Pyomo:全称Python Optimization Modeling Objects,优化建模工具,是一个基于Python的开源软件包,支持多种优化功能,用于制定和分析优化模型(optimization models)。Pyomo可用于定义符号问题(symbolic problems)、创建具体问题实例(create concrete problem instances),并使用标准求解器解决这些实例。Pyomo包含一个pyomo命令,可自动构建和优化模型。源码地址:https://github.com/Pyomo/pyomo ,license为BSD,最新发布版本为6.9.1。
Pyomo支持多种问题类型,包括:
(1).Linear programming(线性规划)
(2).Quadratic programming(二次规划)
(3).Nonlinear programming(非线性规划)
(4).Mixed-integer linear programming(混合整数线性规划)
(5).Mixed-integer quadratic programming(混合整数二次规划)
(6).Mixed-integer nonlinear programming(混合整数非线性规划)
(7).Mixed-integer stochastic programming(混合整数随机规划)
(8).Generalized disjunctive programming(广义析取规划)
(9).Differential algebraic equations(微分代数方程)
(10).Mathematical programming with equilibrium constraints(具有平衡约束的数学规划)
(11).Constraint programming(约束规划)
安装Pyomo,执行命令:pip install pyomo
GLPK:GNU Linear Programming Kit,是开源的线性规划求解器,适用于线性问题,线性规划中会用到。从 https://sourceforge.net/projects/winglpk/ 下载winglpk-4.65.zip,解压缩,并将D:\soft\winglpk-4.65\glpk-4.65\w64目录添加到系统环境变量中。
这里参考 https://github.com/Pyomo/pyomo-gallery 中的线性规划问题示例,简单说明Pyomo的使用。Diet Problem是经典的线性规划问题,目标是选择一组食物,以最低的成本满足营养需求。
Diet Problem可以用以下模型在数学上表述为线性规划问题:

测试代码如下:在原有基础上,新加入了约束条件,即从所有食物中必须选择5种食物
from pyomo.environ import *
infinity = float('inf')
ninfinity = float('-inf')
# 1. creating a model object
model = AbstractModel()
# 2. F and N are declared abstractly using the Set component
model.F = Set() # Foods
model.N = Set() # Nutrients
# 3. the model parameters are defined abstractly using the Param component
model.c = Param(model.F, within=PositiveReals) # Cost of each food
model.a = Param(model.F, model.N, within=NonNegativeReals) # Amount of nutrient in each food
model.Nmin = Param(model.N, within=NonNegativeReals, default=0.0) # Lower bound on each nutrient
model.Nmax = Param(model.N, within=NonNegativeReals, default=infinity) # Upper bound on each nutrient
model.V = Param(model.F, within=PositiveReals) # Volume per serving of food
model.Vmax = Param(within=PositiveReals) # Maximum volume of food consumed
# 4. Var component is used to define the decision variables
model.x = Var(model.F, within=NonNegativeIntegers) # Number of servings consumed of each food
model.y = Var(model.F, within=Binary) # decide whether to choose this food
# 5. Objective component is used to define the cost objective
def cost_rule(model): # Minimize the cost of food that is consumed
return sum(model.c[i]*model.x[i] for i in model.F)
model.cost = Objective(rule=cost_rule, sense=minimize)
# 6. rule functions are used to define constraint expressions in the Constraint component:
def nutrient_rule(model, j): # Limit nutrient consumption for each nutrient
value = sum(model.a[i,j]*model.x[i] for i in model.F)
return inequality(model.Nmin[j], value, model.Nmax[j])
model.nutrient_limit = Constraint(model.N, rule=nutrient_rule)
def volume_rule(model): # Limit the volume of food consumed
return sum(model.V[i]*model.x[i] for i in model.F) <= model.Vmax
model.volume = Constraint(rule=volume_rule)
def select_rule(model):
return sum(model.y[i] for i in model.F) == 5
model.select = Constraint(rule=select_rule)
def linking_upper_rule(model, f):
return model.x[f] <= model.y[f] * 1e6
model.linking_upper = Constraint(model.F, rule=linking_upper_rule)
def linking_lower_rule(model, f):
return model.x[f] >= model.y[f]
model.linking_lower = Constraint(model.F, rule=linking_lower_rule)执行命令如下:
pyomo solve --solver=glpk test_pyomo_linear_programming.py ../test_data/diet.dat执行结果如下图所示:没有增加约束条件时,成本为15.05;增加约束条件后成本为15.4
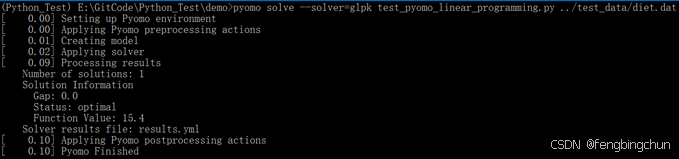
执行完后会生成results.yml文件,内容如下:
# ==========================================================
# = Solver Results =
# ==========================================================
# ----------------------------------------------------------
# Problem Information
# ----------------------------------------------------------
Problem:
- Name: unknown
Lower bound: 15.4
Upper bound: 15.4
Number of objectives: 1
Number of constraints: 28
Number of variables: 18
Number of nonzeros: 121
Sense: minimize
# ----------------------------------------------------------
# Solver Information
# ----------------------------------------------------------
Solver:
- Status: ok
Termination condition: optimal
Statistics:
Branch and bound:
Number of bounded subproblems: 41
Number of created subproblems: 41
Error rc: 0
Time: 0.02000141143798828
# ----------------------------------------------------------
# Solution Information
# ----------------------------------------------------------
Solution:
- number of solutions: 1
number of solutions displayed: 1
- Gap: 0.0
Status: optimal
Message: None
Objective:
cost:
Value: 15.4
Variable:
x[Cheeseburger]:
Value: 3
x[Fish Sandwich]:
Value: 1
x[Fries]:
Value: 5
x[Ham Sandwich]:
Value: 1
x[Lowfat Milk]:
Value: 4
y[Cheeseburger]:
Value: 1
y[Fish Sandwich]:
Value: 1
y[Fries]:
Value: 1
y[Ham Sandwich]:
Value: 1
y[Lowfat Milk]:
Value: 1
Constraint: No values

























 609
609

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








