k dimension tree,一种高维几何搜索的数据结构,一维对应二叉搜索树,适用于多个搜索特征的数据类型。
1.2d树类实现
2d-树的构造核心思想:
每次选取一个维度进行划分
点深度为偶(奇)时,则沿垂直(水平)方向切分
如何保证每次划分尽量居中?
每次切分都在中位点(对应坐标居中点),保证全树不高于O(logn)
代码实现:
先做一个Point类,2D Tree的节点继承Point:
class Point//点类
{
public:
//使用初始化表初始化点类
Point(double a = 0, double b = 0 ,char na='a'):x(a), y(b),name(na){}
Point(const Point &p); //复制构造函数
const double getX();//得到x坐标
const double getY();//得到y坐标
const char getName();//得到name
void setX(double sx);//更改x坐标
void setY(double sy);//更改y坐标
void setName(char sc);//更改y坐标
// bool isSmaller(int dimension,Point &p);
// bool isEqual(Point &p);
// bool isBigger(int dimension,Point &p);
//重载运算符
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream &output, Point &p);
bool operator >(Point &p);
bool operator <(Point &p);
bool operator ==(Point &p);
int P_dimension=0;
protected:
double x;//x坐标
double y;//y坐标
char name;
};
Point::Point(const Point &p){
x=p.x;
y=p.y;
name=p.name;
}
//得到x的值
const double Point::getX(){ return x;}
//得到y的值
const double Point::getY(){ return y;}
//得到name
const char Point::getName(){ return name;}
//更改x的值
void Point::setX(double sx){ x=sx; }
//更改y的值
void Point::setY(double sy){ y=sy; }
//更改name
void Point::setName(char sc){ name=sc; }
//重载运算符
ostream& operator<<(ostream &output, Point &p)
{
output<<"("<<p.x<<","<<p.y<<")"<<endl;
return output;
}
bool Point::operator >(Point &p){
if (P_dimension>=2) return 0;
double coor1[2]={x,y} ;
double coor2[2]={p.getX(),p.getY()} ;
if(coor1[P_dimension]>coor2[P_dimension]) return 1;
else return 0;
}
bool Point::operator <(Point &p){
if (P_dimension>=2) return 0;
double coor1[2]={x,y} ;
double coor2[2]={p.getX(),p.getY()} ;
if(coor1[P_dimension]<coor2[P_dimension]) return 1;
else return 0;
}
bool Point::operator ==(Point &p){
double px=p.getX();
double py=p.getY();
if((x==px)&&(y==py)) return 1;
else return 0;
}
// //根据维度demension比较大小
// bool Point::isSmaller(int dimension,Point &p){
// if (dimension>=2) return 0;
// double coor1[2]={x,y} ;
// double px=p.getX();
// double py=p.getY();
// double coor2[2]={px,py} ;
// if(coor1[dimension]<coor2[dimension]) return 1;
// else return 0;
// }
// bool Point::isEqual(Point &p){
// double px=p.getX();
// double py=p.getY();
// if((x==px)&&(y==py)) return 1;
// else return 0;
// }
// bool Point::isBigger(int dimension,Point &p){
// if (dimension>=2) return 0;
// double coor1[2]={x,y} ;
// double px=p.getX();
// double py=p.getY();
// double coor2[2]={px,py} ;
// if(coor1[dimension]>coor2[dimension]) return 1;
// else return 0;
// }
struct Coordinate{
double m_coor[2]; // 点的坐标
};
struct TreeNode{
Point p;
int m_dimesion;
// 0为x方向划分,1为y方向划分
TreeNode(const Point &p1): p(p1){}
TreeNode* m_pLeftChild; // 左孩子
TreeNode* m_pRightChild; // 右孩子
};
struct RecArea{
// 存放矩形区域左下和右上坐标
Coordinate m_minCoor;
Coordinate m_maxCoor;
};
class KdTree {
private:
int count;
public:
TreeNode* m_pRoot;
KdTree() : m_pRoot(nullptr),count(0){}; //无参构造函数
//KdTree(TreeNode*& rhs) : m_pRoot(rhs),count(0){}; //复制构造函数
bool Empty(); // 判断二叉树是否为空
//void Traverse(int key,void (*visit)(T));//用于遍历二叉树
TreeNode* buildTree(std::vector<Point>&pList, int d);
};//BinartTree 二叉树类
Point findMedialPoint(int dimension, vector<Point>&pList){
int len=pList.size();
//for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) pList[i].P_dimension=dimension;
sort(pList.begin(),pList.end()); // algorithm.h 中的向量排序算法
Point mp=pList[len/2];
cout<<"mp:"<<mp<<endl;
return mp;
}
TreeNode* KdTree::buildTree(std::vector<Point>&pList, int d)
{ // 在深度为d的层次,构造一棵对应于(子)集合pointList(pL)的(子)2d-树
if (pList.empty()) return NULL;
int dimension = d % 2;
for (int i = 0; i < pList.size(); i++) pList[i].P_dimension=dimension; // 确定划分方向
Point medianP = findMedialPoint(dimension, pList);
// 确定中位点
std::vector<Point> pListLeft, pListRight; // 左右子树的点集
for (int i = 0; i < pList.size(); i++)
{
if (medianP>pList[i]) //点pList[i]的dimension轴坐标小于中位点
pListLeft.push_back(pList[i]); // 归入左子树
else if (medianP< pList[i]) // 轴坐标大于中位点
pListRight.push_back(pList[i]); // 归入右子树
else if (!( medianP==pList[i])) // 多个点落在中位线的情况
pListRight.push_back(pList[i]); // 除了中位点外其它归入右子树
}
TreeNode* pTreeNode = new TreeNode(medianP); //创建子树根,复制节点数据为mediaP
pTreeNode->m_pLeftChild = buildTree(pListLeft, d + 1); // 深度d+1构建左子树
pTreeNode->m_pRightChild = buildTree(pListRight, d + 1); // 深度d+1构建右子树
pTreeNode->m_dimesion = dimension; // 设置节点的分割轴方向
return pTreeNode;
}构建树思路:
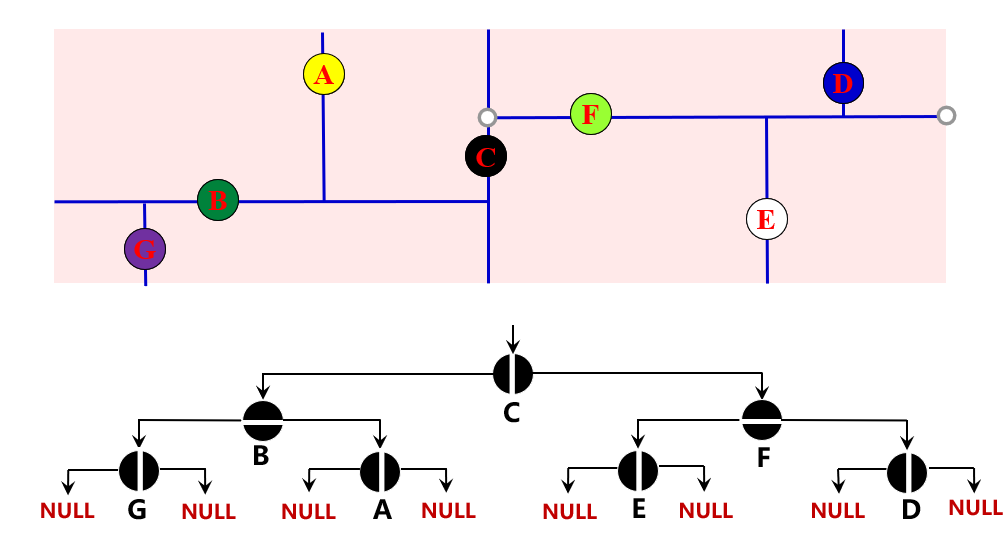
如上图所示的7个点构建二维搜索树,维度定义:dimension 1--x, 0--y;
首先 dimension=1,把七个点按x周排序,找到x轴坐标中点“C”,作为根节点,然后比Cx小的入左子树,比Cx大的入右子树。然后再递归生成子树,次数深度+1,维度改变。
以左子树为例,输入点向量(G B A ),此时dimension=0, 按y坐标排序,为: G-B-A,中位点为B,则G入B左子树,A入右子树,再递归就完成了二维搜索树的构造。
测试:
int main( )
{
int pointnum,quirynum;
cin>>pointnum>>quirynum;
vector<Point > pList;
Point parray[pointnum];
double m_x,m_y;
char m_name;
for(int i=0;i<pointnum;i++){
cin>>m_x>>m_y;
cin>> m_name;
parray[i]=Point(m_x,m_y,m_name);
pList.push_back(parray[i]);
}
//vector<Point> pList(parray,parray+pointnum);
cout<<pList.size()<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<pointnum;i++){
cout<<pList[i]<<endl;
}
KdTree m_2dtree;
m_2dtree.m_pRoot=m_2dtree.buildTree( pList, 1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
输入输出:

首先输入测试点个数,然后输出生成的点向量
在构建2D树时,每生成一个节点,输入节点Point
根节点b,左子树a,右子树c,和预期的相符。
























 3096
3096

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








