【J01】
打印一个整形的32位信息;
/**
*@description: 打印一个整形的所有32位信息。
*@author: YguangY
*@date: 2023/4/4 16:46
**/
public static void print(int num) {
for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.print((num & (1 << i)) == 0 ? "0" : "1");
}
System.out.println();
}
【测试左移后填充】:
[ test01 ]:
//数字1左移后是拿0进行填充的;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int test = 1;
print(test);
print(test<<1); //跑过去之后是拿0填充的
print(test<<2);
print(test<<8);
}
【输出】:

[ test02 ]:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int test = 111111;
print(test);
print(test<<1); //跑过去之后是拿0填充的
print(test<<2);
print(test<<8);
}
//发现———是整体一坨坨移动的。
【输出】:
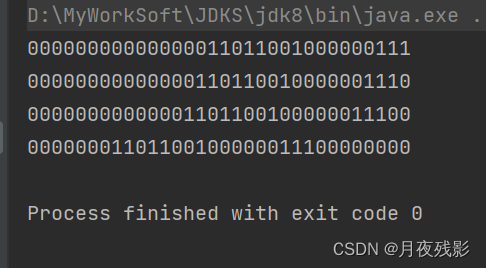
【test03】:
int a = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
System.out.println(a);
print(a);

【发现】:
一个32位整型在系统中,不是全部位数都被占用的!!!最左侧的部分是留着的,真正占用的是从右数的0~30共31个位置;
【test04】:
print(-1);
int a = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
print(a);

【test05】:取反
int b = 123823138;
int c = ~b;
print(b);
print(c);

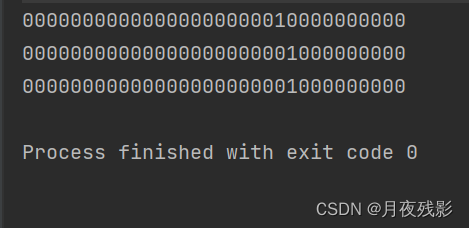
【test06】:右移
int x = 1024;
print(x);
print(x >> 1);
print(x >>> 1);
‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’‘’
int a = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
print(a);
print(a >> 1);
print(a >>> 1);

[test07]:
int c = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int d = -c ;
System.out.println( c );
System.out.println( d );
System.out.println("============================");
print(c);
print(d);

//最小的数取相反数还是它自己。
【J02】:
给定一个参数N , 返回: 1!+2!+3!+4!+ … + N! 的结果。
/**
*@description:
*@author: YguangY
*@date: 2023/4/4 21:29
**/
public static long f2(int N) {
long ans = 0;
long cur = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
cur = cur * i;
ans += cur;
}
return ans;
}
【J03】:
排序经典算法——选择排序;
/**
*@description: 选择排序用到的交换方法;
*@author: YguangY
*@date: 2023/4/5 15:30
**/
public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[i];
arr[i] = tmp;
}
/**
*@description: 选择排序
*@author: YguangY
*@date: 2023/4/5 15:30
**/
public static void selectSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
int N = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int minValueIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < N; j++) {
minValueIndex = arr[j] < arr[minValueIndex] ? j : minValueIndex;
}
swap(arr, i, minValueIndex);
}
}
【J04】:
经典排序算法——冒泡排序;
/**
*@description: 冒泡排序。
*@author: YguangY
*@date: 2023/4/5 15:56
**/
public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
int N = arr.length;
for (int end = N - 1; end >= 0; end--) {
for (int second = 1; second <= end; second++) {
if (arr[second - 1] > arr[second]) {
swap(arr, second - 1, second);
}
}
}
}
/**
*@description: 排序用到的交换方法;
*@author: YguangY
*@date: 2023/4/5 15:30
**/
public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[i];
arr[i] = tmp;
}
【J05】:
经典排序算法——插入排序;
/**
*@description: 插入排序1
*@author: YguangY
*@date: 2023/4/5 16:49
**/
public static void insertSort1(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
int N = arr.length;
for (int end = 1; end < N; end++) {
int newNumIndex = end;
while (newNumIndex - 1 >= 0 && arr[newNumIndex - 1] > arr[newNumIndex]) { //左边有数(防止指针越界) && 左边的数比我大
swap(arr, newNumIndex - 1, newNumIndex);
newNumIndex--;
}
}
}
/**
*@description: 插入排序2————优化的算法
*@author: YguangY
*@date: 2023/4/5 16:49
**/
public static void insertSort2(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
int N = arr.length;
for (int end = 1; end < N; end++) {
//pre是当前的数的前一个位置;
//pre是新数的前一个位置;———新数一开始是在end位置上。
for (int pre = end - 1; pre >= 0 && arr[pre] > arr[pre + 1]; pre--) {
swap(arr, pre, pre + 1);
}
}
}
【J06】:
函数sum( arr , L , R ) 的作用是求数组[L]位置到[R]位置元素的累加和。

请设计两种数据结构,以便令单次查询更加快捷,同时需要满足如下两种情景:
(1):
低频率的查询场景;
(2):
高频率的查询场景(上亿次)。
public static class RangeSum1 {
private int[] arr;
public RangeSum1(int[] array) {
arr = array;
}
public int rangeSum(int L, int R) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = L; i <= R; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
}
public static class RangeSum2 {
private int[] preSum;
public RangeSum2(int[] array) {
int N = array.length;
preSum = new int[N];
preSum[0] = array[0];
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
preSum[i] = preSum[i - 1] + array[i];
}
}
public int rangeSum(int L, int R) {
return L == 0 ? preSum[R] : preSum[R] - preSum[L - 1];
}
}
一种是维护一个矩阵(代码中的RangeSum1 是直接计算L~R,并没有维护矩阵,生成矩阵方法类似,在此不再赘述);
一种是维护一个前缀和数组。
【J07】:研究随机函数
一些对Math.random() 函数的研究;
【test01】:研究概率
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("测试开始");
// Math.random() -> double -> [0,1)
int testTimes = 10000000;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {
if (Math.random() < 0.75) {
count++;
}
}
System.out.println((double) count / (double) testTimes);
System.out.println("=========");
}
【输出】:
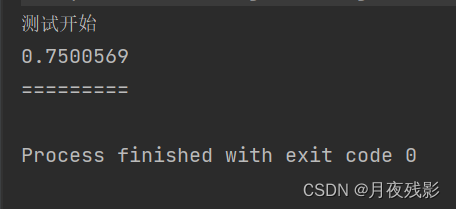
//概率的确非常精准。
【test02】:放缩后当然概率不变了
public static void main(String[] args) {
// [0,1) -> [0,8)
//扩大之后,也是等概率返回的。
int testTimes = 10000000;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {
if (Math.random() * 8 < 5) {
count++;
}
}
System.out.println((double) count / (double) testTimes);
System.out.println((double) 5 / (double) 8);
}

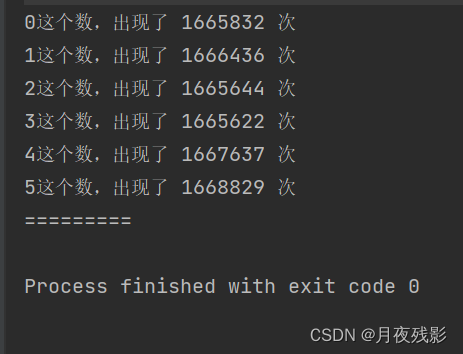
【test03】:放缩后每一个数的概率测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
int testTimes = 10000000;
int K = 10;
// [0,K) -> [0,K-1]
int[] counts = new int[K];
for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {
int ans = (int) (Math.random() * K); // [0,K-1]
counts[ans]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
System.out.println(i + "这个数,出现了 " + counts[i] + " 次");
}
System.out.println("=========");
}

【修改K的值】:
int K = 6;
【test04】:调整出现的概率为平方
[0,x]内的数出现的概率为x , 如何将x变为x的平方呢?
public static void main(String[] args) {
int testTimes = 10000000;
int count = 0;
double x = 0.17;
for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {
if (xToXPower2() < x) {
count++;
}
}
System.out.println((double) count / (double) testTimes);
System.out.println(Math.pow(x,2));
}
// 返回[0,1)的一个小数
// 任意的x,x属于[0,1),[0,x)范围上的数出现概率由原来的x调整成x平方
public static double xToXPower2() {
return Math.max(Math.random(), Math.random());
}
【test05】:调整出现的概率为三次方
[0,x]内的数出现的概率为x , 如何将x变为x的三次方呢?
public static void main(String[] args) {
int testTimes = 10000000;
int count = 0;
double x = 0.3;
for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {
if (xToXPower3() < x) {
count++;
}
}
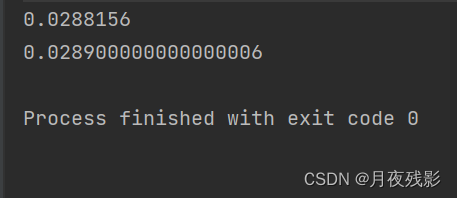
System.out.println((double) count / (double) testTimes);
System.out.println(Math.pow(x,3));
}
// 返回[0,1)的一个小数
// 任意的x,x属于[0,1),[0,x)范围上的数出现概率由原来的x调整成x平方
public static double xToXPower3() {
return Math.max(Math.random(), Math.max( Math.random(),Math.random() ) );
}

【test06】:使用min的话概率如何计算呢?
min ( 事件A , 事件B )
=》

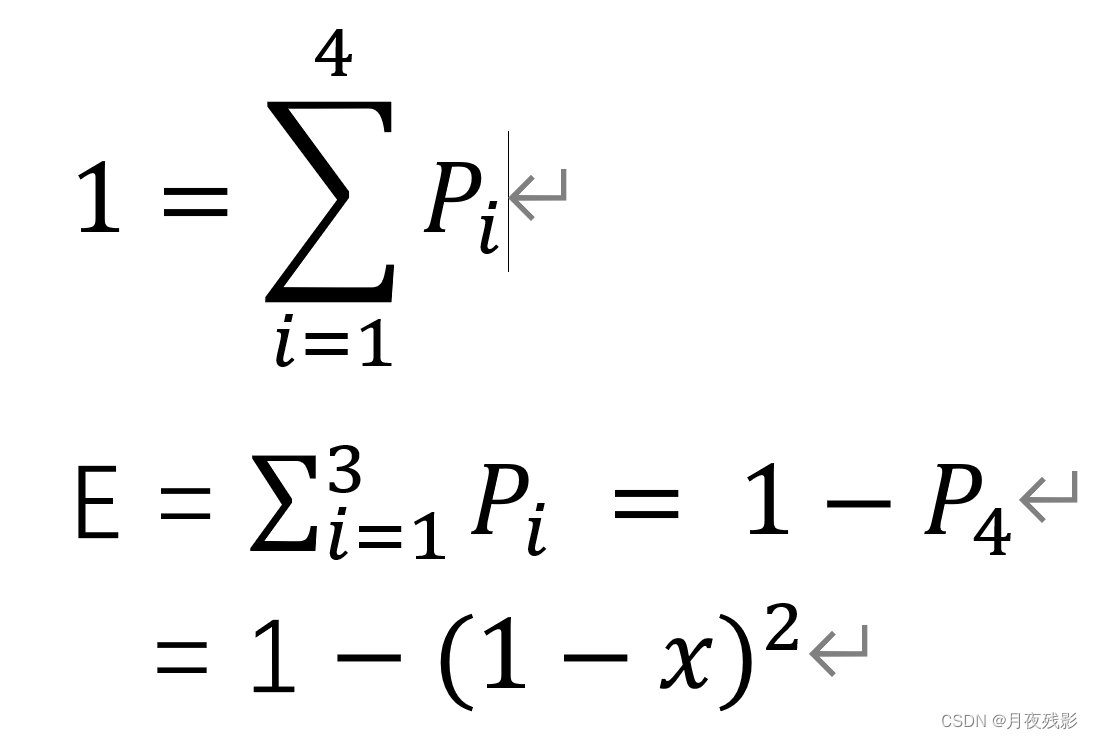
public static void main(String[] args) {
int testTimes = 10000000;
int count = 0;
double x = 0.2;
for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {
if (xToXPower3() < x) {
count++;
}
}
System.out.println((double) count / (double) testTimes);
System.out.println(1-Math.pow(1-x, 2));
}
// 返回[0,1)的一个小数
// 任意的x,x属于[0,1),[0,x)范围上的数出现概率由原来的x调整成x平方
public static double xToXPower3() {
return Math.min( Math.random() , Math.random() );
}

1-(1-0.2)方 ==0.36.
【J08】:
条件函数F()等概率返回 1~5 ;
目标函数G()要求等概率返回 1~7;
【test01】:测试零一发生器的概率
首先改造成零一发生器;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int testTimes = 10000000;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {
if (f2() == 0) {
count++;
}
}
System.out.println((double) count / (double) testTimes);
}
// lib里的,不能改!
// 1~5 里等概率返回一个!!!
public static int f1() {
return (int) (Math.random() * 5) + 1;
}
// 随机机制,只能用f1,
// 等概率返回0和1
public static int f2() {
int ans = 0;
do {
ans = f1();
} while (ans == 3); //f1得到的不是3 , 才能从循环里出来;
return ans < 3 ? 0 : 1;
}

//说明零一发生器改造成功了;
【test02】: 0~7等概率返回
// lib里的,不能改!
// 1~5 里等概率返回一个!!!
public static int f1() {
return (int) (Math.random() * 5) + 1;
}
// 随机机制,只能用f1,
// 等概率返回0和1
public static int f2() {
int ans = 0;
do {
ans = f1();
} while (ans == 3); //f1得到的不是3 , 才能从循环里出来;
return ans < 3 ? 0 : 1;
}
// 得到000 ~ 111 做到等概率 0 ~ 7等概率返回一个
public static int f3() {
return (f2() << 2) + (f2() << 1) + f2();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int testTimes = 10000000;
int[] counts = new int[8];
for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {
int num = f3();
counts[num]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
System.out.println(i + "这个数,出现了 " + counts[i] + " 次");
}
}

【test03】:1~7等概率返回
// lib里的,不能改!
// 1~5 里等概率返回一个!!!
public static int f1() {
return (int) (Math.random() * 5) + 1;
}
// 随机机制,只能用f1,
// 等概率返回0和1
public static int f2() {
int ans = 0;
do {
ans = f1();
} while (ans == 3); //f1得到的不是3 , 才能从循环里出来;
return ans < 3 ? 0 : 1;
}
// 得到000 ~ 111 做到等概率 0 ~ 7等概率返回一个
public static int f3() {
return (f2() << 2) + (f2() << 1) + f2();
}
// 0 ~ 6等概率返回一个
public static int f4() {
int ans = 0;
do {
ans = f3();
} while (ans == 0);
return ans;
}
public static int g() {
return f4() ;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] counts = new int[8];
int testTimes = 10000000;
for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {
int num = g();
counts[num]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
System.out.println(i + "这个数,出现了 " + counts[i] + " 次");
}
}

【test04】:
f()函数是3~19上等概率随机的 , 要求目标函数 g() 在20 ~ 56 上等概率随机;
// 3~19 里等概率返回一个!!!
public static int f1() {
return (int) (Math.random() * 17) + 3;
}
// 等概率返回0和1
public static int f2() {
int ans = 0;
do {
ans = f1();
} while (ans == 11); //f1得到的不是11 , 才能从循环里出来;
return ans < 11 ? 0 : 1;
}
// 得到000000 ~ 111111 做到等概率 0 ~ 63等概率返回一个
public static int f3() {
return (f2()<<5 )+ (f2()<<4) + (f2()<<3) + (f2() << 2) + (f2() << 1) + f2();
}
// 20 ~ 56等概率返回一个
public static int f4() {
int ans = 0;
do {
ans = f3();
} while (ans < 20 || ans > 56);
return ans;
}
public static int g() {
return f4() ;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] counts = new int[100];
int testTimes = 10000000;
for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {
int num = g();
counts[num]++;
}
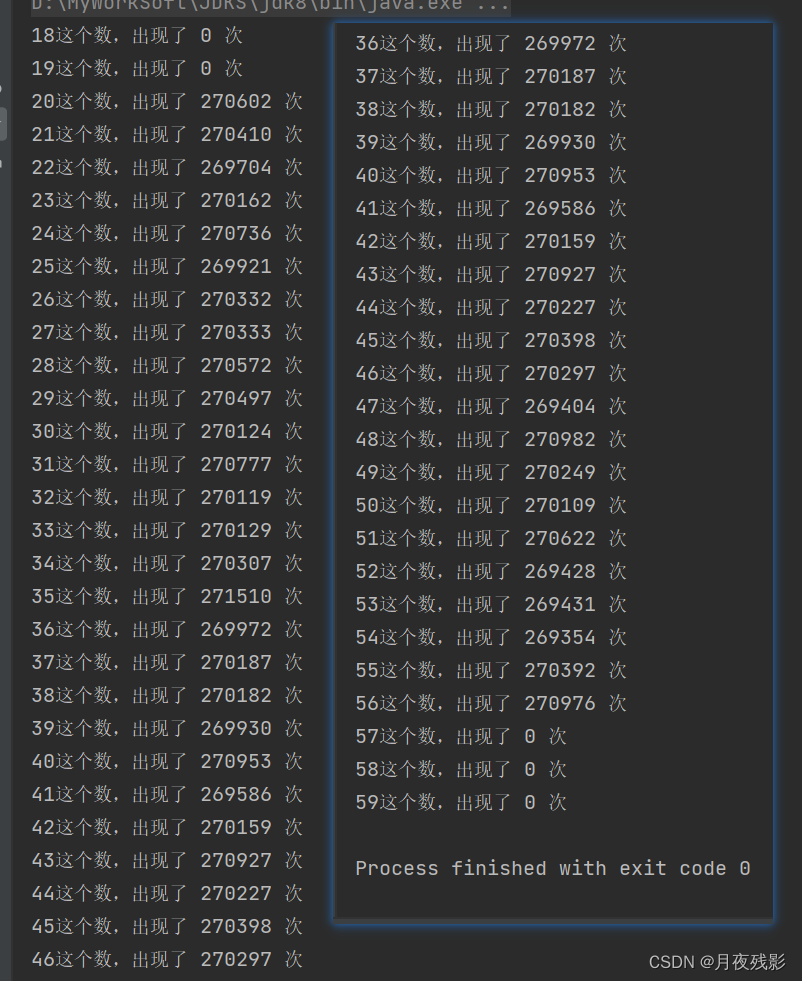
for (int i = 18; i < 60; i++) {
System.out.println(i + "这个数,出现了 " + counts[i] + " 次");
}
}
【J09】:
f()函数得到0的概率是P , 得到1的概率是(1-P) , 即只返回0和1 , 但是是不等概率的;
g()函数是目标函数,现在要求目标函数要等概率返回0和1;
// 你只能知道,x会以固定概率返回0和1,但是x的内容,你看不到!
public static int x() {
return Math.random() < 0.84 ? 0 : 1;
}
// 等概率返回0和1
public static int y() {
int ans = 0;
do {
ans = x();
} while (ans == x()); //在这个地方又调用了生成器!!!
//即———第一次等于第二次的话,直接重做~ ~ ~ ! ! !
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
int b =y();
arr[b]++;
}
System.out.println(arr[0]);
System.out.println(arr[1]);
System.out.println(arr[2]);
System.out.println(arr[3]);
}

【J10】:
对数器;
//使用对数器验证——选择排序、插入排序是否正确。
public static void selectionSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
swap(arr, i, minIndex);
}
}
public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
public static void insertionSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) { // 0 ~ i 做到有序
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0 && arr[j] > arr[j + 1]; j--) {
swap(arr, j, j + 1);
}
}
}
/**
* @description: 长度随机,内容随机的数组。
* @author: YguangY
* @date: 2023/4/7 10:23
**/
// 返回一个数组arr,arr长度[0,maxLen-1],arr中的每个值[0,maxValue-1]
public static int[] lenRandomValueRandom(int maxLen, int maxValue) {
int len = (int) (Math.random() * maxLen);
int[] ans = new int[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
ans[i] = (int) (Math.random() * maxValue);
}
return ans;
}
public static int[] copyArray(int[] arr) {
int[] ans = new int[arr.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
ans[i] = arr[i];
}
return ans;
}
// arr1和arr2一定等长
public static boolean isSorted(int[] arr) {
if (arr.length < 2) {
return true;
}
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (max > arr[i]) { //一直递增才是有序的!!!
return false;
}
max = Math.max(max, arr[i]);
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int maxLen = 5;
int maxValue = 1000;
int testTime = 10000;
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
int[] arr1 = lenRandomValueRandom(maxLen, maxValue);
int[] tmp = copyArray(arr1);
selectionSort(arr1);
insertionSort(tmp);
if (!isSorted(arr1)) {
System.out.println("选择排序错了!");
//也可以在此处进行BUG的定位~~~
}
if (!isSorted(tmp)) {
System.out.println("插入排序错了");
//也可以在此处进行BUG的定位~~~
}
}
}








 该文展示了Java中关于整型的位操作,包括打印32位二进制、左移、右移、取反等,并探讨了整型的表示范围。此外,文章还详细介绍了几种经典的排序算法实现,如选择排序、插入排序和冒泡排序。同时,讨论了如何优化范围求和查询以及随机函数的使用,包括概率分布的验证和调整概率的方法。
该文展示了Java中关于整型的位操作,包括打印32位二进制、左移、右移、取反等,并探讨了整型的表示范围。此外,文章还详细介绍了几种经典的排序算法实现,如选择排序、插入排序和冒泡排序。同时,讨论了如何优化范围求和查询以及随机函数的使用,包括概率分布的验证和调整概率的方法。
















 839
839

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








