一. 2G-3G-LTE网络架构 (TS23.002)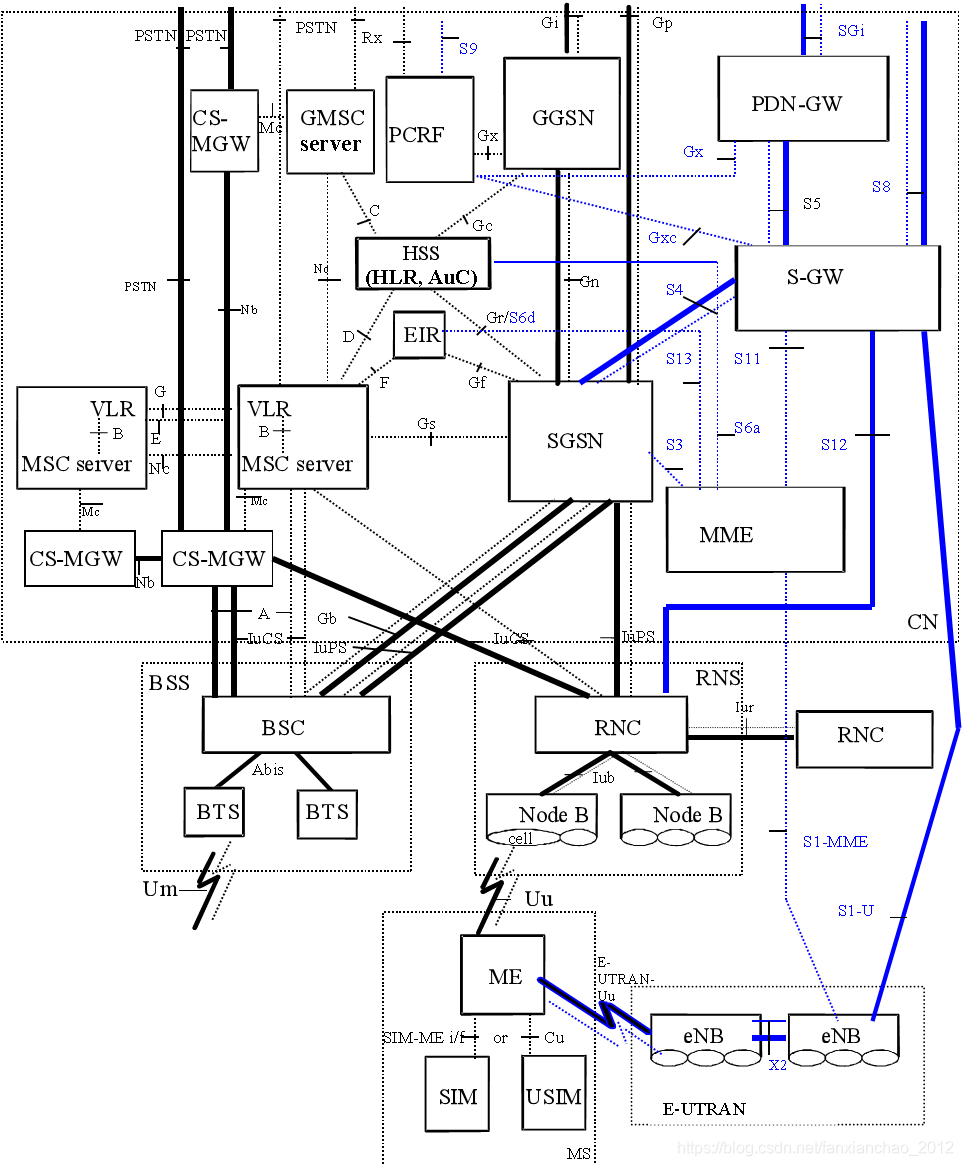
1. GSM网路架构
简化架构如下:
1.1MS: The Mobile Station 移动站
1.2UE: User equipment 用户设备
1.3Um interface: 空口名字
1.4 BTS: Base Transciever Station 基站,与手机通信,进行功率控制和基站间切换
1.5 BSC: Base Station Controller 基站控制器,控制一个区域里多各基站
1.6 Abis interface: 基站与基站控制器的连接接口名字,用电缆连接.
1.7 A interface: 基站控制器与核心网之间连接叫A接口,
1.8 MSC: Mobile-services Switching Centre移动服务交换中心,控制更大一个范围如一个城市
The Mobile-services Switching Centre (MSC) constitutes the interface between the radio system and the fixed networks. The MSC performs all necessary functions in order to handle the circuit switched services to and from the mobile stations.
When needed, the MSC can be implemented in two different entities: the MSC Server, handling only signalling, and the CS-MGW, handling user's data. A MSC Server and a CS-MGW make up the full functionality of a MSC.
移动服务交换中心(MSC)是无线电系统和固定网络之间的接口。该MSC执行所有必要的功能,以处理从移动站到移动站的电路转换服务。当需要时,MSC可以在两个不同的实体中实现:MSC服务器(只处理信令)和CS-MGW(处理用户数据)。一个MSC服务器和一个CS-MGW组成了一个MSC的全部功能。
1.9: MSC server:
The MSC Server mainly comprises the call control (CC) and mobility control parts of a MSC.The MSC Server is responsible for the control of mobile originated and mobile terminated CC CS Domain calls. It terminates the user-network signalling and translates it into the relevant network – network signalling. The MSC Server also contains a VLR to hold the mobile subscriber's service data and CAMEL related data
MSC服务器主要包括MSC的呼叫控制(CC)和移动控制部分。MSC服务器负责控制移动起源和移动终止的CC CS域呼叫。它终止用户网络信令,并将其转换为相关的网络-网络信令。MSC服务器还包含一个VLR,用于保存移动订阅者的服务数据和驼峰相关数据
1.10 CS-MGW:
A CS-MGW may terminate bearer channels from a switched circuit network and media streams from a packet network (e.g. RTP streams in an IP network). Over Iu, the CS-MGW may support media conversion, bearer control and payload processing (e.g. codec, echo canceller, conference bridge) for support of different Iu options for CS services (AAL2/ATM based as well as RTP/UDP/IP based)
CS-MGW可以终止来自交换电路网络的承载信道和来自分组网络的媒体流(例如IP网络中的RTP流)。在Iu以上,CS- mgw可以支持媒体转换、承载控制和有效负载处理(例如编解码器、回音取消器、会议桥接器),以支持CS服务的不同Iu选项(基于AAL2/ATM以及基于RTP/UDP/IP)
1.11GMSC
If a network delivering a call to the PLMN cannot interrogate the HLR, the call is routed to an MSC. This MSC will interrogate the appropriate HLR and then route the call to the MSC where the mobile station is located. The MSC which performs the routing function to the actual location of the MS is called the Gateway MSC (GMSC).When needed, the GMSC can be implemented in two different entities: the GMSC Server, handling only signalling, as defined below, and the CS-MGW, defined above. A GMSC Server and a CS-MGW make up the full functionality of a GMSC.
如果一个网络传送一个呼叫到PLMN不能询问HLR,呼叫被路由到一个MSC。该MSC将询问适当的HLR,然后将呼叫路由到移动站所在的MSC。执行路由功能到MS实际位置的MSC称为网关MSC (GMSC)。当需要时,GMSC可以在两个不同的实体中实现:GMSC服务器,只处理信号,如下面定义的,和CS-MGW,上面定义的。一个GMSC服务器和一个CS-MGW构成了一个GMSC的全部功能
1.12GMSC Server
The GMSC server mainly comprises the call control and mobility control parts of a GMSC
1.13 VLR: Visitor Location Register
The VLR area is the part of the network controlled by a VLR. A VLR area may consist of one or several MSC areas
1.14HLR: Home Location Register
The Home Location Register (HLR) is the location register to which a mobile subscriber is assigned for record purposes such as subscriber information. For EPS, the HLR functionality is provided via HSS
1.15AuC: authentication center
2.GRPS网路架构
简化架构如下:
较GSM网络,GPRS在BSC中增加了PCU单元,将数据从CS域剥离出来,即PS域和CS域分开.
2.1PCU: packet control unit 分组数据控制单元
2.2Gb: PCU单元与SGSN单元连接接口
2.3SGSN: serving GPRS support Node
The location register function in the SGSN stores subscription information and location information for Packet Switched (PS) services for each subscriber registered in the SGSN
2.4GGSN: Getway GPRS support Node
The location register function in the GGSN stores subscriber information and routeing information (needed to tunnel packet data traffic destined for a GPRS MS to the SGSN where the MS is registered) for each subscriber for which the GGSN has at least one PDP context active.The GGSN is needed only in a PLMN which supports GPRS with GERAN or UTRAN access.
在LTE网络中,GGSN更名为PDN GW
3.3G网络架构
简化架构如下: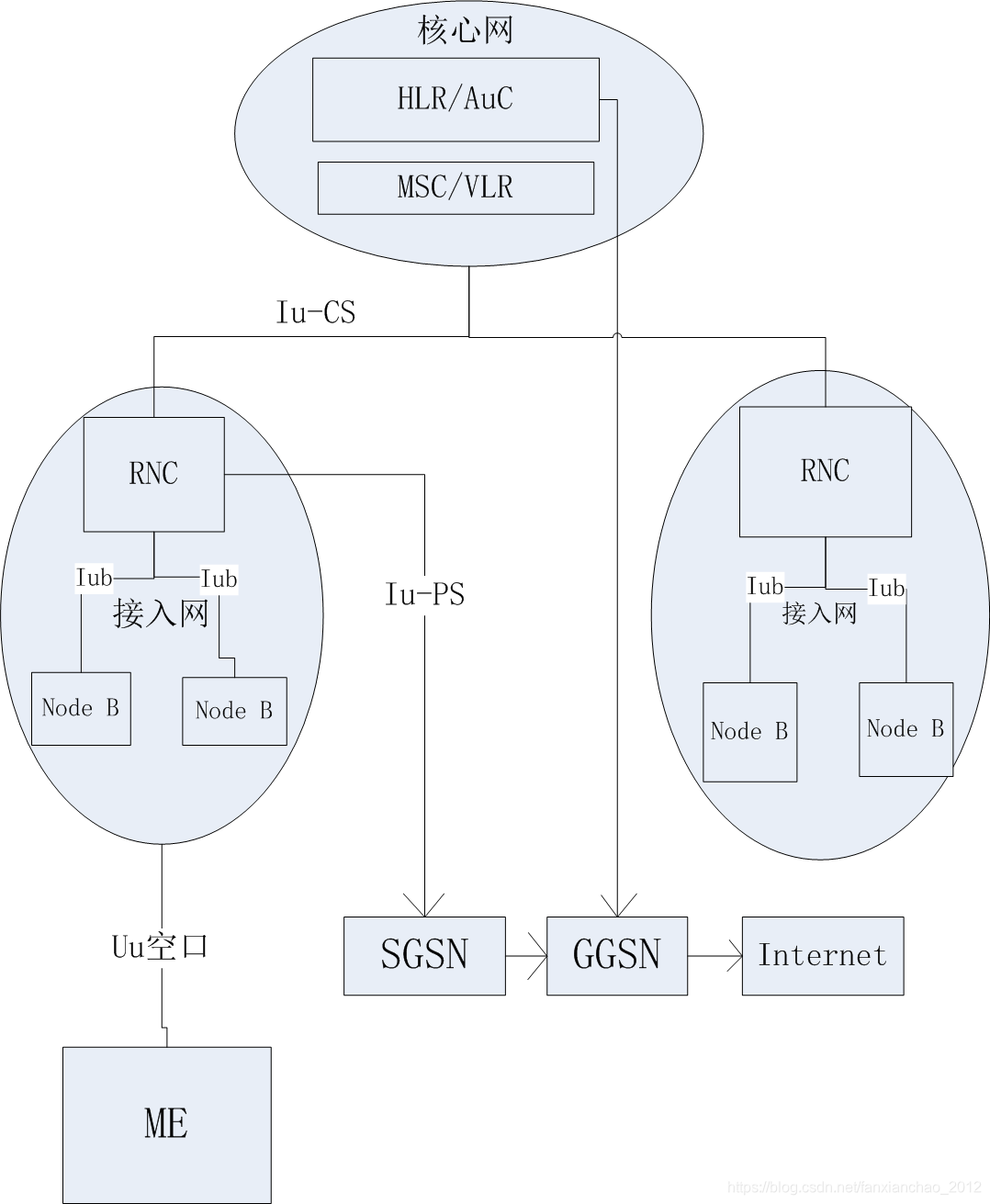
对比GPRS网络架构,3G(WCDMA)网络架构没有太大变化,只是改名字而已.
3.1空口: Um->Uu
3.2基站: BTS->Node B
3.3BSC与PCU合并为RNC
3.4基站到RNC接口: Abis->Iub
3.5CS域: 由A接口->Iu-CS
3.6PS域: 由Gb接口->Iu-PS
4.LTE网络架构
简化网络架构:
更细化: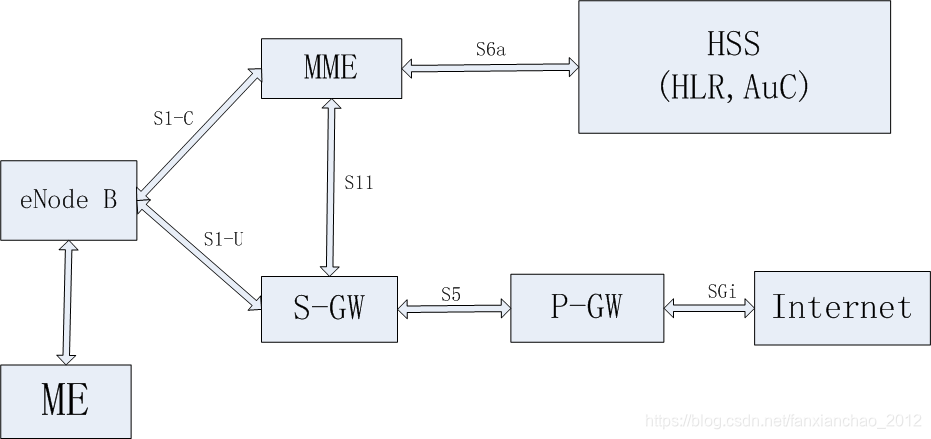
4.1 LTE网络结构相对2G-3G,由核心网->基站控制器->基站 3级架构变成 核心网->基站 2级架构,基站控制器部分功能转到基站完成
4.2 相对3G,LTE架构变化如下:
(1)LTE没由CS域,数据,语音全走IP包(S1-U接口)
(2)LTE分为S1-C控制平面和S1-U用户平面
(3)基站与基站连接接口为X2
4.3 LTE核心网包括 MME和S-GW两大块,其中MME主要走信令,用于位置更新,鉴权加密,而功率控制和基站切换由eNode B实现.S-GW走数据,语音.
4.4MME: Mobility Management Entity移动性管理实体
4.5S-GW: service gateway 服务网关
4.6P-GW: PDN gateway分组数据网关
4.7PDN:packet data network 分组数据网络
二. 5G网络架构(TS38.300)
简化架构:
5G简略架构如图所示,NG-RAN表示无线接入网,5GC表示核心网
An NG-RAN node is either:
- a gNB, providing NR user plane and control plane protocol terminations towards the UE; or
- an ng-eNB, providing E-UTRA user plane and control plane protocol terminations towards the UE.
The gNBs and ng-eNBs are interconnected with each other by means of the Xn interface. The gNBs and ng-eNBs are also connected by means of the NG interfaces to the 5GC, more specifically to the AMF (Access and Mobility Management Function) by means of the NG-C interface and to the UPF (User Plane Function) by means of the NG-U interface (see TS 23.501 [3]).
NG-RAN节点包含两种类型:gNB(5G基站):提供NR用户平面和控制平面协议和功能;ng-eNB(下一代的4G基站):提供E-UTRA用户平面和控制平面协议和功能。
gNB与ng-eNB之间通过Xn接口连接,gNB/ng-eNB通过NG-C接口与AMF(Access and Mobility Management Function)连接,通过NG-U接口与UPF(User Plane Function)连接。

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








