深度学习的高级NLP技术

随着深度学习解决了图像分类问题, 文本分类是深度学习的下一个新兴主题 。 对于那些不知道的人,文本分类是自然语言处理中的常见任务,它将不定长度的文本序列转换为文本类别。 你怎么用呢?
- 寻找评论的情绪。
- 在Facebook等平台上查找有毒评论
- 在Quora上查找Insincere问题。 目前正在进行的Kaggle比赛
- 在网站上找到虚假评论
- 文字广告是否会被点击
以及更多。 整个互联网充满了文本,并且按算法对信息进行分类只会给我们带来更多的好处,至少在AI领域是如此。
在这里,我将使用Quora的Insincere问题中的数据来讨论人们正在构建和共享以执行此任务的不同模型。 显然,这些独立的模型不会使您成为排行榜的佼佼者,但是我希望接下来的讨论对希望了解更多有关文本分类的人们有所帮助。 在这方面,这将是很长的篇幅。
附带说明:如果您想了解有关NLP的更多信息,我想向您推荐这本有关高级 语言 学习专业课程中很棒的自然语言处理课程。 这门课程涵盖了自然语言处理中从基础到高级的一系列任务:情感分析,摘要,对话状态跟踪等。
因此,让我尝试研究人们用来进行文本分类的一些模型,并为他们提供一个简短的直觉。
1. TextCNN:
Yoon Kim在论文《 卷积神经网络的句子分类》中首次提出了使用CNN进行文本分类的想法。 代替图像像素,任务的输入是表示为矩阵的句子或文档。 矩阵的每一行对应一个单词向量。 也就是说,每一行都是代表一个单词的单词向量。 因此,最大长度为70的序列给出的图像为70(最大序列长度)x300(嵌入尺寸)
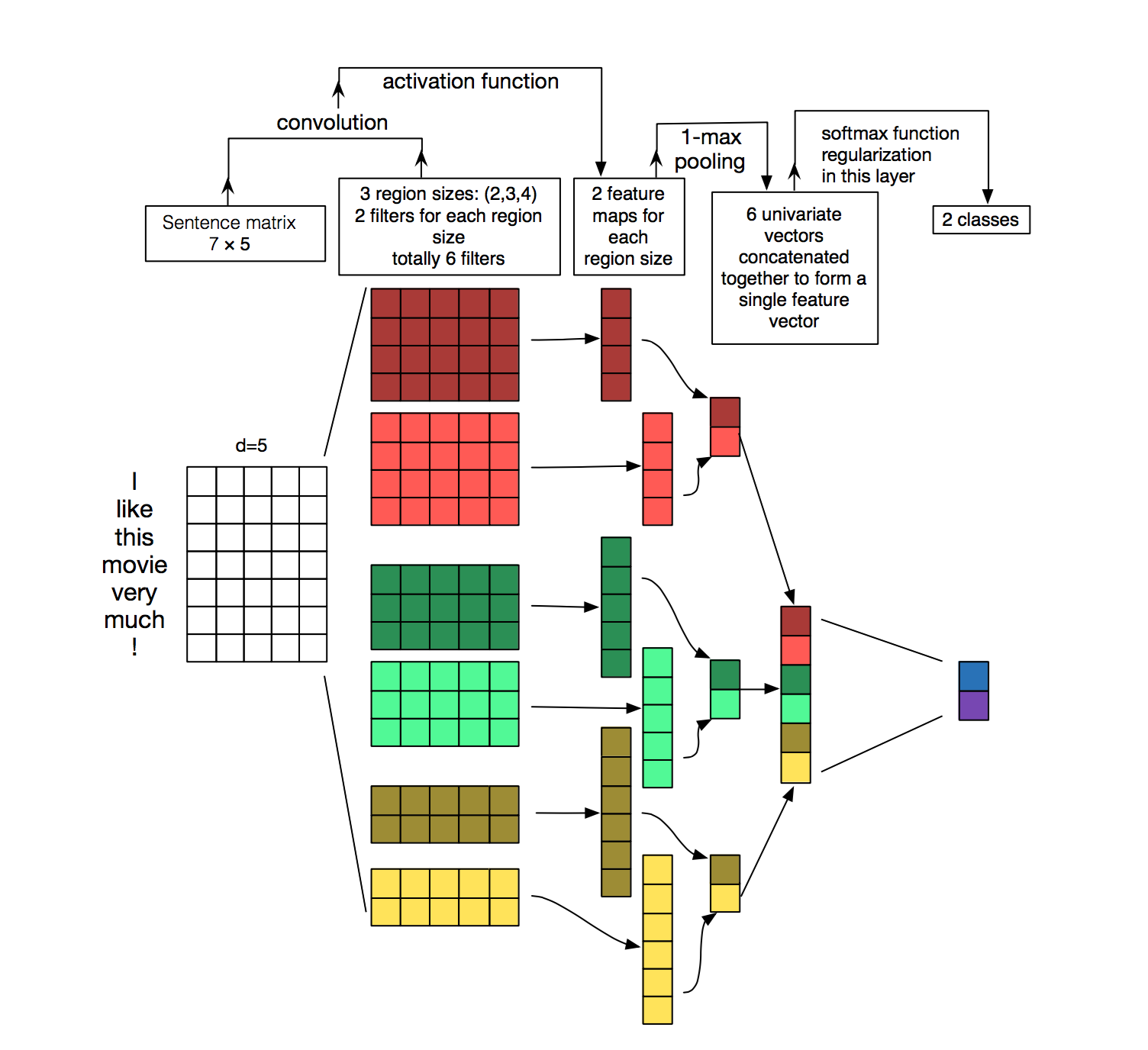
现在有些直觉。 虽然对于图像,我们也水平移动了conv过滤器,但由于在这里我们将内核大小固定为filter_size x embed_size,即(3,300),我们将向下移动卷积,因为我们的过滤器大小为3,所以一次要看三个词在这种情况下。 人们还可以将过滤器大小视为单字组,双字组,三字组等。由于我们分别查看的是1,2、3和5个单词的上下文窗口。 这是用Keras编码的文本分类网络:
# https://www.kaggle.com/yekenot/2dcnn-textclassifier
def model_cnn(embedding_matrix):
filter_sizes = [1,2,3,5]
num_filters = 36
inp = Input(shape=(maxlen,))
x = Embedding(max_features, embed_size, weights=[embedding_matrix])(inp)
x = Reshape((maxlen, embed_size, 1))(x)
maxpool_pool = []
for i in range(len(filter_sizes)):
conv = Conv2D(num_filters, kernel_size=(filter_sizes[i], embed_size),
kernel_initializer='he_normal', activation='elu')(x)
maxpool_pool.append(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(maxlen - filter_sizes[i] + 1, 1))(conv))
z = Concatenate(axis=1)(maxpool_pool)
z = Flatten()(z)
z = Dropout(0.1)(z)
outp = Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")(z)
model = Model(inputs=inp, outputs=outp)
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
我编写了一个简化且注释良好的代码,以在kaggle内核上运行此网络(从许多其他内核获取输入),以进行本次比赛。 请去那里看看以了解预处理步骤以及该模型中vec嵌入的用法。 您将学到一些东西。 如果发现有用,请升级内核。 该内核在公共排行榜上的得分约为0.661。
2.双向RNN(LSTM / GRU):
TextCNN处理很多事情。 例如,它处理近距离的单词。 它可以一起看到“纽约”。 但是它仍然不能照顾到特定文本序列中提供的所有上下文。 它仍然不学习似乎学习数据的顺序结构,其中每个单词都依赖于前一个单词。 或上一句话中的一个字。
RNN可以帮助我们。 他们能够使用隐藏状态记住以前的信息,并将其连接到当前任务。
长短期内存网络(LSTM)是RNN的子类,专门用于长时间记忆信息。 此外,双向LSTM在两个方向上都保持上下文信息,这在文本分类任务中非常有用(但不适用于时间序列预测任务)。
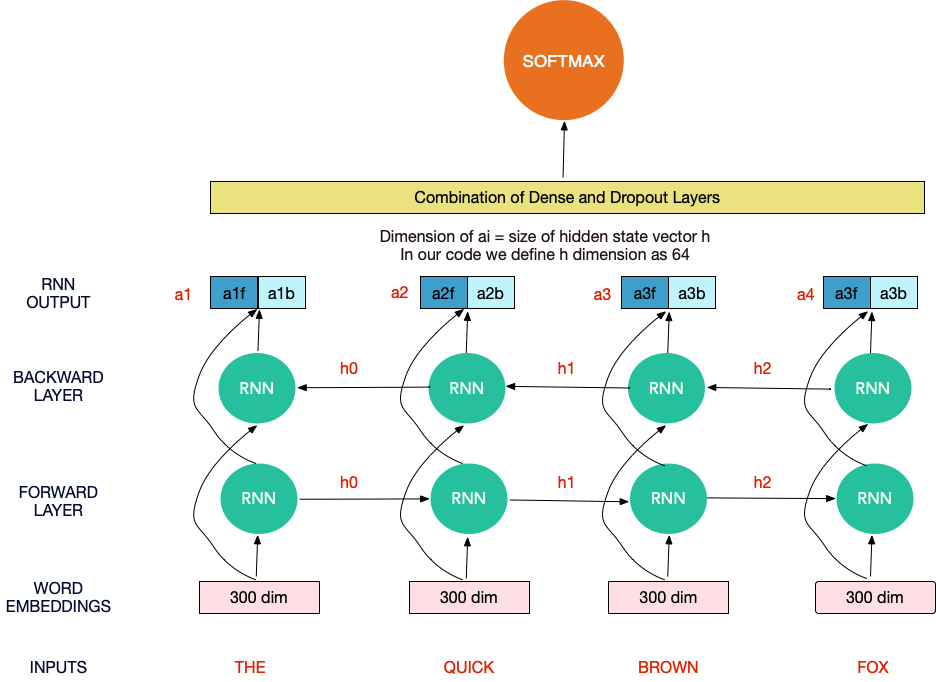
对于双向RNN的最简单的解释,可以将RNN单元视为将一个隐藏状态(一个向量)和一个单词向量作为输入,并给出一个输出向量和下一个隐藏状态。
Hidden state, Word vector ->(RNN Cell) -> Output Vector , Next Hidden state
对于长度为4的序列(例如“您将永远不会相信”),RNN单元将给出4个输出向量。 可以将其串联起来,然后用作密集前馈体系结构的一部分。
在双向RNN中,唯一的变化是我们以正常方式阅读文本,也以相反的方式阅读文本。 因此,我们并行堆叠了两个RNN,因此我们要附加8个输出向量。
一旦获得输出矢量,我们就将它们通过一系列密集层发送,最后通过softmax层发送以构建文本分类器。
由于RNN的局限性,例如不记得长期依赖关系,因此在实践中,我们几乎总是使用LSTM / GRU对长期依赖关系进行建模。 在这种情况下,您可以想到上图中的RNN单元被LSTM单元或GRU单元替代。 下面提供了示例模型。 构建模型时,可以将CuDNNGRU与CuDNNLSTM互换使用。
# BiDirectional LSTM
def model_lstm_du(embedding_matrix):
inp = Input(shape=(maxlen,))
x = Embedding(max_features, embed_size, weights=[embedding_matrix])(inp)
'''
Here 64 is the size(dim) of the hidden state vector as well as the output vector. Keeping return_sequence we want the output for the entire sequence. So what is the dimension of output for this layer?
64*70(maxlen)*2(bidirection concat)
CuDNNLSTM is fast implementation of LSTM layer in Keras which only runs on GPU
'''
x = Bidirectional(CuDNNLSTM(64, return_sequences=True))(x)
avg_pool = GlobalAveragePooling1D()(x)
max_pool = GlobalMaxPooling1D()(x)
conc = concatenate([avg_pool, max_pool])
conc = Dense(64, activation="relu")(conc)
conc = Dropout(0.1)(conc)
outp = Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")(conc)
model = Model(inputs=inp, outputs=outp)
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
我编写了一个简化且注释良好的代码,以在kaggle内核上运行此网络(从许多其他内核获取输入),以进行本次比赛。 请去那里看看以了解预处理步骤以及该模型中vec嵌入的用法。 您将学到一些东西。 如果发现有用,请升级内核。 该内核在公共排行榜上的得分约为0.671。
3.注意模型
注意的概念相对较新,因为它来自CMU和Microsoft于2016年共同撰写的文档分类的分层注意网络 。
因此,过去,我们通常通过提取关键字来从文本中查找特征。 有些单词比另一些单词更有助于确定文本的类别。 但是在这种方法中,我们有点丢失了文本的顺序结构。 使用LSTM和深度学习方法,尽管我们能够照顾到序列结构,但是却失去了为更重要的单词赋予更高权重的能力。 我们可以两全其美吗?
这就是您的关注。 用作者的话说:
并非所有单词都对句子含义的表示有同等的贡献。 因此,我们引入注意力机制来提取对句子的意义很重要的单词,并聚合这些信息性单词的表示形式以形成句子矢量
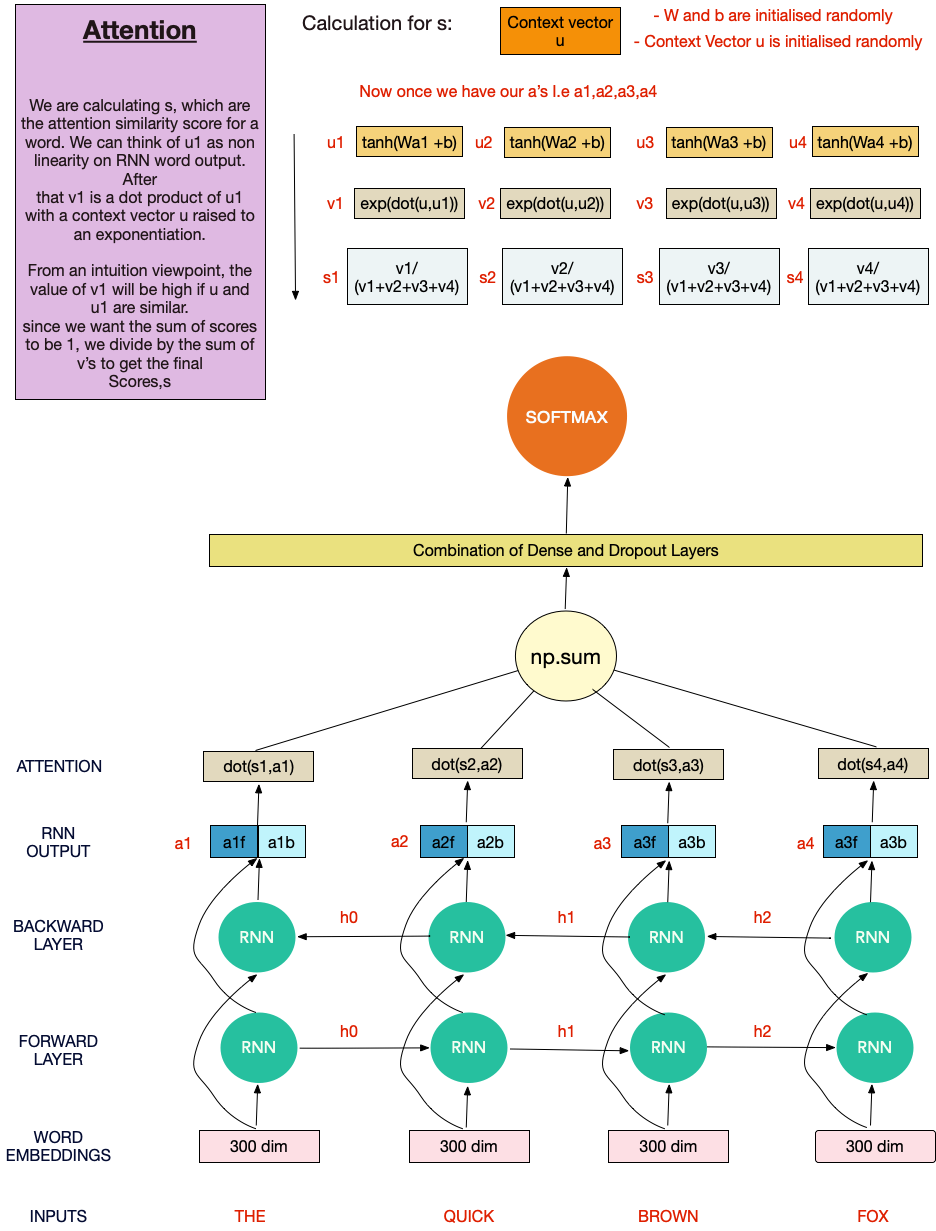
本质上,我们要为文本中的每个单词创建分数,这是单词的注意力相似度得分。
为此,我们从权重矩阵(W),偏差向量(b)和上下文向量u开始。 所有这些都将通过优化算法来学习。
然后是一系列的数学运算。 有关更多说明,请参见该图。 我们可以将u1视为RNN单词输出上的非线性。 在此之后,v1是u1的点积,上下文向量u升为幂。 从直觉上看,如果u和u1相似,则v1的值将很高。 由于我们希望分数总和为1,因此我们将v除以v的总和即可得出最终分数,s
然后将这些最终分数乘以RNN输出的单词,以根据其重要性对单词进行加权。 之后,将输出求和并通过密集层和softmax发送,以执行文本分类任务。
def dot_product(x, kernel):
"""
Wrapper for dot product operation, in order to be compatible with both
Theano and Tensorflow
Args:
x (): input
kernel (): weights
Returns:
"""
if K.backend() == 'tensorflow':
return K.squeeze(K.dot(x, K.expand_dims(kernel)), axis=-1)
else:
return K.dot(x, kernel)
class AttentionWithContext(Layer):
"""
Attention operation, with a context/query vector, for temporal data.
Supports Masking.
Follows the work of Yang et al. [ https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~diyiy/docs/naacl16.pdf ]
"Hierarchical Attention Networks for Document Classification"
by using a context vector to assist the attention
# Input shape
3D tensor with shape: `(samples, steps, features)`.
# Output shape
2D tensor with shape: `(samples, features)`.
How to use:
Just put it on top of an RNN Layer (GRU/LSTM/SimpleRNN) with return_sequences=True.
The dimensions are inferred based on the output shape of the RNN.
Note: The layer has been tested with Keras 2.0.6
Example:
model.add(LSTM(64, return_sequences=True))
model.add(AttentionWithContext())
# next add a Dense layer (for classification/regression) or whatever...
"""
def __init__(self,
W_regularizer=None, u_regularizer=None, b_regularizer=None,
W_constraint=None, u_constraint=None, b_constraint=None,
bias=True, **kwargs):
self.supports_masking = True
self.init = initializers.get('glorot_uniform')
self.W_regularizer = regularizers.get(W_regularizer)
self.u_regularizer = regularizers.get(u_regularizer)
self.b_regularizer = regularizers.get(b_regularizer)
self.W_constraint = constraints.get(W_constraint)
self.u_constraint = constraints.get(u_constraint)
self.b_constraint = constraints.get(b_constraint)
self.bias = bias
super(AttentionWithContext, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def build(self, input_shape):
assert len(input_shape) == 3
self.W = self.add_weight((input_shape[-1], input_shape[-1],),
initializer=self.init,
name='{}_W'.format(self.name),
regularizer=self.W_regularizer,
constraint=self.W_constraint)
if self.bias:
self.b = self.add_weight((input_shape[-1],),
initializer='zero',
name='{}_b'.format(self.name),
regularizer=self.b_regularizer,
constraint=self.b_constraint)
self.u = self.add_weight((input_shape[-1],),
initializer=self.init,
name='{}_u'.format(self.name),
regularizer=self.u_regularizer,
constraint=self.u_constraint)
super(AttentionWithContext, self).build(input_shape)
def compute_mask(self, input, input_mask=None):
# do not pass the mask to the next layers
return None
def call(self, x, mask=None):
uit = dot_product(x, self.W)
if self.bias:
uit += self.b
uit = K.tanh(uit)
ait = dot_product(uit, self.u)
a = K.exp(ait)
# apply mask after the exp. will be re-normalized next
if mask is not None:
# Cast the mask to floatX to avoid float64 upcasting in theano
a *= K.cast(mask, K.floatx())
# in some cases especially in the early stages of training the sum may be almost zero
# and this results in NaN's. A workaround is to add a very small positive number ε to the sum.
# a /= K.cast(K.sum(a, axis=1, keepdims=True), K.floatx())
a /= K.cast(K.sum(a, axis=1, keepdims=True) + K.epsilon(), K.floatx())
a = K.expand_dims(a)
weighted_input = x * a
return K.sum(weighted_input, axis=1)
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return input_shape[0], input_shape[-1]
def model_lstm_atten(embedding_matrix):
inp = Input(shape=(maxlen,))
x = Embedding(max_features, embed_size, weights=[embedding_matrix], trainable=False)(inp)
x = Bidirectional(CuDNNLSTM(128, return_sequences=True))(x)
x = Bidirectional(CuDNNLSTM(64, return_sequences=True))(x)
x = AttentionWithContext()(x)
x = Dense(64, activation="relu")(x)
x = Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")(x)
model = Model(inputs=inp, outputs=x)
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
我编写了一个简化且注释良好的代码,以在kaggle内核上运行此网络(从许多其他内核获取输入),以进行本次比赛。 请去那里看看以了解预处理步骤以及该模型中vec嵌入的用法。 您将学到一些东西。 如果发现有用,请升级内核。 该内核在公共排行榜上的得分约为0.682。
希望对您有所帮助! 请检查所有网络的内核,并查看注释。 我将尝试写这篇文章的第2部分,在此我想谈谈胶囊网络以及在比赛中使用的更多技术。
这里又是内核链接: TextCNN , BiLSTM / GRU , 注意
如果发现内核有用,请对其进行投票。
参考文献:
- CNN for NLP
- https://en.diveintodeeplearning.org/d2l-zh.pdf
- https://gist.github.com/cbaziotis/7ef97ccf71cbc14366835835198c09809d2
- http://univagora.ro/jour/index.php/ijccc/article/view/3142
- Shujian在Kaggle上的内核
最初于 2018 年12月17日 在 mlwhiz.com 上 发布 。
From: https://hackernoon.com/what-kagglers-are-using-for-text-classification-c695b58b5709





















 1131
1131

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








