本篇博客用来记录Coursera上的一门课程——Malicious Software and its Underground Economy。
第一周
-Admin blabbing (泄露)
- Most security threats start from the web
- A malicious web page leverages a defect in a program to gain arbitrary code execution
- The exploit downloads and installs a malware sample, that infects the victim
-Malicious Software
(Malware) refers to any unwanted software and executable code that is used to perform an unauthorized, often harmful, action on a computing device. It is an umbrella-term for various types of harmful software, including viruses, worms, Trojans (特洛伊木马), rootkits (隐匿技术), and botnets (僵尸网络).
Means of Distribution
| Means | Requires Host | Runs Independently |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Spreading | Virus | Worm |
| Non-Spreading | Root-kit; Trojan horse | Dialer; Spyware; Keylogger |
- Virus
- Self-replicating
Needs a host to infect
- Boot (Brain virus), overwrite, parasitic (寄生的), cavity (腔,洞), entry point obfuscation (迷惑), code integration (W95/Zmist virus)
-Worm
- Self-replication, spreads (autonomously) over network
- Exploits vulnerabilities affecting a large number of hosts
- Sends itself via email
- e.g., Internet worm, Netsky, Sobig, Code Red, Blaster, Slammer
-Trojan horse
- Malicious program disguised as a legitimate software
- Many different malicious actions
- Spy on sensitive user data
- Hide presence (e.g., root-kit)
- Allow remote access (e.g., Back Orifice (孔), NetBus)
-Root-kit
- Used to keep access to a compromised system
- Usually hides files, processes, network connections
- User- and kernel-level
The number of Fake AV (anti-virus) is also huge.
-Malicious Software (PART 2)
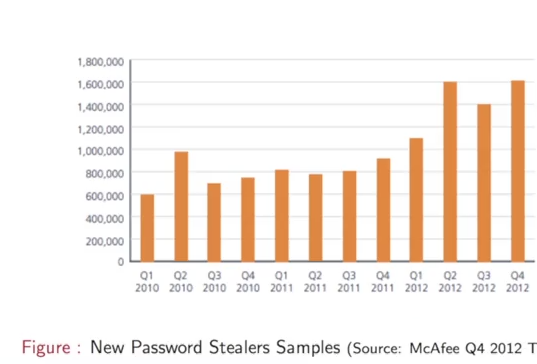
图中可以看出,new password stealers samples 逐年增长。另外,total malicious signed binaries也在增长。
Fight Malware: the Foremost (最重要的) Goals
- Understand malware behaviors
- to (automatically) identify and classify families of malware
- (to) automatically generate effective malware detection models
- Collect malware samples
- How about infection (传染) strategies?
- Analyze samples
- Static analysis
- studying a program’s properties without executing it
- reverse engineering may be hampered 阻碍 (e.g., obfuscation, encryption)
- Dynamic analysis
- studying a program’s properties by executing it
- environment-limited analysis
- Static analysis
- Extract (and generalize) malicious behavior
- Host
- Network
- Generate and deploy detection models
Problems Hard
- Lack of general definition of malicious behavior
- Cat-and-mouse game: attackers have much freedom
- Victims often (unwittingly) help attackers
-Botnets
Bot
- Autonomous programs performing tasks
- More recent trend in malicious development
Benign bots
- First bots were programs used for Internet Relay Chat (IRC) 多人在线交谈
- React to events in IRC channels
- Typically offer useful services
Early definition of bot
An IRC user who is actually a program. On IRC, typically the robot provides some useful service. Examples are NickServ, which tires to prevent random users from adopting nicks already clamed by others.
Eggdrop bot (1993)
- used to manage IRC chat channels when the operator was away
- malicous IRC bots started to evolve
- takeover wars to control certain IRC channels
- trash talking (flooding)
- also involved in Denial of Service (DoS) 拒绝服务 to force IRC net split
- IRC proxies to hide attackers’ origin
- a number of parallel, malicious developments
How did we get here?
- Early 1990s. IRC bots
- automated management of IRC channels
- 1990-2000: Distributed DoS tools (distribution)
- Trinoo. TFN2k, Stacheldraht
- 1998-2000: Trojan Horse (remote control)
- BackOrifice, BackOrifice2k, SubSeven
- 2001-today: Worms (spreading)
- Code Red, Blaster, Sasser








 本文档概述了Coursera课程《恶意软件及其地下经济》的内容,包括恶意软件的种类,如病毒、蠕虫、特洛伊木马和根套件,并探讨了它们的传播方式、恶意行为和防御策略。特别提到了botnets的演变、控制机制以及检测方法,如网络行为建模和rootkit隐藏技术。
本文档概述了Coursera课程《恶意软件及其地下经济》的内容,包括恶意软件的种类,如病毒、蠕虫、特洛伊木马和根套件,并探讨了它们的传播方式、恶意行为和防御策略。特别提到了botnets的演变、控制机制以及检测方法,如网络行为建模和rootkit隐藏技术。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 2624
2624

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








