作者:Peter
编辑:Peter
介绍一个简单而不简约的基于LightGBM的实战项目,主要内容包含:
数据探索性分析EDA
基于LightGBM的建模
基于网格搜索的模型优化
麻雀虽小,五脏俱全
1 导入库
In [1]:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 100)
from IPython.display import display_html
import plotly_express as px
import plotly.graph_objects as go
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif"]=["SimHei"] # 设置字体
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"]=False # 解决“-”负号的乱码问题
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
import missingno as ms
import gc
from datetime import datetime
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split,StratifiedKFold,GridSearchCV
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from imblearn.under_sampling import ClusterCentroids
from imblearn.over_sampling import KMeansSMOTE, SMOTE
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, recall_score, precision_score, f1_score, auc
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score,precision_recall_curve, confusion_matrix,classification_report
# Classifiers
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn import tree
from pydotplus import graph_from_dot_data
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier,AdaBoostClassifier
from catboost import CatBoostClassifier
import lightgbm as lgb
import xgboost as xgb
from scipy import stats
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")2 数据信息
2.1 导入数据
In [2]:
df = pd.read_csv("信贷数据.csv")
dfOut[2]:
| Income | Age | Sex | History_Credit_Limit | History_Default_Times | Default | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 462087 | 26 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 362324 | 32 | 0 | 13583 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 332011 | 52 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 252895 | 39 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 352355 | 50 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 995 | 442985 | 24 | 1 | 5000 | 0 | 0 |
| 996 | 402396 | 39 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 997 | 442684 | 36 | 1 | 10000 | 0 | 0 |
| 998 | 382029 | 43 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 999 | 422612 | 39 | 0 | 91040 | 1 | 0 |
1000 rows × 6 columns
2.2 数据基本信息
In [3]:
df.columnsOut[3]:
Index(['Income', 'Age', 'Sex', 'History_Credit_Limit', 'History_Default_Times',
'Default'],
dtype='object')缺失值情况:
In [4]:
df.isnull().sum()Out[4]:
Income 0
Age 0
Sex 0
History_Credit_Limit 0
History_Default_Times 0
Default 0
dtype: int64历史违约次数统计:
In [5]:
df["History_Default_Times"].value_counts()Out[5]:
History_Default_Times
0 615
1 203
2 129
3 43
4 7
5 3
Name: count, dtype: int64In [6]:
df["Sex"].value_counts()Out[6]:
Sex
1 507
0 493
Name: count, dtype: int64男女人数几乎相同,很均衡。
目标变量是否违约的人数对比:
In [7]:
df["Default"].value_counts()Out[7]:
Default
0 601
1 399
Name: count, dtype: int64In [8]:
df[df["History_Default_Times"] == 2]Out[8]:
| Income | Age | Sex | History_Credit_Limit | History_Default_Times | Default | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 392372 | 47 | 1 | 71000 | 2 | 1 |
| 12 | 362640 | 20 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 13 | 352044 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 14 | 312971 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 18 | 282051 | 37 | 0 | 63639 | 2 | 1 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 941 | 442329 | 44 | 1 | 28649 | 2 | 0 |
| 942 | 392150 | 57 | 1 | 44058 | 2 | 0 |
| 959 | 352358 | 38 | 1 | 265208 | 2 | 0 |
| 991 | 392087 | 43 | 1 | 236726 | 2 | 0 |
| 994 | 342022 | 20 | 0 | 57001 | 2 | 0 |
129 rows × 6 columns
需要注意的是:历史违约次数大于0,不代表一定是违约客户。比如历史违约次数为2,最终是否违约的客户两种情况都有。
是否违约的客户收入存在差异:
In [9]:
fig = px.violin(df, x="Default",y="Income")
fig.show()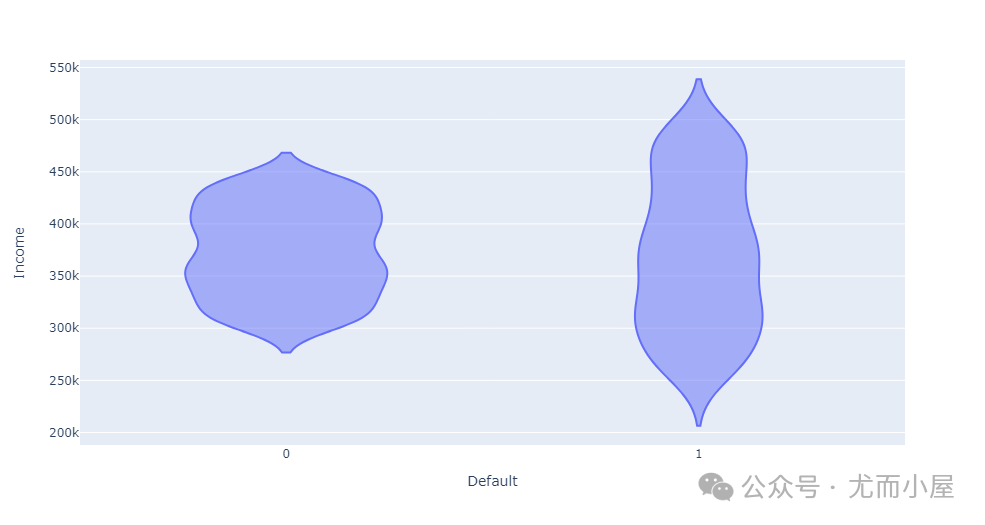
基于seaborn绘制密度图:
In [10]:
sns.displot(data=df,x="Income",hue="Default",kind="kde")
plt.show()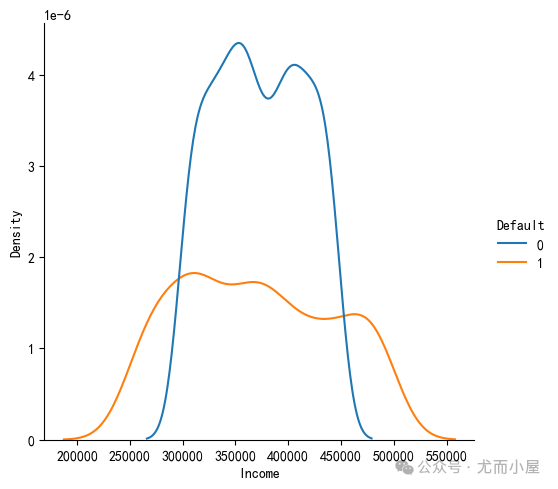
可以看到在低收入和高收入人群中容易发生违约。
In [11]:
fig = px.violin(df, x="Default",y="Age")
fig.show()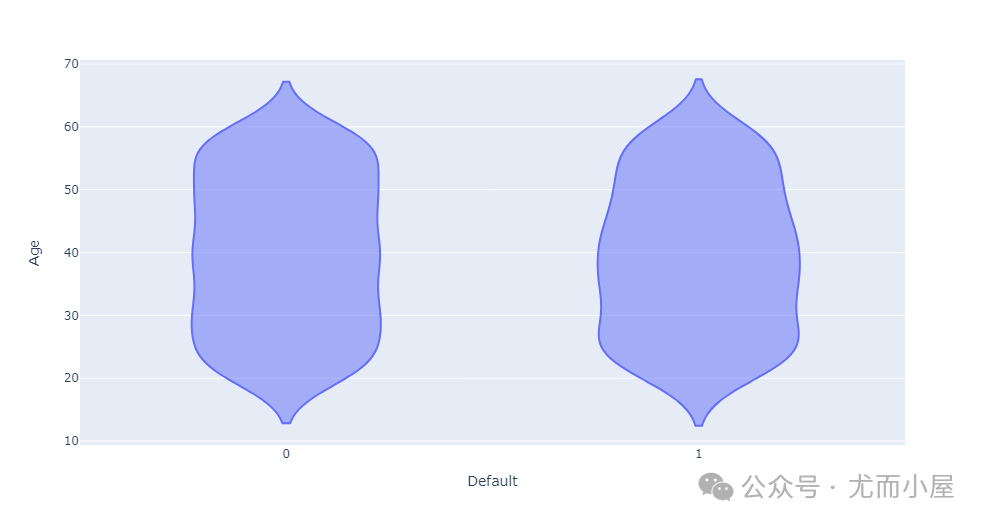
基于seaborn的实现:
In [12]:
sns.displot(data=df,x="Age",hue="Default",kind="kde")
plt.show()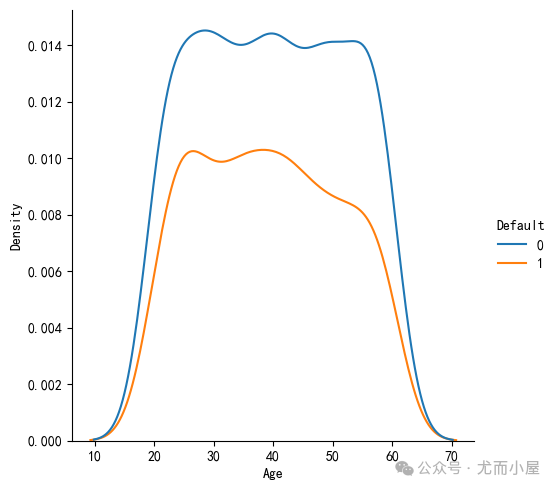
可以看到是是否违约客户的年龄段分布是一致的。
3 LightGBM建模
3.1 切分数据
In [13]:
# 提取特征和目标变量
X = df.drop(columns="Default")
Y = df["Default"]划分训练集和测试集数据:
In [14]:
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,Y,test_size=0.2,random_state=42)3.2 模型训练
建立基础版的lightgbm模型:
In [15]:
from lightgbm import LGBMClassifier
model = LGBMClassifier()
model.fit(X_train, y_train) # 模型训练
[LightGBM] [Info] Number of positive: 318, number of negative: 482
gain, best gain: -inf
......Out[15]:
LGBMClassifier
LGBMClassifier()
# 通过下面的代码查看官方解释
LGBMClassifier?3.3 模型预测
In [16]:
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
y_predOut[16]:
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,
1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
0, 0], dtype=int64)3.4 模型评估
1、对比测试集中的实际值和预测值:
In [17]:
predict_true = pd.DataFrame()
predict_true["预测值"] = list(y_pred)
predict_true["实际值"] = list(y_test)
predict_trueOut[17]:
| 预测值 | 实际值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 195 | 0 | 0 |
| 196 | 0 | 1 |
| 197 | 1 | 1 |
| 198 | 0 | 0 |
| 199 | 0 | 1 |
200 rows × 2 columns
筛选预测值和实际值相等的数据:结果表明是162条记录
In [18]:
predict_true[predict_true["预测值"] == predict_true["实际值"]]Out[18]:
| 预测值 | 实际值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 192 | 0 | 0 |
| 193 | 1 | 1 |
| 195 | 0 | 0 |
| 197 | 1 | 1 |
| 198 | 0 | 0 |
162 rows × 2 columns
In [19]:
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_pred, y_test)
accuracyOut[19]:
0.81可以看到模型在测试集上的准确率为81%
也可以计算为:
In [20]:
162 / 200 # 相同数目为162, 总共是200条Out[20]:
0.812、ROC-AUC曲线的绘制:
In [21]:
y_pred_proba = model.predict_proba(X_test)
y_pred_proba[:5]Out[21]:
array([[0.97884615, 0.02115385],
[0.99221142, 0.00778858],
[0.72394845, 0.27605155],
[0.75366821, 0.24633179],
[0.95015727, 0.04984273]])In [22]:
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve # ROC-AUC曲线
fpr, tpr, thres = roc_curve(y_test, y_pred_proba[:,1])In [23]:
plt.plot(fpr, tpr)
plt.title("ROC_AUC Curve of Default")
plt.show()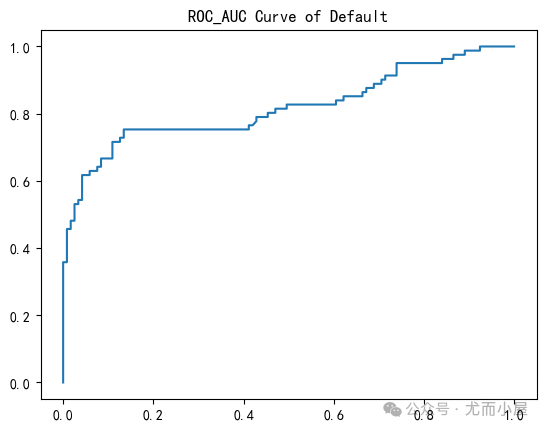
3、查看具体的AUC值:
In [24]:
# 计算AUC的值
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
score = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_proba[:,1])
scoreOut[24]:
0.8182902790745933.5 特征重要性
In [25]:
# feature_importances_
model.feature_importances_Out[25]:
array([1179, 668, 96, 906, 131])In [26]:
model.feature_name_Out[26]:
['Income', 'Age', 'Sex', 'History_Credit_Limit', 'History_Default_Times']In [27]:
features = dict(zip(model.feature_importances_,model.feature_name_))
featuresOut[27]:
{1179: 'Income',
668: 'Age',
96: 'Sex',
906: 'History_Credit_Limit',
131: 'History_Default_Times'}In [28]:
sorted(features.items(),key=lambda x:x[0], reverse=True)Out[28]:
[(1179, 'Income'),
(906, 'History_Credit_Limit'),
(668, 'Age'),
(131, 'History_Default_Times'),
(96, 'Sex')]可以看到基于重要性程度排序后,Income是最重要的,而年龄是最不重要的。
上面的数据信息部分中我们也观察到,是否违约的客户的年龄分布是一致的,也就是说和年龄关系不大。
也可以将特征及其重要性生成DataFrame数据:
In [29]:
features_df = pd.DataFrame({"features": model.feature_name_,"importances": model.feature_importances_})
features_dfOut[29]:
| features | importances | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Income | 1179 |
| 1 | Age | 668 |
| 2 | Sex | 96 |
| 3 | History_Credit_Limit | 906 |
| 4 | History_Default_Times | 131 |
In [30]:
features_df.sort_values("importances", ascending=False)Out[30]:
| features | importances | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Income | 1179 |
| 3 | History_Credit_Limit | 906 |
| 1 | Age | 668 |
| 4 | History_Default_Times | 131 |
| 2 | Sex | 96 |
4 模型调优
基于网格搜索的模型调优:
In [31]:
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV4.1 设定网格搜索对象
设定待搜索的参数及其取值范围:
In [32]:
parameters = {"num_leaves": [10, 15, 13],
"n_estimators":[10,20,30],
"learning_rate":[0.05,0.1,0.2]
}In [33]:
model = LGBMClassifier() # 基础模型实例化
# 定义搜索实例化对象
grid_search = GridSearchCV(model, # 基础模型
parameters, # 搜索参数
scoring="roc_auc", # 评价指标
cv=5 # 交叉验证5次
)In [34]:
grid_search.fit(X_train, y_train) # 模型训练4.2 建立新模型
输出最佳的参数组合:
In [35]:
dict_params = grid_search.best_params_
dict_paramsOut[35]:
{'learning_rate': 0.05, 'n_estimators': 30, 'num_leaves': 10}基于最佳的参数组合建立新模型:
In [36]:
new_model = LGBMClassifier(num_leaves=10, # 使用最佳参数
n_estimators=30,
learning_rate=0.05
)4.3 模型训练
模型再次训练:
In [37]:
new_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
[LightGBM] [Info] Number of positive: 318, number of negative: 482
[LightGBM] [Info] Auto-choosing col-wise multi-threading, the overhead of testing was 0.001194 seconds.
You can set `force_col_wise=true` to remove the overhead.
[LightGBM] [Info] Total Bins 498
[LightGBM] [Info] Number of data points in the train set: 800, number of used features: 5
[LightGBM] [Info] [binary:BoostFromScore]: pavg=0.397500 -> initscore=-0.415893
[LightGBM] [Info] Start training from score -0.4158934.4 模型评估
1、查看ROC-AUC曲线:
In [38]:
y_pred_proba = new_model.predict_proba(X_test)
y_pred_proba[:5]Out[38]:
array([[0.77658791, 0.22341209],
[0.80601961, 0.19398039],
[0.69243702, 0.30756298],
[0.7962625 , 0.2037375 ],
[0.80601961, 0.19398039]])In [39]:
fpr, tpr, thres = roc_curve(y_test, y_pred_proba[:,1])
plt.plot(fpr, tpr)
plt.title("ROC_AUC Curve of Default")
plt.show()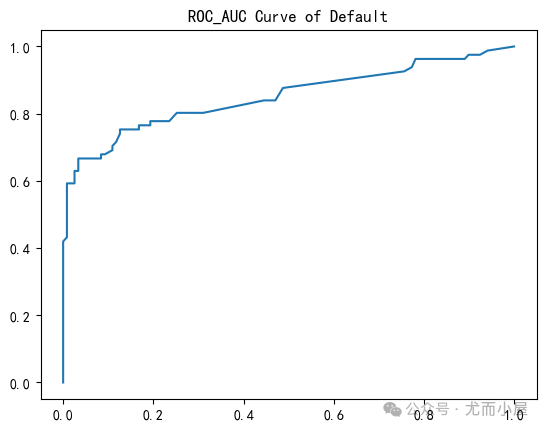
2、具体的AUC值:
In [40]:
# 计算AUC的值
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
score = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_proba[:,1])
scoreOut[40]:
0.85071065463222323、再次查看模型的准确率:
In [41]:
# 新模型下的准确率
y_pred_new = new_model.predict(X_test)
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_pred_new, y_test)
accuracyOut[41]:
0.84相比较于基础模型的准确率81%,提升了3%

往期精彩回顾
适合初学者入门人工智能的路线及资料下载(图文+视频)机器学习入门系列下载机器学习及深度学习笔记等资料打印《统计学习方法》的代码复现专辑交流群
欢迎加入机器学习爱好者微信群一起和同行交流,目前有机器学习交流群、博士群、博士申报交流、CV、NLP等微信群,请扫描下面的微信号加群,备注:”昵称-学校/公司-研究方向“,例如:”张小明-浙大-CV“。请按照格式备注,否则不予通过。添加成功后会根据研究方向邀请进入相关微信群。请勿在群内发送广告,否则会请出群,谢谢理解~(也可以加入机器学习交流qq群772479961)






















 3209
3209











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








