1、pandas导入、查看版本
#pandas导入
import pandas as pd
#pandas输出版本信息
print(pd.__version__)
#pandas输出详细版本信息、 Python版本、相关程序包、操作系统等信息以json格式输出
print(pd.show_versions(as_json=True))
#pandas输出相关信息以默认格式输出
print(pd.show_versions())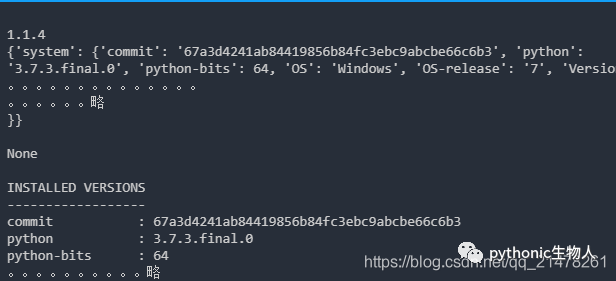
2、使用python list、python dict、numpy.ndarray创建pandas.Series
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
mylist = list('abcedfghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz')# python list
myarr = np.arange(26)#numpy.ndarray
mydict = dict(zip(mylist, myarr))#python dict
ser1 = pd.Series(mylist)
ser2 = pd.Series(myarr)
ser3 = pd.Series(mydict)
print(ser1.head(2))
print(ser2.head(2))
print(ser3.head(2))
3、将pandas.Series转化为pandas.DataFrame
需求: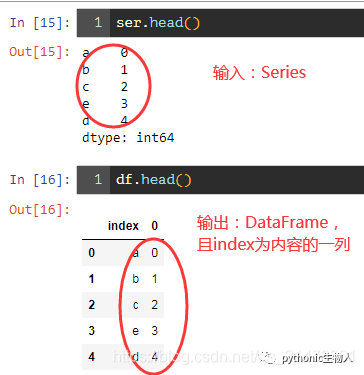 解决:
解决:
mylist = list('abcedfghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz')
myarr = np.arange(26)
mydict = dict(zip(mylist, myarr))
ser = pd.Series(mydict)
#to_frame()结合reset_index()使用
df = ser.to_frame().reset_index()
print(df.head())
4、将多个pandas.Series合并为一个pandas.DataFrame
# 输入
import numpy as np
ser1 = pd.Series(list('abcedfghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'))
ser2 = pd.Series(np.arange(26))
# 解决方法1
df = pd.concat([ser1, ser2], axis=1)
# 解决方法2
df = pd.DataFrame({'col1': ser1, 'col2': ser2})
print(df.head())```
## 5、修改pandas.Series index名称
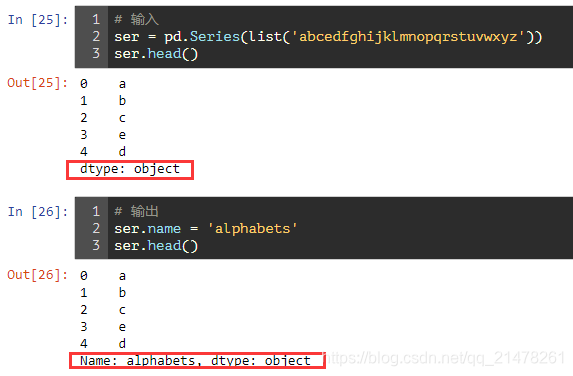
## 6、 移除pandas.Series1中和pandas.Series2共同的部分
```python
ser1 = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
ser2 = pd.Series([4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
ser1[~ser1.isin(ser2)]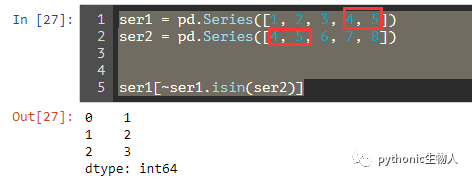
7、求pandas.Series1和pandas.Series2共的交集、并集、差集
ser1 = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
ser2 = pd.Series([4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
ser_u = pd.Series(np.union1d(ser1, ser2)) # union
ser_i = pd.Series(np.intersect1d(ser1, ser2)) # intersect
ser_s = ser_u[~ser_u.isin(ser_i)]# Subtraction
print("交集")
print(ser_i)
print("并集")
print(ser_u)
print("差集")
print(ser_s)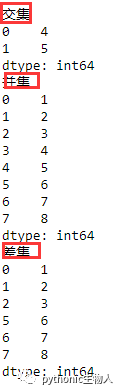
8、求pandas.Series分位数(最小值、1/4分位数、中位数、3/4分位数、最大值)
state = np.random.RandomState(100)
ser = pd.Series(state.normal(10, 5, 25))
np.percentile(ser, q=[0, 25, 50, 75, 100])#可是设置其它任何想输出的分位数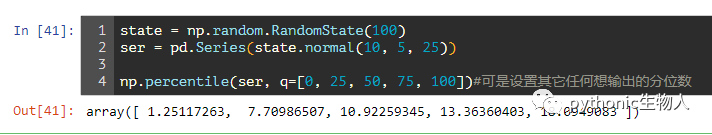
9、求pandas.Series()频数
ser = pd.Series(np.take(list('abcdefgh'), np.random.randint(8, size=30)))
ser.value_counts()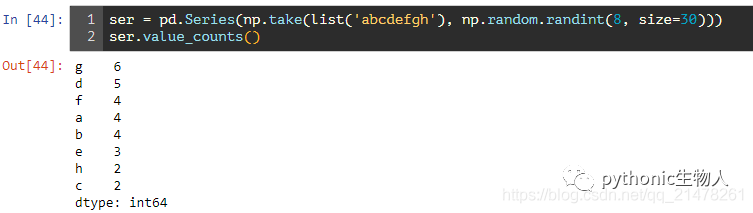
10、输出pandas.Series()中频数排第一二位的、其它的替换为other
np.random.RandomState(100)
ser = pd.Series(np.random.randint(1, 5, [12]))
print("Top 2 Freq:", ser.value_counts())
ser[~ser.isin(ser.value_counts().index[:2])] = 'Other'
ser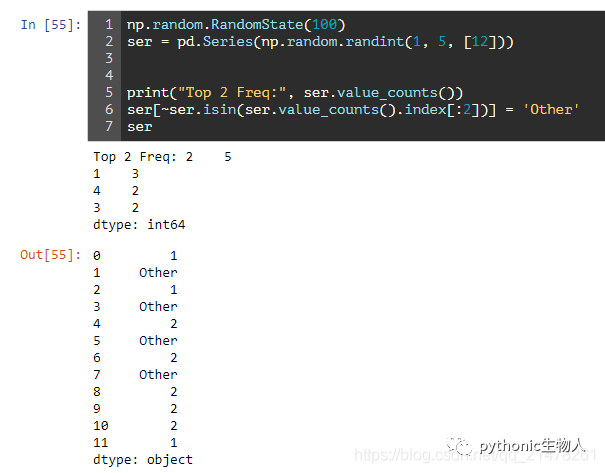
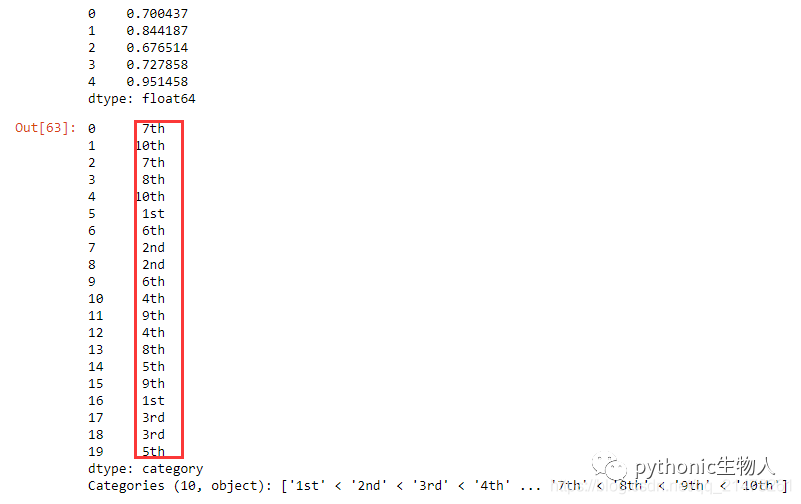
11、将pandas.Series()均分为10个区间、每个值使用区间名称标记
np.random.seed(666) #让结果可重复
ser = pd.Series(np.random.random(20))
print(ser.head())
pd.qcut(ser,
q=[0, .10, .20, .3, .4, .5, .6, .7, .8, .9, 1],
labels=[
'1st', '2nd', '3rd', '4th', '5th', '6th', '7th', '8th', '9th',
'10th'
])
12、将pandas.Series()转换为指定shape的pandas.DataFrame
ser = pd.Series(np.random.randint(1, 10, 35))
df = pd.DataFrame(ser.values.reshape(7,5))
print(df)
13、取出pandas.Series()中满足条件数据的位置index
np.random.seed(666)
ser = pd.Series(np.random.randint(1, 10, 7))
print(ser)
np.argwhere(ser.values % 3 == 0)#数据为3的倍数的数据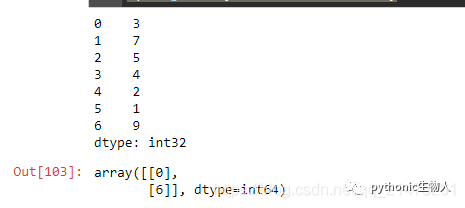
14、取出pandas.Series()指定位置的数据
ser = pd.Series(list('abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'))
pos = [0, 4, 8, 14, 20]#待取出位置
ser.take(pos)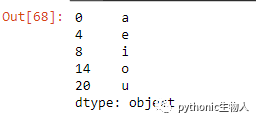
15、pandas.Series()水平、垂直合并
ser1 = pd.Series(range(5))
ser2 = pd.Series(list('abcde'))
# 垂直合并
ser3 = ser1.append(ser2)
print(ser3)
# 水平合并
df = pd.concat([ser1, ser2], axis=1)
print(df)
16、输出pandas.Series()子集的index号
获取ser2在ser1中的index号
ser1 = pd.Series([10, 9, 6, 5, 3, 1, 12, 8, 13])
ser2 = pd.Series([1, 3, 10, 13])
# 方法1
[np.where(i == ser1)[0].tolist()[0] for i in ser2]
# 方法2
[pd.Index(ser1).get_loc(i) for i in ser2]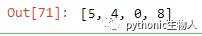
17、求真实和预测pd.Series之间的均方误差损失函数(MSE,mean squared error)
truth = pd.Series(range(10))
pred = pd.Series(range(10)) + np.random.random(10)
np.mean((truth-pred)**2)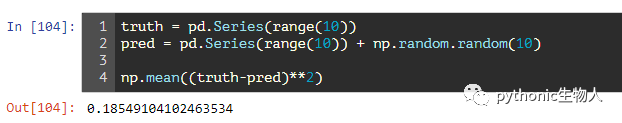
18、pd.Series字符串型数据首字母大写转换
ser = pd.Series(['how', 'to', 'kick', 'ass?'])
# 方法一title()结合title()
ser.map(lambda x: x.title())
# 方法二upper()结合lambda
ser.map(lambda x: x[0].upper() + x[1:])
# 方法三title()结合列表推导式
pd.Series([i.title() for i in ser])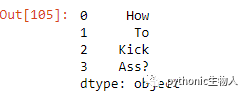
19、pd.Series字符串型数据字符长度计算
ser = pd.Series(['how', 'to', 'kick', 'ass?'])
ser.map(lambda x: len(x))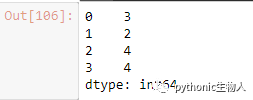
20、pd.Series中两两数之间差异
ser = pd.Series([1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, 27, 35])
print(ser.diff().tolist())
21、pd.Series中日期字符串转换为datetime格式
ser = pd.Series(['01 Jan 2010', '02-02-2011', '20120303', '2013/04/04', '2014-05-05', '2015-06-06T12:20'])
# 方法一
from dateutil.parser import parse
ser.map(lambda x: parse(x))
# 方法二
pd.to_datetime(ser)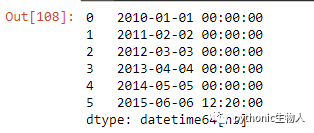
22、获取pd.Series日期字符串中时间对象
ser = pd.Series(['01 Jan 2011', '02-02-2011', '20120303', '2013/04/04', '2014-05-05', '2015-06-06T12:20'])
from dateutil.parser import parse
ser_ts = ser.map(lambda x: parse(x))
# 处于该月中的那一天
print("Date: ", ser_ts.dt.day.tolist())
# week number
print("Week number: ", ser_ts.dt.weekofyear.tolist())
# 处于该年的第多少天
print("Day number of year: ", ser_ts.dt.dayofyear.tolist())
# 处于该年周几
print("Day of week: ", ser_ts.dt.day_name().tolist())#pythonic生物人修改,原文ser_ts.dt.weekday_name.tolist()有误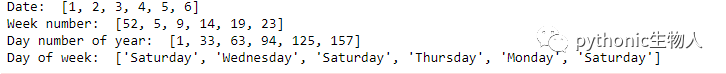
23、pd.Series日期字符串中修改为按指定日期输出
import pandas as pd
ser = pd.Series(['Jan 2010', 'Feb 2011', 'Mar 2012'])
# 方法1
from dateutil.parser import parse
# Parse the date
ser_ts = ser.map(lambda x: parse(x))
# Construct date string with date as 4
ser_datestr = ser_ts.dt.year.astype('str') + '-' + ser_ts.dt.month.astype('str') + '-' + '04'
# Format it.
[parse(i).strftime('%Y-%m-%d') for i in ser_datestr]
# 方法2
ser.map(lambda x: parse('04 ' + x))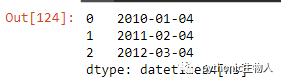
24、输出pd.Series中至少包含两个元音字符的数据
ser = pd.Series(['Apple', 'Orange', 'Plan', 'Python', 'Money'])
from collections import Counter
mask = ser.map(lambda x: sum([Counter(x.lower()).get(i, 0) for i in list('aeiou')]) >= 2)
ser[mask]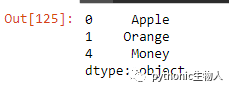
25、输出pd.Series中有效的email地址
# 三种方法
emails = pd.Series(['buying books at amazom.com', 'rameses@egypt.com', 'matt@t.co', 'narendra@modi.com'])
# Solution 1 (as series of strings)
import re
pattern ='[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\\.[A-Za-z]{2,4}'
mask = emails.map(lambda x: bool(re.match(pattern, x)))
emails[mask]
# Solution 2 (as series of list)
emails.str.findall(pattern, flags=re.IGNORECASE)
# Solution 3 (as list)
[x[0] for x in [re.findall(pattern, email) for email in emails] if len(x) > 0]26、pd.Series1按pd.Series2分组并求均值
fruit = pd.Series(np.random.choice(['apple', 'banana', 'carrot'], 10))
weights = pd.Series(np.linspace(1, 10, 10))
weights.groupby(fruit).mean()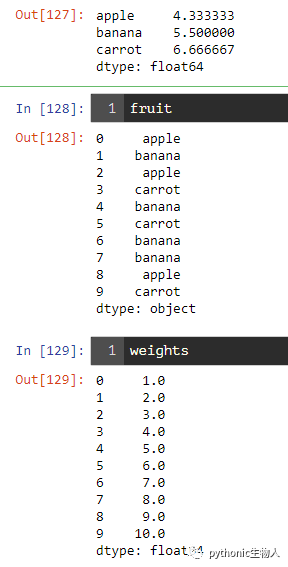
27、计算两个pd.Series之间的欧式距离
p = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
q = pd.Series([10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1])
# 方法1
sum((p - q)**2)**.5
# 方法2
np.linalg.norm(p-q)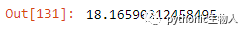
28、求pd.Series局部峰值index
ser = pd.Series([2, 10, 3, 4, 9, 10, 2, 7, 3])
dd = np.diff(np.sign(np.diff(ser)))
peak_locs = np.where(dd == -2)[0] + 1
peak_locs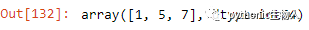
29、pd.Series字符串数据中使用最低频字符填充空格
my_str = 'dbc deb abed gade'
ser = pd.Series(list('dbc deb abed gade'))
freq = ser.value_counts()
print(freq)
least_freq = freq.dropna().index[-1]
"".join(ser.replace(' ', least_freq))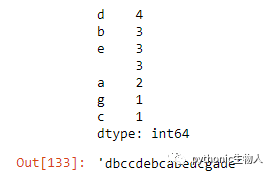
30、创建时间序列数据,赋予随机值
ser = pd.Series(np.random.randint(1,10,10), pd.date_range('2000-01-01', periods=10, freq='W-SAT'))
ser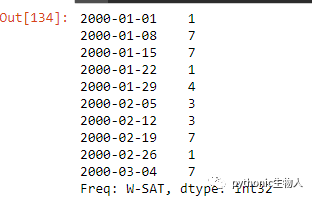
31、缺省的时间序列值 不同方式填充
ser = pd.Series([1,10,3, np.nan], index=pd.to_datetime(['2000-01-01', '2000-01-03', '2000-01-06', '2000-01-08']))
ser.resample('D').ffill() # 前填充
ser.resample('D').bfill() # f后填充
ser.resample('D').bfill().ffill() # 先后填充,如后无值则前填充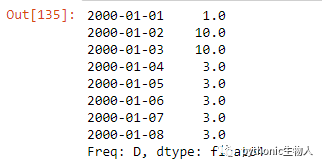
32、找出pd.Series中自相关性最大的数据
ser = pd.Series(np.arange(20) + np.random.normal(1, 10, 20))
autocorrelations = [ser.autocorr(i).round(2) for i in range(11)]
print(autocorrelations[1:])
print('Lag having highest correlation: ', np.argmax(np.abs(autocorrelations[1:]))+1)
33、从一个csv 文件中每间隔50行取数据生成pandas.DataFrame
#三种方法
# Solution 1: Use chunks and for-loop
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/BostonHousing.csv', chunksize=50)
df2 = pd.DataFrame()
for chunk in df:
df2 = df2.append(chunk.iloc[0,:])
# Solution 2: Use chunks and list comprehension
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/BostonHousing.csv', chunksize=50)
df2 = pd.concat([chunk.iloc[0] for chunk in df], axis=1)
df2 = df2.transpose()
# Solution 3: Use csv reader
import csv
with open('BostonHousing.csv', 'r') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
out = []
for i, row in enumerate(reader):
if i%50 == 0:
out.append(row)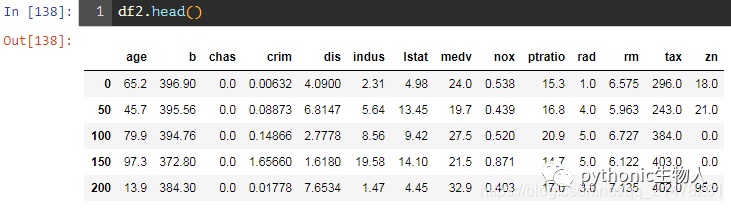
34、从一个csv 文件取数据生成pandas.DataFrame(新增加一分类列)
##两种方式
# Solution 1: Using converter parameter
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/BostonHousing.csv',
converters={'medv': lambda x: 'High' if float(x) > 25 else 'Low'})
# Solution 2: Using csv reader
import csv
with open('BostonHousing.csv', 'r') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
out = []
for i, row in enumerate(reader):
if i > 0:
row[13] = 'High' if float(row[13]) > 25 else 'Low'
out.append(row)
df = pd.DataFrame(out[1:], columns=out[0])
print(df.head())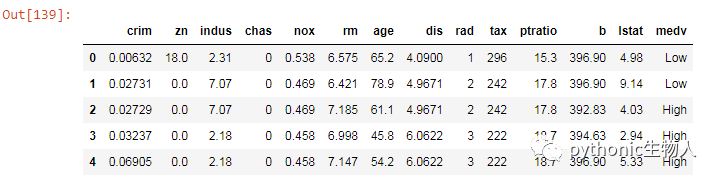
35、生成一个按规定步长平移的pandas.DataFrame
L = pd.Series(range(15))
def gen_strides(a, stride_len=5, window_len=5):
n_strides = ((a.size-window_len)//stride_len) + 1
return np.array([a[s:(s+window_len)] for s in np.arange(0, a.size, stride_len)[:n_strides]])
gen_strides(L, stride_len=2, window_len=4)
36、从一个csv 文件读取指定列生成pandas.DataFrame
#usecols参数设置
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/BostonHousing.csv', usecols=['crim', 'medv'])
print(df.head())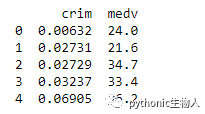
37、输出DataFrame的行数、列数、数据类型、类型频数、Series转list
import pandas as pd
#https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/Cars93_miss.csv
df = pd.read_csv('./Cars93_miss.csv')
# DataFrame的行数和列数
print(df.shape)
# DataFrame各列数据类型
print(df.dtypes.head())
# 每种数据类型的频数
print(df.dtypes.value_counts())
# DataFrame基础统计
df_stats = df.describe()
# pd.Series转list
df['Model'].tolist()[0]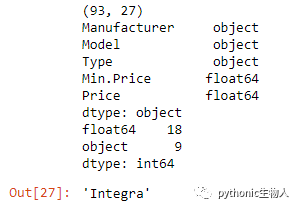
38、输出满足某个规则的DataFrame数据行和列号
df = pd.read_csv('./Cars93_miss.csv')
#输出Price值最大时的行和列号
row, col = np.where(df.values == np.max(df.Price))#df.values输出DataFrame的值,为numpy.ndarray类型
print('%s\t%s'%(row,col))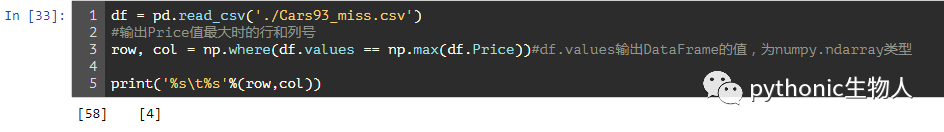
39、修改DataFrame的列名称
#修改某一列的名称
df=df.rename(columns = {'Type':'CarType'})
# 或者
#df.columns.values[2] = "CarType"
# map函数修改某一匹配的名称:此处将名称中的.替换为下划线
df.columns = df.columns.map(lambda x: x.replace('.', '_'))
df.columns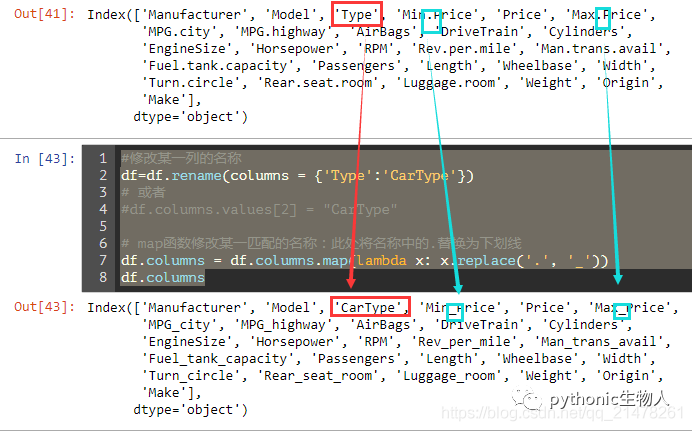
40、DataFrame中是否有缺省值确认
df = pd.read_csv('./Cars93_miss.csv')
df.isnull().values.any()
41、DataFrame中缺省值统计
n_missings_each_col = df.apply(lambda x: x.isnull().sum())#每列缺省值计数
print(n_missings_each_col)
n_missings_each_col.argmax()#缺省值数最多列的列号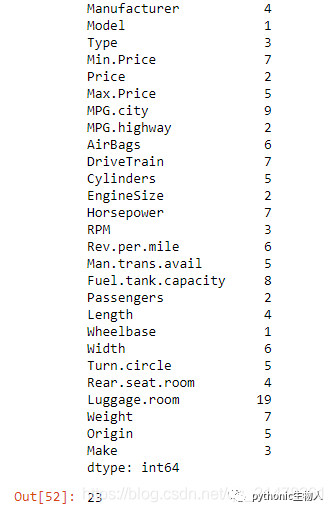
42、各自列均值填充DataFrame中各自列缺省值
df = pd.read_csv('./Cars93_miss.csv')
df_out = df[['Min.Price', 'Max.Price']] = df[['Min.Price', 'Max.Price']].apply(lambda x: x.fillna(x.mean()))
print(df_out.head())43、各自列均值、中值填充DataFrame中各自列缺省值(使用apply)
df = pd.read_csv('./Cars93_miss.csv')
d = {'Min.Price': np.nanmean, 'Max.Price': np.nanmedian}
df[['Min.Price', 'Max.Price']] = df[['Min.Price', 'Max.Price']].apply(lambda x, d: x.fillna(d[x.name](x)), args=(d, ))44、从DataFrame选择子DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(-1, 5), columns=list('abcde'))
# 选择子DataFrame
type(df[['a']])
type(df.loc[:, ['a']])
type(df.iloc[:, [0]])
# 选择Series
type(df.a)
type(df['a'])
type(df.loc[:, 'a'])
type(df.iloc[:, 1])45、 改变DataFrame列顺序
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(-1, 5), columns=list('abcde'))
# 方法1:传入一个list
df[list('cbade')]
# 方法2:自定义函数
def switch_columns(df, col1=None, col2=None):
colnames = df.columns.tolist()
i1, i2 = colnames.index(col1), colnames.index(col2)
colnames[i2], colnames[i1] = colnames[i1], colnames[i2]
return df[colnames]
df1 = switch_columns(df, 'a', 'c')
# 方法3:
df[sorted(df.columns)]
# 方法4:
df.sort_index(axis=1, ascending=False, inplace=True)46、大DataFrame修改默认显示的行和列数
df = pd.read_csv('./Cars93_miss.csv.txt')
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 10)#输出10列
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 10)#输出10行
df47、DataFrame数据小数位数设置
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.random(4)**10, columns=['random'])
#方法1: Rounding
df.round(4)
#方法2: Use apply to change format
df.apply(lambda x: '%.4f' % x, axis=1)
# or
df.applymap(lambda x: '%.4f' % x)
#方法3: Use set_option
pd.set_option('display.float_format', lambda x: '%.4f' % x)
#方法4: Assign display.float_format
pd.options.display.float_format = '{:.4f}'.format
print(df)48、 DataFrame数据小数转百分比显示
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.random(4), columns=['random'])
out = df.style.format({
'random': '{0:.2%}'.format,
})49、DataFrame数据每隔20行读取
df = pd.read_csv('./Cars93_miss.csv.txt')
print(df.iloc[::20, :][['Manufacturer', 'Model', 'Type']])
50、创建DataFrame主键
df = pd.read_csv('./Cars93_miss.csv', usecols=[0,1,2,3,5])
df[['Manufacturer', 'Model', 'Type']] = df[['Manufacturer', 'Model', 'Type']].fillna('missing')
df.index = df.Manufacturer + '_' + df.Model + '_' + df.Type
print(df.index.is_unique)51、获取DataFrame某一列中第n大的值索引
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1, 30, 30).reshape(10,-1), columns=list('abc'))
n = 5#第5大
df['a'].argsort()[::-1][n]52、获取DataFrame某一列中第n大的值大于指定值得索引
ser = pd.Series(np.random.randint(1, 100, 15))
print('ser: ', ser.tolist(), 'mean: ', round(ser.mean()))
np.argwhere(ser > ser.mean())[1]
53、获取DataFrame中行和大于100的行
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(10, 40, 60).reshape(-1, 4))
# 求行和
rowsums = df.apply(np.sum, axis=1)#axis=1指定行
df.iloc[np.where(rowsums > 100)]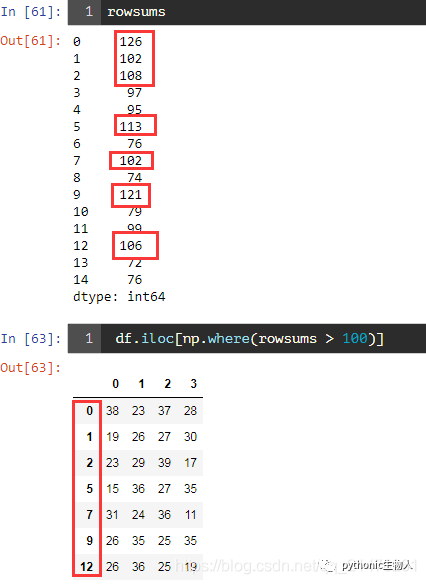
54、 Series or DataFrame中使用分位数填充超限区域
#需求:使用0.05分位数和0.95分位数分别替换小于和大于该分位数的区域
ser = pd.Series(np.logspace(-2, 2, 30))
def cap_outliers(ser, low_perc, high_perc):
low, high = ser.quantile([low_perc, high_perc])#指定分位数
print(low_perc, '%ile: ', low, '|', high_perc, '%ile: ', high)
ser[ser < low] = low
ser[ser > high] = high
return(ser)
capped_ser = cap_outliers(ser, .05, .95)55、去除指定值将DataFrame转换为最大方阵
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(-20, 50, 100).reshape(10,-1))
print(df)
#去除负值
arr = df[df > 0].values.flatten()
arr_qualified = arr[~np.isnan(arr)]
#寻找最大可能的方阵维度
n = int(np.floor(arr_qualified.shape[0]**.5))
#方阵转换
top_indexes = np.argsort(arr_qualified)[::-1]
output = np.take(arr_qualified, sorted(top_indexes[:n**2])).reshape(n, -1)
print(output)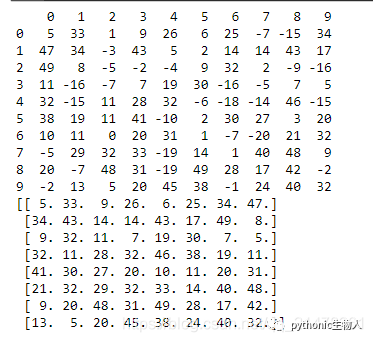
56、DataFrame两行交换
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(25).reshape(5, -1))
def swap_rows(df, i1, i2):
a, b = df.iloc[i1, :].copy(), df.iloc[i2, :].copy()
df.iloc[i1, :], df.iloc[i2, :] = b, a
return df
print(swap_rows(df, 1, 2))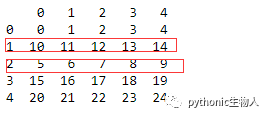
57、DataFrame逆序输出
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(25).reshape(5, -1))
print(df)
#方法 1
df.iloc[::-1, :]
#方法 2
print(df.loc[df.index[::-1], :])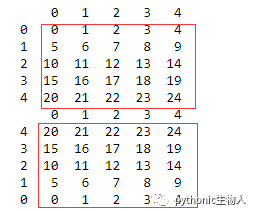
58、DataFrame转对角矩阵
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(25).reshape(5,-1), columns=list('abcde'))
print(df)
df_onehot = pd.concat([pd.get_dummies(df['a']), df[list('bcde')]], axis=1)
print(df_onehot)
59、DataFrame那一列含有最多行最大值
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 40).reshape(10, -1))
print(df)
print('Column with highest row maxes: ', df.apply(np.argmax, axis=1).value_counts().index[0])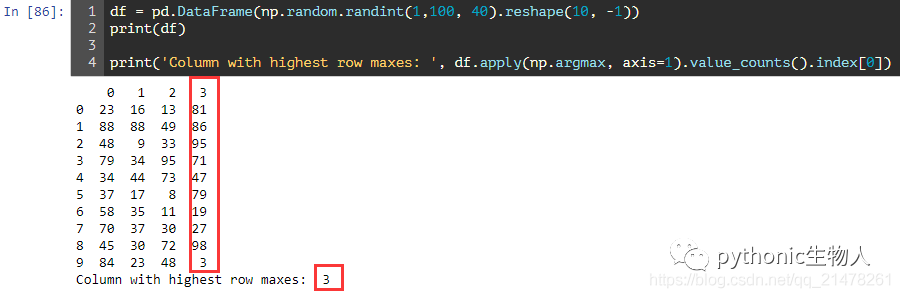
60、DataFrame创建新列:每行为行号(按欧几里得距离而来)
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 40).reshape(10, -1), columns=list('pqrs'), index=list('abcdefghij'))
print(df)
import numpy as np
# init outputs
nearest_rows = []
nearest_distance = []
# iterate rows.
for i, row in df.iterrows():
curr = row
rest = df.drop(i)
e_dists = {} # init dict to store euclidean dists for current row.
# iterate rest of rows for current row
for j, contestant in rest.iterrows():
# compute euclidean dist and update e_dists
e_dists.update({j: round(np.linalg.norm(curr.values - contestant.values))})
# update nearest row to current row and the distance value
nearest_rows.append(max(e_dists, key=e_dists.get))
nearest_distance.append(max(e_dists.values()))
df['nearest_row'] = nearest_rows
df['dist'] = nearest_distance
df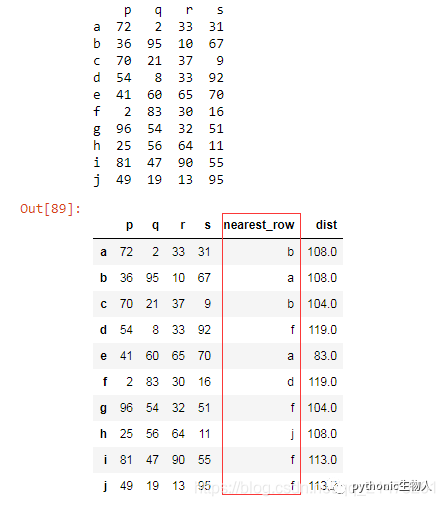
61、求DataFrame各列之间「最大」相关系数
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 80).reshape(8, -1), columns=list('pqrstuvwxy'), index=list('abcdefgh'))
print(df)
abs_corrmat = np.abs(df.corr())
max_corr = abs_corrmat.apply(lambda x: sorted(x)[-2])
print('Maximum Correlation possible for each column: ', np.round(max_corr.tolist(), 2))
62、DataFrame创建一列:包含每行中最小值与最大值比值
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 80).reshape(8, -1))
print(df)
#方法 1
min_by_max = df.apply(lambda x: np.min(x)/np.max(x), axis=1)
#方法 2
min_by_max = np.min(df, axis=1)/np.max(df, axis=1)
min_by_max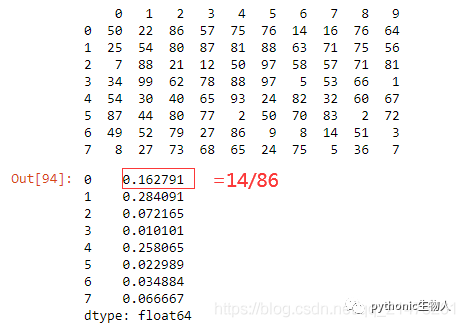
63、DataFrame创建一列:包含每行中第二大的值
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 80).reshape(8, -1))
out = df.apply(lambda x: x.sort_values().unique()[-2], axis=1)
df['penultimate'] = out
df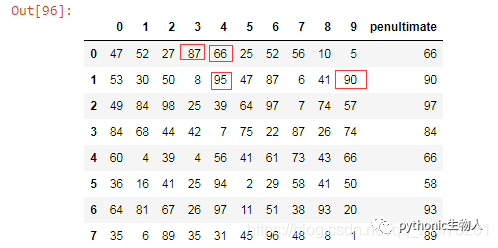
64、DataFrame每列按特定方式归一化
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 80).reshape(8, -1))
# 均值、标准差归一化
out1 = df.apply(lambda x: ((x - x.mean())/x.std()).round(2))
print('均值、标准差归一化:\n',out1)
# 最大最小值归一化
out2 = df.apply(lambda x: ((x.max() - x)/(x.max() - x.min())).round(2))
print('最大最小值归一化:\n', out2)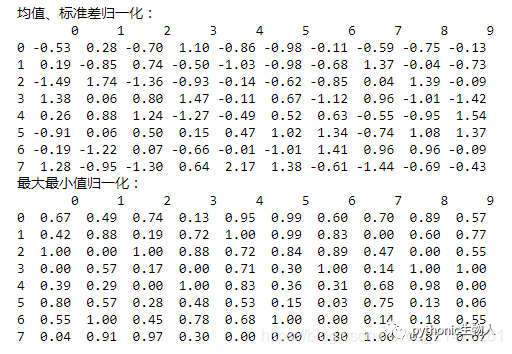
65、计算DataFrame每行与后一行的相关系数
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 80).reshape(8, -1))
[df.iloc[i].corr(df.iloc[i+1]).round(2) for i in range(df.shape[0])[:-1]]
66、DataFrame对角线元素替换为0
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1,100, 100).reshape(10, -1))
print(df)
for i in range(df.shape[0]):
df.iat[i, i] = 0
df.iat[df.shape[0]-i-1, i] = 0
df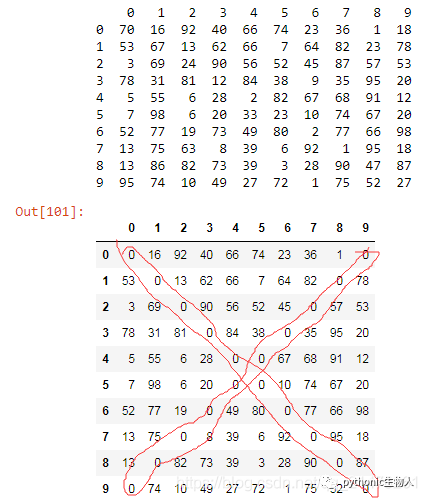
67、DataFrame按某列分组、提取某个分组
df = pd.DataFrame({'col1': ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'] * 3,
'col2': np.random.rand(9),
'col3': np.random.randint(0, 15, 9)})
print(df)
df_grouped = df.groupby(['col1'])#按col1列分组
#获取指定分组,此处取apple组
# 方法 1
df_grouped.get_group('apple')
# 方法 2
for i, dff in df_grouped:
if i == 'apple':
print(dff)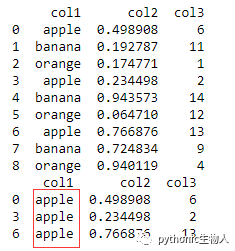
68、DataFrame按另外列分组、提取当前列中指定值(看下方例子,需求不好描述)
df = pd.DataFrame({'fruit': ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'] * 3,
'taste': np.random.rand(9),
'price': np.random.randint(0, 15, 9)})
print(df)
df_grpd = df['taste'].groupby(df.fruit)#taste值按fruit类别排序
df_grpd.get_group('banana').sort_values().iloc[-2]#获取fruit中的banana组,取第二大值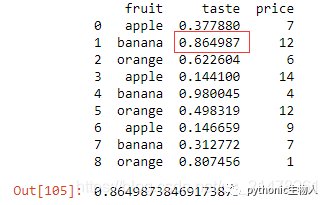
69、DataFrame分组(看下方例子,需求不好描述)
df = pd.DataFrame({'fruit': ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'] * 3,
'rating': np.random.rand(9),
'price': np.random.randint(0, 15, 9)})
print(df)
out = df.groupby('fruit', as_index=False)['price'].mean()#按fruit分组、求每类fruit的均价
print(out)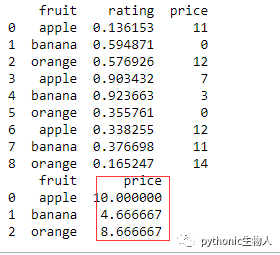
70、两个DataFrame使用类似SQL 中INNER JOIN拼接
# Join dataframes df1 and df2 by ‘fruit-pazham’ and ‘weight-kilo’.
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'fruit': ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'] * 3,
'weight': ['high', 'medium', 'low'] * 3,
'price': np.random.randint(0, 15, 9)
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'pazham': ['apple', 'orange', 'pine'] * 2,
'kilo': ['high', 'low'] * 3,
'price': np.random.randint(0, 15, 6)
})
print('df1:\n')
print(df1)
print('df2:\n')
print(df2)
# Solution
pd.merge(df1,
df2,
how='inner',
left_on=['fruit', 'weight'],
right_on=['pazham', 'kilo'],
suffixes=['_left', '_right'])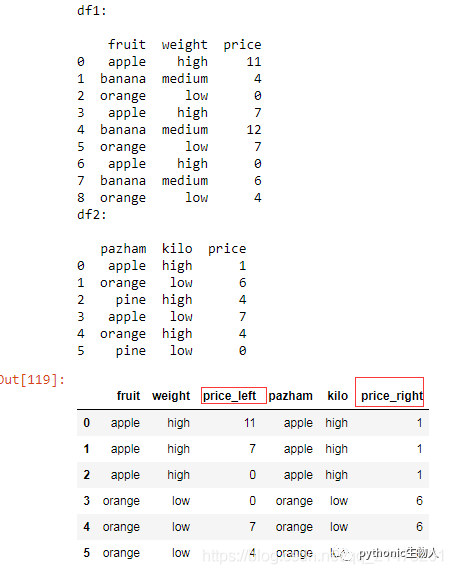
71、移除DataFrame1中在DataFrame2出现的行
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'fruit': ['apple', 'orange', 'banana'] * 3,
'weight': ['high', 'medium', 'low'] * 3,
'price': np.arange(9)
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'fruit': ['apple', 'orange', 'pine'] * 2,
'weight': ['high', 'medium'] * 3,
'price': np.arange(6)
})
print('df1:\n')
print(df1)
print('df2:\n')
print(df2)
#
print(df1[~df1.isin(df2).all(1)])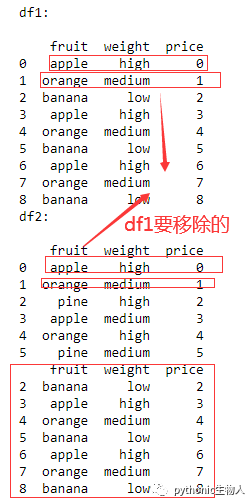
72、取出DataFrame中两列值相等的行号
df = pd.DataFrame({
'fruit1': np.random.choice(['apple', 'orange', 'banana'], 10),
'fruit2': np.random.choice(['apple', 'orange', 'banana'], 10)
})
print(df)
np.where(df.fruit1 == df.fruit2)
73、DataFrame中新建两列:滞后列和提前列(看下方例子,需求BT)
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1, 100, 20).reshape(-1, 4),
columns=list('abcd'))
print(df)
df['a_lag1'] = df['a'].shift(1)#a列每行值向后移一位
df['b_lead1'] = df['b'].shift(-1)#b列每行值向前移一位
print(df)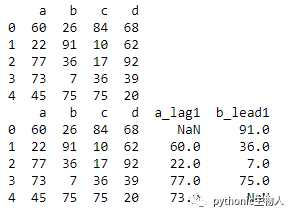
74、DataFrame中所有值出现频次统计
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(1, 10, 20).reshape(-1, 4),
columns=list('abcd'))
pd.value_counts(df.values.ravel())
75、拆分DataFrame中某列文本为两列
df = pd.DataFrame([
"STD, City State", "33, Kolkata West Bengal",
"44, Chennai Tamil Nadu", "40, Hyderabad Telengana",
"80, Bangalore Karnataka"
],
columns=['row'])
print(df)
df_out = df.row.str.split(',|\t', expand=True)#拆分
new_header = df_out.iloc[0]#第一列设置为标题
df_out = df_out[1:]
df_out.columns = new_header
print(df_out)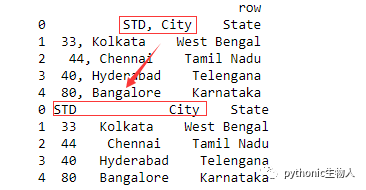
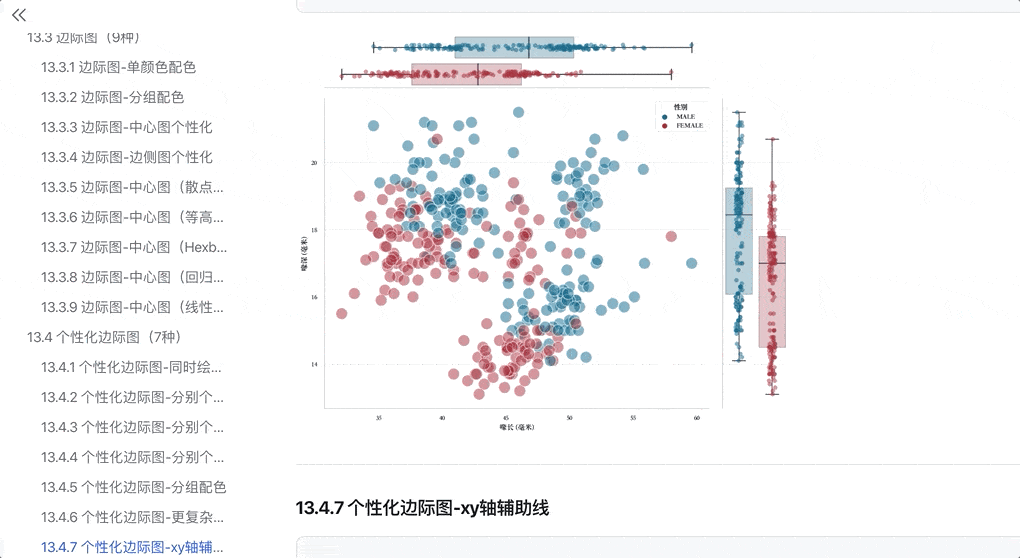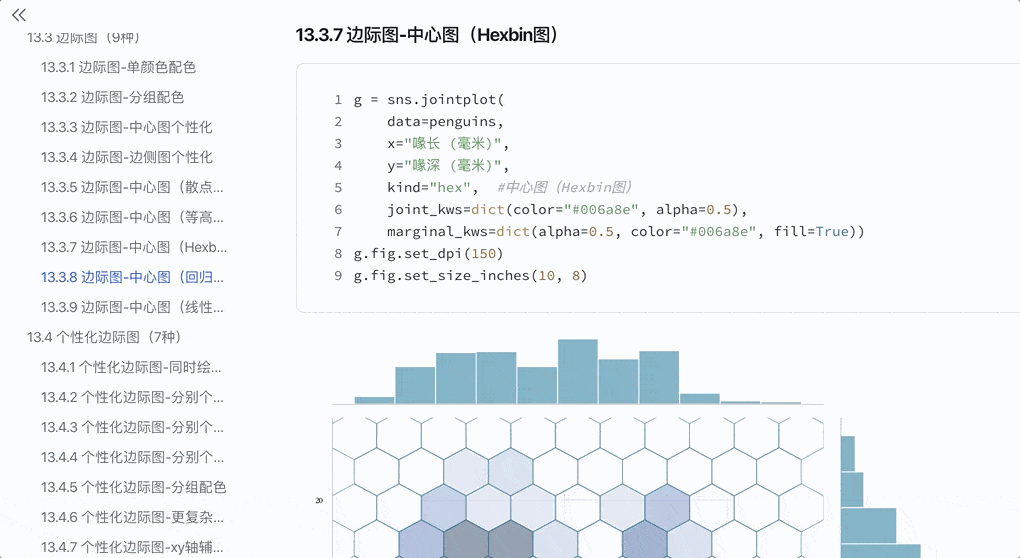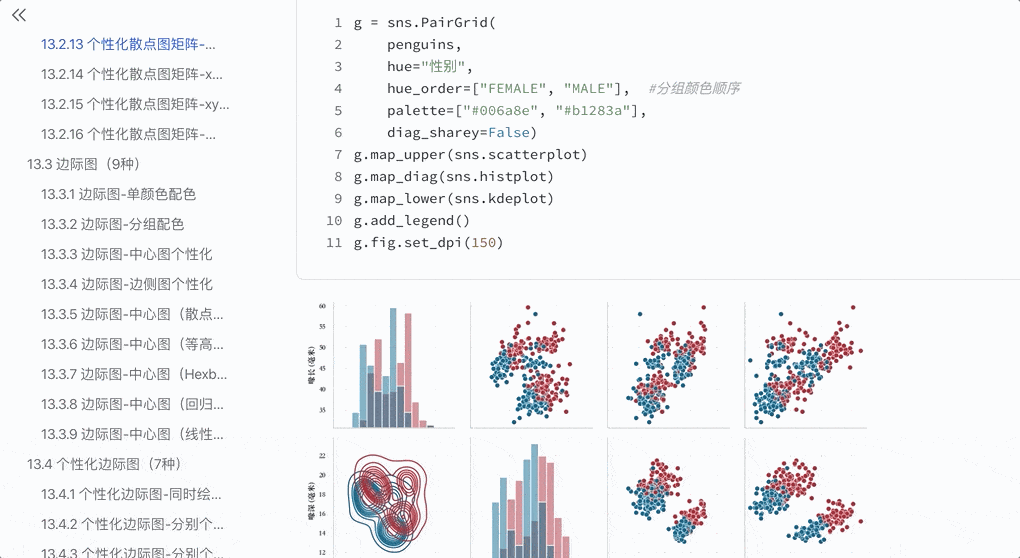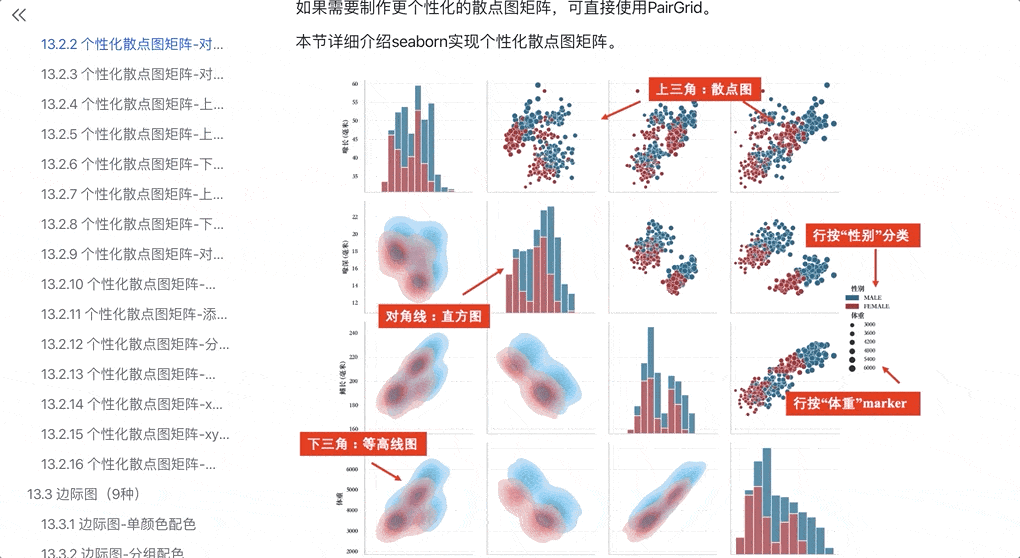
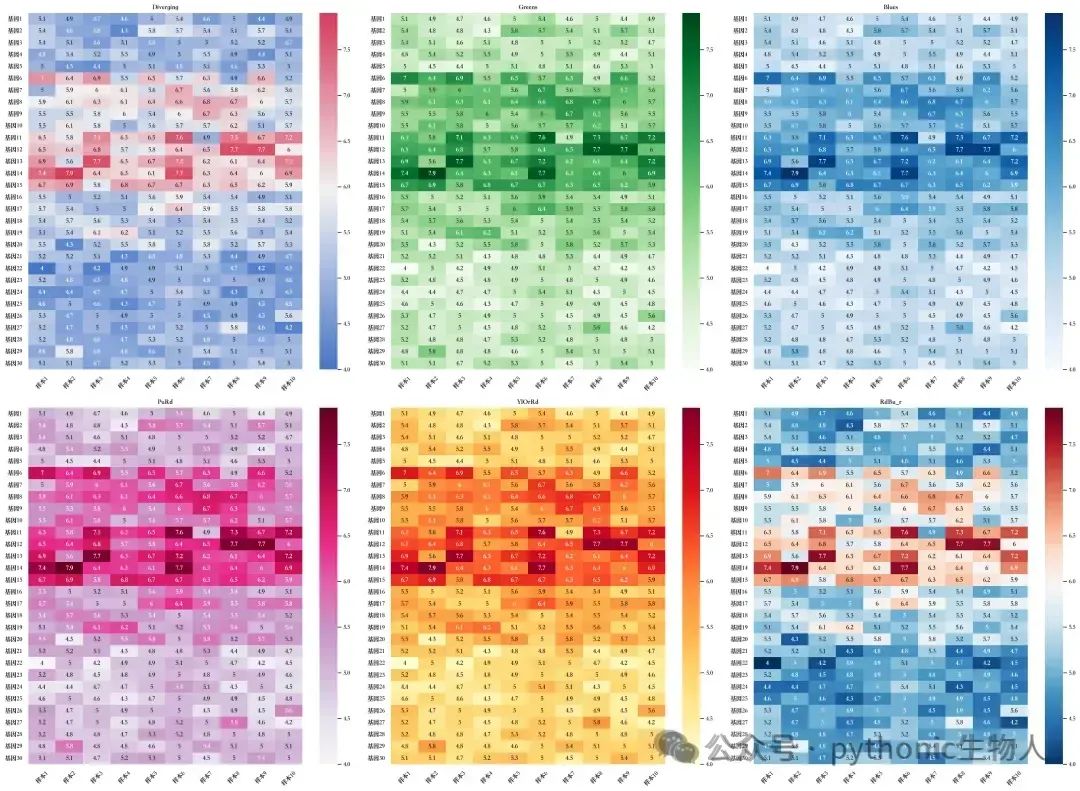
-END-分享一份原创可视化教程:530张图形+8000行代码+详细代码注释+后续免费更新+学习交流群,部分目录,

往期精彩回顾
适合初学者入门人工智能的路线及资料下载(图文+视频)机器学习入门系列下载机器学习及深度学习笔记等资料打印《统计学习方法》的代码复现专辑交流群
欢迎加入机器学习爱好者微信群一起和同行交流,目前有机器学习交流群、博士群、博士申报交流、CV、NLP等微信群,请扫描下面的微信号加群,备注:”昵称-学校/公司-研究方向“,例如:”张小明-浙大-CV“。请按照格式备注,否则不予通过。添加成功后会根据研究方向邀请进入相关微信群。请勿在群内发送广告,否则会请出群,谢谢理解~(也可以加入机器学习交流qq群772479961)






















 315
315

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








