之前一段时间做了一个少数民族语言的文字检测与识别的项目,一共有6种语言,其中的彝语的识别相对简单,部分彝语文档图片如下。由于印刷体版式工整,加之彝语的结构较为简单,遂采取了单字符分割+识别(此算法同样可适用于汉字、韩语、日语等类似结构文字的单字符分割部分)的流程来进行彝语的识别工作。(其实主要还是因为训练样本不够啊,外加甲方希望能得到单字符的坐标,不然直接用CRNN来做序列识别可能会更简单一点,卒。。。)

上图所示为彝语打印文档的一张扫描件示例图。由图可见彝语的结构跟汉字在某些程度上有些相似之处,比如都属于方块字,存在上下结构和左右结构等。由图可发现彝语的识别可以采用单字符分割+识别的方式来进行处理。下面是我对这部分(单字符分割)的处理代码。(此代码经修改后同样可适用于汉字、韩语、日语等类似结构文字的单字符分割部分)
import cv2 # 版本为3.3.10,安装4.0及以上版本可能会不兼容
import os
import numpy as np
def display(img):
cv2.imshow("1", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
def get_split_line(img, projection_row):
split_line_list = []
flag = False
start = 0
end = 0
for i in range(0, len(projection_row)):
if flag == False and projection_row[i] > 0:
flag = True
start = i
elif flag and (projection_row[i] == 0 or i == len(projection_row) - 1):
flag = False
end = i
if end - start < 15: # need specify or rewrite
flag = True
continue
else:
split_line_list.append((start, end))
return split_line_list
def get_contours(img):
contour_list = []
contours = cv2.findContours(img, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for i in range(0, len(contours[1])):
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[1][i])
contour_list.append((x, y, w, h))
# cv2.rectangle(img_input, (x,y), (x+w, y+h), (0,0,255))
return contour_list
def sort_merge(contour_row):
contour_row = sorted(contour_row, key=lambda x: x[0]) # sort by x
# print(contour_row)
i = 0
for _ in contour_row: # 这部分的合并规则用的是刘成林老师paper中的方法
if i == len(contour_row) - 1 or contour_row[i][0] == -1:
break
# print(contour_row[i])
rectR = contour_row[i + 1]
rectL = contour_row[i]
ovlp = rectL[0] + rectL[2] - rectR[0]
dist = abs((rectR[0] + rectR[2] / 2) - (rectL[0] - rectL[2] / 2))
w_L = rectL[0] + rectL[2]
w_R = rectR[0] + rectR[2]
span = (w_R if w_R > w_L else w_L) - rectL[0]
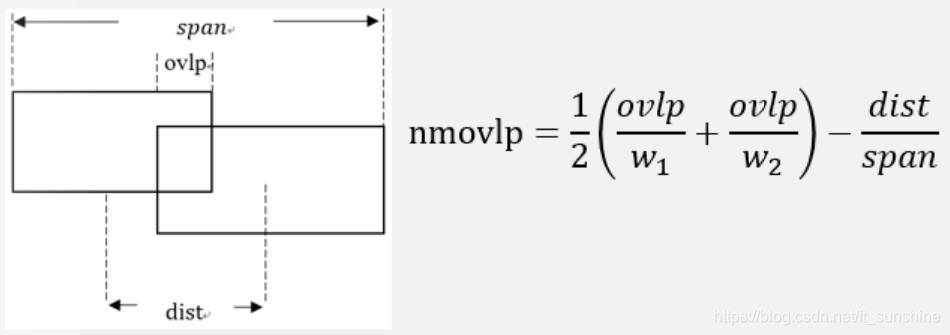
nmovlp = (ovlp / rectL[2] + ovlp / rectR[2]) / 2 - dist / span / 8
if nmovlp > 0:
x = rectL[0]
y = (rectL[1] if rectL[1] < rectR[1] else rectR[1])
w_L = rectL[0] + rectL[2]
w_R = rectR[0] + rectR[2]
w = (w_R if w_R > w_L else w_L) - x
h_L = rectL[1] + rectL[3]
h_R = rectR[1] + rectR[3]
h = (h_R if h_R > h_L else h_L) - y
contour_row[i] = (x, y, w, h)
contour_row.pop(i + 1) # after pop , index at i
contour_row.append((-1, -1, -1, -1)) # add to fix bug(the better way is use iterator)
i -= 1
i += 1
# print(contour_row)
return contour_row
def combine_verticalLine(contour_row):
i = 0
pop_num = 0
for _ in contour_row:
rect = contour_row[i]
if rect[0] == -1:
break
if rect[2] == 0:
i += 1
continue
if rect[3] * 1.0 / rect[2] > 4:
if i != 0 and i != len(contour_row) - 1:
rect_left = contour_row[i - 1]
rect_right = contour_row[i + 1]
left_dis = rect[0] - rect_left[0] - rect_left[2]
right_dis = rect_right[0] - rect[0] - rect[2]
# if left_dis <= right_dis:
if left_dis <= right_dis and rect_left[2] < rect_right[2]:
x = rect_left[0]
y = (rect_left[1] if rect_left[1] < rect[1] else rect[1])
w = rect[0] + rect[2] - rect_left[0]
h_1 = rect_left[1] + rect_left[3]
h_2 = rect[1] + rect[3]
h_ = (h_1 if h_1 > h_2 else h_2)
h = h_ - y
contour_row[i - 1] = (x, y, w, h)
contour_row.pop(i)
contour_row.append((-1, -1, -1, -1))
pop_num += 1
# don't need recursive merge, causing it's left and right merge
else:
x = rect[0]
y = (rect[1] if rect[1] < rect_right[1] else rect_right[1])
w = rect_right[0] + rect_right[2] - rect[0]
h_1 = rect_right[1] + rect_right[3]
h_2 = rect[1] + rect[3]
h_ = (h_1 if h_1 > h_2 else h_2)
h = h_ - y
contour_row[i] = (x, y, w, h)
contour_row.pop(i + 1)
contour_row.append((-1, -1, -1, -1))
pop_num += 1
i += 1
for i in range(0, pop_num):
contour_row.pop()
return contour_row
def split_oversizeWidth(contour_row):
i = 0
for _ in contour_row:
rect = contour_row[i]
if rect[2] * 1.0 / rect[3] > 1.2: # height/width>1.2 -> split
x_new = int(rect[0] + rect[2] / 2 + 1)
y_new = rect[1]
w_new = rect[0] + rect[2] - x_new
h_new = rect[3]
contour_row[i] = (rect[0], rect[1], int(rect[2] / 2), rect[3])
contour_row.insert(i + 1, (x_new, y_new, w_new, h_new))
i += 1
return contour_row
def image_preprocess(img_input):
gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(img_input, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray_img = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray_img, (3, 3), 3)
_, img = cv2.threshold(gray_img, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_OTSU) # 将一幅灰度图二值化 input-one channel
_, img = cv2.threshold(img, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_CROSS, (3, 3))
img = cv2.erode(img, kernel)
# height,width=img.shape[:2]
# img=cv2.resize(img,(int(width/2),int(height/2)),interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
# display(img)
return img
def get_segmentation_result(img): # has been eroded
projection_row = cv2.reduce(img, 1, cv2.REDUCE_SUM, dtype=cv2.CV_32S) # projection
split_line_list = get_split_line(img, projection_row) # split image as row
segmentation_result = []
for i in split_line_list:
img_row = img[i[0]:i[1], :]
contour_row = get_contours(img_row)
contour_row = sort_merge(contour_row)
contour_row = split_oversizeWidth(contour_row)
contour_row = combine_verticalLine(contour_row)
segmentation_result.append(contour_row)
for (x, y, w, h) in contour_row: # draw
y += i[0]
cv2.rectangle(img_input, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 0, 255))
# cv2.imwrite("./test1/n003.jpg",img_input)
return segmentation_result
pic_path = './img003.jpg'
img_input = cv2.imread(pic_path, 1) # (2975, 1787, 3) 但是图片查看器显示的是 1787 * 2975
img = image_preprocess(img_input) # erode
segmentation_result = get_segmentation_result(img) # store segmentation result : [(x,y,w,h),(),...]
# cv2.imwrite("./save.jpg", img_input)
display(img_input)
代码运行结果如下:

此代码经过一定的修改可适用于很多的场景,大家有需要可以尝试一下。
下面大致说一下代码的流程(关注get_segmentation_result部分),字符分割的代码部分主要是采用“投影+连通域”的方式来实现。首先对图像进行二值化与腐蚀(断开印刷过程中可能存在的粘连)的操作,之后对预处理后的图片进行水平投影,得到图片中所有的文本行。然后分别对图片中的每一个文本行进行一系列操作,得到其连通域,然后再对连通域进行合并(合并规则是刘成林老师的一篇paper中的方法,代码中已经注释,具体操作步骤见下图),针对合并错的部分进行切分操作(针对过宽的部分),最后再对没有合并的部分高宽比很大的竖形字符进行单独的合并。进行完上述操作之后,就可以得到不错的分割效果。(具体流程和操作步骤仅供参考)
有问题欢迎多交流,共同进步~
























 3852
3852











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








