一、空值处理:
1. 查找空值 null:
select * from emp where emp.empdesc = null;
select * from emp where emp.empdesc is null;
2. 空值 null 不能做“加、减、乘、除、比较”等运算:
select * from emp where emp.empsalary >= null; select * from emp where emp.empsalary <= null;
select * from emp where emp.empsalary is not null;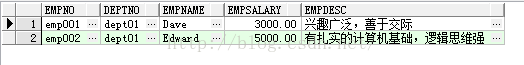
3. nvl、coalesce 将空值转换为实际值:
nvl 只能接受两个参数,而 coalesce 可以接受多个参数,返回第一个不是 null 的值。例如下边的两个 SQL 是等价的:
/* 数据准备 */ create table coal( c1 number(6, 2), c2 number(6, 2), c3 number(6, 2), c4 number(6, 2), c5 number(6, 2), c6 number(6, 2) ); insert into coal values(null, null, 1, null, 2, null); insert into coal values(null, null, null, 3, null, 2); /* coal 表数据 */ select * from coal;
下边两句等价,coalesce 函数从第一个参数开始从左到右,依次判断是否为 null, 返回第一不为 null 的值,直至最后一个参数的值。
/* nvl、coalesce 下边两句等价 */ select coalesce(c1, c2, c3, c4, c5, c6) c from coal; select nvl(nvl(nvl(nvl(nvl(c1, c2), c3), c4), c5), c6) c from coal;
二、rownum 限制返回的行数:
1. rownum 是返回数据一个排序标识:
rownum 会依次对返回的每一条数据做一个标识,经常在分页的时候会见到。这里红色着重标注“返回”两字,是指 rownum 不是记录的固有标识(比如 rowId 是记录的物理标志),这个下边会举例。先说 rownum 的用法:
select * from emp where rownum <= 2;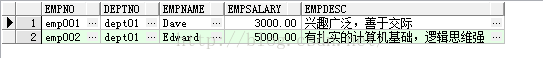
2. rownum 不是记录的固有标志:只有数据返回以后才能用 rownum,只是返回数据的一个标识,例如下边的查询结果就为空:
select * from emp where rownum = 2
而如果想要返回结果集的第二条数据,需要嵌套一层,这也是分页的做法:
select * from (select emp.*, rownum rown from emp) where rown = 2
三、模糊查询的通配符与转义字符:
1. 模糊查询的两个通配符 ‘%’、‘_’:
‘%’ 是替代一个或多个字符,而 ‘_’ 是替代一个字符。‘%’ 都清楚,只举例 ‘_’:
select * from emp where emp.empno like '_mp%';
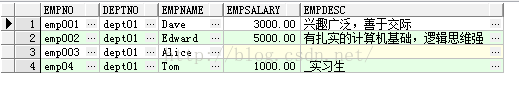
模糊查询条件改为 ‘_p’ 就查不出结果,‘_’ 只能匹配一个字符:
select * from emp where emp.empno like '_p%';
2. sql 中查询类似 ‘_’、‘%’ 特殊字符的,用 ‘/’ escape ‘/’ 实现:
select * from emp where emp.empdesc like '/_%' escape '/';

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








