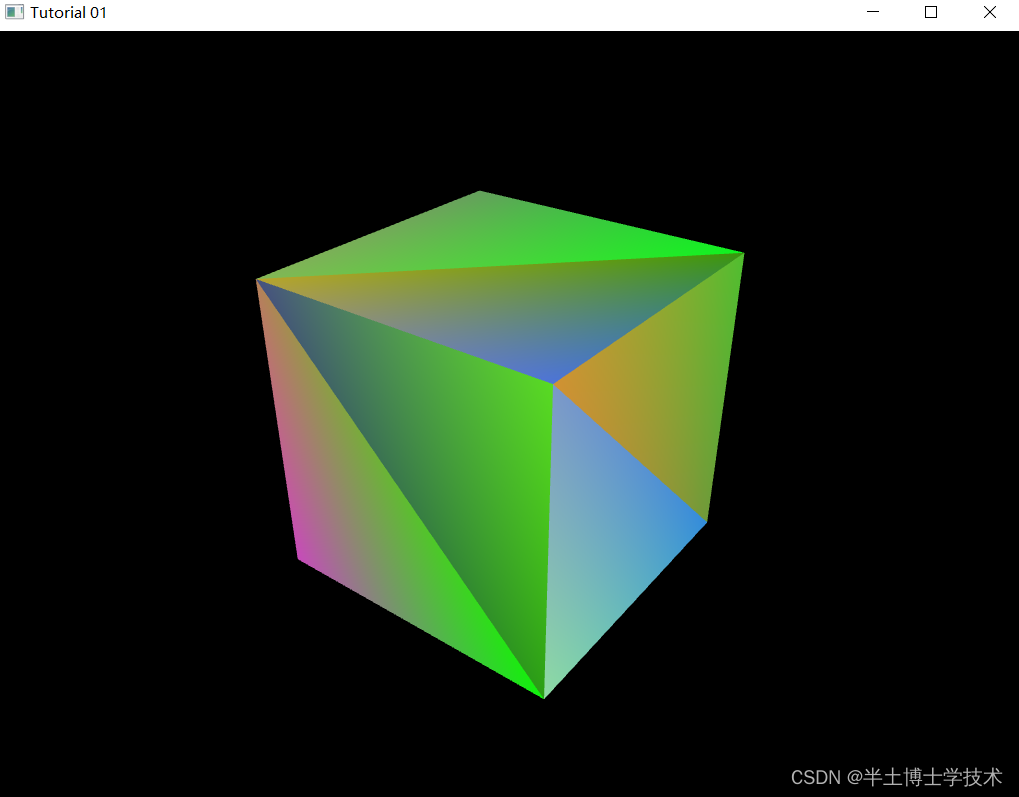
运行结果:






















 853
853











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










