Java,Spring,SpringBoot和Axon示例
介绍
这个术语第一次出现在1997年的软件工程词典中。它出现在Bertrand Meyer的“ 面向对象的软件构造 ”一书中。 该软件体系结构旨在缓解已知的面向对象体系结构的警告。
在这种情况下,这些警告尤其是:
- 写入和读取几乎始终会给系统带来非常不同的负载。
- 写操作通常比读操作复杂得多。 此外,它们影响应用程序的不同范围 。 写操作需要确保正确,有效和一致的数据正确到达存储。
- 写入和读取操作之间的安全问题也有所不同。
- 数据通常存储在数据库中的方式是使用3NF或经过优化且与其接近的某种方式。 当我们读取数据时,我们通常会建立视图以向用户提供可读数据。 因此,几乎不会对呈现给用户的数据进行规范化。 这也称为非规范化数据 。
通过这个非常简单的列表,您可以看到读写操作以不同的方式进行,它们有不同的关注点,它们产生了不同的性能关注点,并且它们产生了不同的负载,这些负载可能以非常不同的方式给系统带来很大压力。
CQRS也是DDD(域驱动设计)的一种形式。 最初并不认为它是实际的DDD。 但是,通过开发,它总是迫使建筑师首先考虑设计。 每个应用程序都有至少一个有界上下文。 受限制的上下文很难定义,但是从本质上讲,它们隔离了应用程序的职责,例如,借记卡的处理,图书馆图书存档器,患者数据。
例如,后者可以分为多个子域。 可能存在一个单独的域来跟踪像HIV这样的慢性疾病,而另一个域则可以跟踪普通流感。 两者都有不同的数据问题。 作为慢性疾病,HIV患者一生中将需要跟踪更多数据,例如T细胞计数,病毒载量和其他血液数据。
流感患者不需要太多监控。 与第一个域相关的隐私问题比第二个域更多。 评估领域有点技巧,需要工程师的分析能力才能确定它们。
一旦定义了域,就可以开始为其设计CQRS了。 就像您已经看到的那样,此设计的主要关注点是读取操作和写入操作的分离。 写操作不能是读操作。 同样,“读取”操作也不能是“写入”操作。
指令
命令定义为可以在不返回值的情况下对数据进行突变的任何操作。 本质上,这些都是写操作。 用CRUD术语来说,它们是创建,更新和删除操作。 您也可以将它们称为CUD 。
查询
查询被定义为永不突变数据且始终返回的任何操作。 最后,这些基本上都是读取操作。 查询操作仅是读取操作。 它们只是CRUD术语中的R。
楷模
有许多实现CQRS的方法 。 重点始终是尽可能使读取操作与写入操作分开。 在我们的实现中,我们还将分离操作并使用事件源 。 这将使我们能够进一步分离保存数据的媒介。 我们将使用两个不同的数据库。 一个数据库将成为命令流的一部分,而另一个数据库将成为读取流的一部分。
实作
首先让我们看一下所有运动部件如何工作:
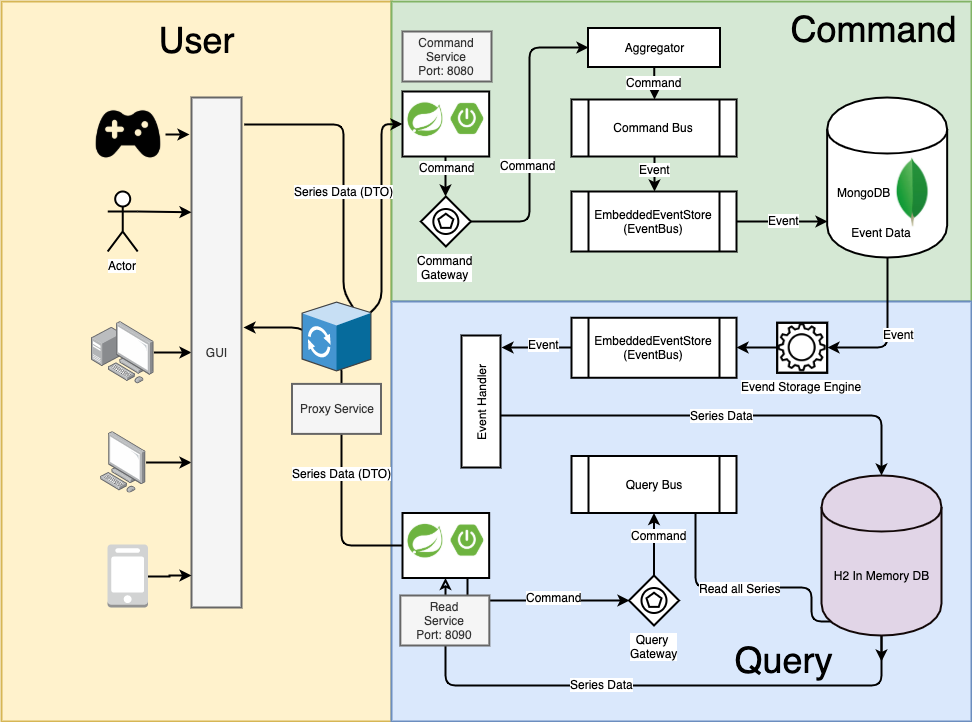
在此示例中,我将尝试使其尽可能简单。 那里还有更多详细的选择。 有更多复杂,动态和可扩展的选项。 这些选项之一是使用RabbitMQ或任何其他类型的消息排队系统来进一步分离所有组件。
但是,这将注意力转移到本教程的范围之外。 这里的重点是提出一个以CQRS的所有基本点为核心的解决方案。
这是我们需要的所有依赖项:
< project xmlns = "http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" >
< modelVersion > 4.0.0 </ modelVersion >
< groupId > org.jesperancinha.video </ groupId >
< artifactId > video-series-app </ artifactId >
< version > 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT </ version >
< parent >
< groupId > org.springframework.boot </ groupId >
< artifactId > spring-boot-starter-parent </ artifactId >
< version > 2.2.2.RELEASE </ version >
< relativePath />
</ parent >
< modules >
< module > video-series-command </ module >
< module > video-series-query </ module >
< module > video-series-core </ module >
</ modules >
< packaging > pom </ packaging >
< properties >
< java.version > 13 </ java.version >
< h2.version > 1.4.200 </ h2.version >
< lombok.version > 1.18.10 </ lombok.version >
< spring-tx.version > 5.2.2.RELEASE </ spring-tx.version >
< axon.version > 4.2 </ axon.version >
</ properties >
< dependencyManagement >
< dependencies >
<!-- Inner dependencies -->
< dependency >
< groupId > org.jesperancinha.video </ groupId >
< artifactId > video-series-core </ artifactId >
< version > ${project.version} </ version >
</ dependency >
<!-- External Dependencies -->
< dependency >
< groupId > com.h2database </ groupId >
< artifactId > h2 </ artifactId >
< version > ${h2.version} </ version >
< scope > runtime </ scope >
</ dependency >
< dependency >
< groupId > org.springframework </ groupId >
< artifactId > spring-tx </ artifactId >
< version > ${spring-tx.version} </ version >
</ dependency >
< dependency >
< groupId > org.axonframework </ groupId >
< artifactId > axon-spring-boot-starter </ artifactId >
< version > ${axon.version} </ version >
< exclusions >
< exclusion >
< groupId > org.axonframework </ groupId >
< artifactId > axon-server-connector </ artifactId >
</ exclusion >
</ exclusions >
</ dependency >
< dependency >
< groupId > org.axonframework </ groupId >
< artifactId > axon-mongo </ artifactId >
< version > ${axon-mongo.version} </ version >
</ dependency >
< dependency >
< groupId > org.projectlombok </ groupId >
< artifactId > lombok </ artifactId >
< version > ${lombok.version} </ version >
< optional > true </ optional >
</ dependency >
</ dependencies >
</ dependencyManagement >
</ project >请注意,我正在使用轴突框架。 这是在最流行的框架上实施的一些与CQRS设计非常匹配的东西。 即,我们将首先了解EventHandlers和Aggregator的工作方式, EventBus的工作方式以及CommandBus的工作方式。 我们还将查看它如何与MongoDB配合使用 ,以最终用新数据更新数据库。
核心
在本模块中,我将考虑该应用程序共有的所有内容。 我也可以将此模块命名为common。 为了运行我们的应用程序,我们将需要考虑一些重要的事情。 考虑到它的复杂性,我将只实现一次读取所有操作和一个保存操作。 这些分别是我的查询和命令。
我们需要一个DTO才能将数据输入我们的系统:
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class VideoSeriesDto {
private String name;
private Integer volumes;
private BigDecimal cashValue;
private String genre;
}通过编写器发送数据是需要读者以及编写器都理解的操作。 我们唯一的常用命令应该位于此处:
@Data
@Builder
public class AddSeriesEvent {
private String id;
private String name;
private Integer volumes;
private BigDecimal cashValue;
private String genre;
} 最后,从所看到的模式中我们知道,“写入服务”和“读取服务”都需要访问EventStore 。 本质上,这就是我们的mongoDB数据库。 Axon具有非常好的现成的库,使我们能够轻松地实现此事件源机制。 这就是我选择此功能的部分原因。 它使实现的形式非常简单:
@Slf 4j
@Configuration
public class AxonConfig {
@Value ( "${spring.data.mongodb.host:127.0.0.1}" )
private String mongoHost;
@Value ( "${spring.data.mongodb.port:27017}" )
private int mongoPort;
@Value ( "${spring.data.mongodb.database:test}" )
private String mongoDatabase;
@Bean
public TokenStore tokenStore (Serializer serializer) {
return MongoTokenStore.builder().mongoTemplate(axonMongoTemplate()).serializer(serializer).build();
}
@Bean
public EventStorageEngine eventStorageEngine (MongoClient client) {
return MongoEventStorageEngine.builder().mongoTemplate(DefaultMongoTemplate.builder().mongoDatabase(client).build()).build();
}
@Bean
public MongoTemplate axonMongoTemplate () {
return DefaultMongoTemplate.builder().mongoDatabase(mongo(), mongoDatabase).build();
}
@Bean
public MongoClient mongo () {
MongoFactory mongoFactory = new MongoFactory();
mongoFactory.setMongoAddresses(Collections.singletonList( new ServerAddress(mongoHost, mongoPort)));
return mongoFactory.createMongo();
}
} 命令服务
首先,我们需要实现命令的表示形式。 就我们的命令服务而言,我们只有一条命令可以添加更多视频系列。 因此,我们的命令具有与实际系列相同的属性。 注意id字段:
@Data
@Builder
@EqualsAndHashCode
@ToString
public class AddVideoSeriesCommand {
@TargetAggregateIdentifier
private String id;
private String name;
private Integer volumes;
private BigDecimal cashValue;
private String genre;
} id字段确实是String 。 这实际上是我们的操作ID 。 它可以通过多种方式实现。 我们只需要确保它始终是唯一的字符串,数字或我们选择的任何内容即可。
现在是时候实现聚合器了,它将通过命令总线发送我们的命令并使它到达我们的命令处理程序:
@Slf 4j
@NoArgsConstructor
@Aggregate
@Data
public class VideoSeriesAggregate {
@AggregateIdentifier
private String id;
@CommandHandler
public VideoSeriesAggregate (AddVideoSeriesCommand command) {
apply(AddSeriesEvent.builder()
.id(UUID.randomUUID().toString())
.cashValue(command.getCashValue())
.genre(command.getGenre())
.name(command.getName())
.volumes(command.getVolumes()).build()
);
}
@EventSourcingHandler
public void on (AddSeriesEvent event) {
this .id = event.getId();
}
} 注意EventSourcingHandler 。 它似乎并没有做很多事情,但是请记住,在此代码部分中,您正在查看Aggregate元素的内容。 如果您查看mongo数据库,将会发现以下内容:
{
"_id" : ObjectId( "5df8ac587a0bba4960afce68" ),
"aggregateIdentifier" : "ed313d16-8d94-480a-85a0-b6897bcca4f5" ,
"type" : "SeriesAggregate" ,
"sequenceNumber" : NumberLong( 0 ),
"serializedPayload" : "<org.jesperancinha.video.core.events.AddSeriesEvent><id>ed313d16-8d94-480a-85a0-b6897bcca4f5</id><name>wosssda</name><volumes>10</volumes><cashValue>123.2</cashValue><genre>woo</genre></org.jesperancinha.video.core.events.AddSeriesEvent>" ,
"timestamp" : "2019-12-17T10:22:16.640261Z" ,
"payloadType" : "org.jesperancinha.video.core.events.AddSeriesEvent" ,
"payloadRevision" : null ,
"serializedMetaData" : "<meta-data><entry><string>traceId</string><string>398a250f-8086-40e7-a767-1aa793231f62</string></entry><entry><string>correlationId</string><string>398a250f-8086-40e7-a767-1aa793231f62</string></entry></meta-data>" ,
"eventIdentifier" : "2ac1a49f-0124-4f6e-b13f-140c8f36979a"
} 注意aggregateIndentifier。 那是你的身份证。 您需要EventSourcingHandler才能完成请求,并将您的事件源到EventStore。
现在,我们只需要通过实现Controller来完成我们的应用程序:
@RestController
@RequestMapping ( "/video-series" )
public class VideoSeriesController {
private final CommandGateway commandGateway;
public VideoSeriesController (CommandGateway commandGateway) {
this .commandGateway = commandGateway;
}
@PostMapping
public void postNewVideoSeries (@RequestBody VideoSeriesDto videoSeriesDto) {
commandGateway.send(
AddVideoSeriesCommand.builder()
.name(videoSeriesDto.getName())
.volumes(videoSeriesDto.getVolumes())
.genre(videoSeriesDto.getGenre())
.cashValue(videoSeriesDto.getCashValue())
.build());
}
}注意,我们正在注入CommandGateway 。 这正是允许我们将命令发送到系统中的网关。
最后, Spring Boot Launcher :
@SpringBootApplication
@Import (AxonConfig.class)
public class VideoAppCommandLauncher {
public static void main (String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(VideoAppCommandLauncher.class);
}
} 为了完成我们的应用程序,我们仍然需要配置我们的Spring Boot Launcher :
# spring
server.port = 8080
# h2
spring.h2.console.path = /spring-h2-video-series-command-console
spring.h2.console.enabled = true
# datasource
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:h2:file:~/spring-datasource-video-series-command-url;auto_server=true
spring.datasource.driver-class-name = org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username = sa
spring.datasource.password = sa
# hibernate
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
spring.jpa.show-sql = true
# mongodb
spring.data.mongodb.host = localhost
spring.data.mongodb.port = 27017
spring.data.mongodb.database = cqrs
查询服务
查询服务本质上是EventStore的读取器,并且将在无需用户干预的情况下对其进行操作。 查询服务需要执行查询。 通过这种方式,我实现了一个命令来做到这一点:
public class FindAllVideoSeriesCommand {
} 请注意,该命令最终只是一个空类。 那是故意的。 我们不需要参数来通过读取所有操作,但是我们确实需要其表示形式。
因为我们正在访问数据库并存储记录,所以我们现在需要实现负责此数据的实体 :
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
@Entity
@Table (name = "VIDEO_SERIES" )
public class VideoSeries {
@Id
@GeneratedValue (strategy = IDENTITY)
@Column
private Long id;
@Column
private String name;
@Column
private Integer volumes;
@Column
private BigDecimal cashValue;
@Column
private String genre;
} 您可能已经猜到了,在此实现中,我们将使用JPA存储库 :
public interface VideoSeriesRepository extends JpaRepository < VideoSeries , Long > {
} 在查询方面,我们有EventHandlers ,其形状与Aggregate非常相似。 当然不同之处在于,一旦获得事件或命令,它们将立即处理:
@Service
@ProcessingGroup ( "video-series" )
public class VideoSeriesEventHandler {
private final VideoSeriesRepository videoSeriesRepository;
public VideoSeriesEventHandler (VideoSeriesRepository videoSeriesRepository) {
this .videoSeriesRepository = videoSeriesRepository;
}
@EventHandler
public void on (AddSeriesEvent event) {
videoSeriesRepository.save(VideoSeries
.builder()
.name(event.getName())
.volumes(event.getVolumes())
.genre(event.getGenre())
.cashValue(event.getCashValue())
.build());
}
@QueryHandler
public List<VideoSeriesDto> handle (FindAllVideoSeriesCommand query) {
return videoSeriesRepository.findAll().stream().map(
videoSeries -> VideoSeriesDto.builder()
.name(videoSeries.getName())
.volumes(videoSeries.getVolumes())
.cashValue(videoSeries.getCashValue())
.genre(videoSeries.getGenre())
.build()).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
} 请注意,而不是CommandHandler,我们现在有QueryHandler。 在EventSourcingHandler中,我们现在有了EventHandler。 有注释用于分别区分comand服务和查询服务中发生的情况。 另外,ID不存在。 该ID并不重要,因为没有数据将进入事件存储。 所有数据都直接由JPA存储库处理。
现在WECAN我们的注意力集中在控制器的查询服务控制器:
@RestController
@RequestMapping ( "/video-series" )
public class VideoSeriesController {
@Autowired
private QueryGateway queryGateway;
@GetMapping
public List<VideoSeriesDto> gertAllVideoSeries () {
return queryGateway.query( new FindAllVideoSeriesCommand(), ResponseTypes.multipleInstancesOf(VideoSeriesDto.class))
.join();
}
} 最后是我们的查询启动器:
@SpringBootApplication
@Import (AxonConfig.class)
public class VideoAppQueryLauncher {
public static void main (String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(VideoAppQueryLauncher.class);
}
} 要完成我们的应用程序,我们需要对其进行配置:
# spring
server.port = 8090
# h2
spring.h2.console.path = /spring-h2-video-series-query-console
spring.h2.console.enabled = true
# datasource
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:h2:file:~/spring-datasource-video-series-query-url;auto_server=true
spring.datasource.driver-class-name = org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username = sa
spring.datasource.password = sa
# hibernate
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = none
spring.jpa.show-sql = true
# mongodb
spring.data.mongodb.host = localhost
spring.data.mongodb.port = 27017
spring.data.mongodb.database = cqrs 给它一些结构:
drop table if exists VIDEO_SERIES;
create table VIDEO_SERIES
(
ID bigint auto_increment primary key not null ,
NAME varchar ( 100 ) not null ,
VOLUMES int not null ,
CASH_VALUE decimal not null ,
GENRE varchar ( 100 ) not null
); 最后是一些数据:
insert into VIDEO_SERIES ( NAME , VOLUMES, CASH_VALUE, GENRE) values ( 'Modern Family' , 12 , 12.3 , 'SITCOM' );
insert into VIDEO_SERIES ( NAME , VOLUMES, CASH_VALUE, GENRE) values ( 'Six Feet Under' , 10 , 34.3 , 'DRAMA' );
insert into VIDEO_SERIES ( NAME , VOLUMES, CASH_VALUE, GENRE) values ( 'Queer as Folk' , 24 , 55.3 , 'DRAMA' );
我们终于准备好进行一些测试。 我所做的测试非常简单。 首先,我执行了一个请求以查看所有当前数据:
$ curl localhost:8090/video-series
[{ "name" : "Modern Family" , "volumes" :12, "cashValue" :12.3, "genre" : "SITCOM" },{ "name" : "Six Feet Under" , "volumes" :10, "cashValue" :34.3, "genre" : "DRAMA" },{ "name" : "Queer as Folk" , "volumes" :24, "cashValue" :55.3, "genre" : "DRAMA" }]如您所见,我们得到三个系列。 让我们添加一个新的:
$ curl localhost:8090/video-series
[{ "name" : "Modern Family" , "volumes" :12, "cashValue" :12.3, "genre" : "SITCOM" },{ "name" : "Six Feet Under" , "volumes" :10, "cashValue" :34.3, "genre" : "DRAMA" },{ "name" : "Queer as Folk" , "volumes" :24, "cashValue" :55.3, "genre" : "DRAMA" }]您现在应该看到:
$ curl localhost:8090/video-series
[{ "name" : "Modern Family" , "volumes" :12, "cashValue" :12.3, "genre" : "SITCOM" },{ "name" : "Six Feet Under" , "volumes" :10, "cashValue" :34.3, "genre" : "DRAMA" },{ "name" : "Queer as Folk" , "volumes" :24, "cashValue" :55.3, "genre" : "DRAMA" },{ "name" : "True Blood" , "volumes" :30, "cashValue" :1323.2, "genre" : "Bloody" }请注意,尽管我们可以看到这可行,但了解此应用程序幕后发生的事情非常重要。 “写”和“读”操作之间的分隔以及它们分别被命名为命令和查询操作的事实是构成此体系结构的基础。 体系结构设计的解耦越好,它就越好。
在DDD和CQRS领域中有成千上万的极端案例和特殊情况。 事件源只是实现此目的的方法之一。 在我们的示例中,我们使用Spring,SpringBoot和Axon在网络上获取命令和事件。
我们没有使用任何消息队列系统。 我确实打算为此写另一篇文章,但这将在以后发表。 我暂时希望您喜欢这个非常简单的示例的教程。
如果您有任何疑问或想让我知道您对此的意见,请在下面发表评论或直接通过jofisaes@gmail.com与我联系。
我已将完整的实现放在GitLab上 。
感谢您的阅读
From: https://hackernoon.com/cqrs-command-query-responsibility-segregation-8vb32x3





















 1045
1045

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








