一 Widget Element RenderObject 之间的关系
1 Widget
在Flutter 中,万物皆是Widget,无论是可见的还是功能型的。一切都是Widget.
官方文档中说的Widget 使用配置和状态来描述View 界面应该长什么样子。
它不仅可以表示UI元素,也可以表示一些功能性的组件如:用于手势检测的 GestureDetector、用于APP主题数据传递的Theme、布局元素等等
两个重要的方法
一个是通过 createElement 来创建 Element 对象的,
一个是根据 key 来决定更新行为的 canUpdate 方法。
在这个方法中会对比runtimeType (也就是widget 的类型)和 key 是否相同
@immutable
abstract class Widget extends DiagnosticableTree {
/// Initializes [key] for subclasses.
const Widget({this.key});
final Key? key;
@protected
@factory
Element createElement();
/// A short, textual description of this widget.
@override
String toStringShort() {
final String type = objectRuntimeType(this, 'Widget');
return key == null ? type : '$type-$key';
}
@override
void debugFillProperties(DiagnosticPropertiesBuilder properties) {
super.debugFillProperties(properties);
properties.defaultDiagnosticsTreeStyle = DiagnosticsTreeStyle.dense;
}
@override
@nonVirtual
bool operator ==(Object other) => super == other;
@override
@nonVirtual
int get hashCode => super.hashCode;
static bool canUpdate(Widget oldWidget, Widget newWidget) {
return oldWidget.runtimeType == newWidget.runtimeType &&
oldWidget.key == newWidget.key;
}
// Return a numeric encoding of the specific `Widget` concrete subtype.
// This is used in `Element.updateChild` to determine if a hot reload modified the
// superclass of a mounted element's configuration. The encoding of each `Widget`
// must match the corresponding `Element` encoding in `Element._debugConcreteSubtype`.
static int _debugConcreteSubtype(Widget widget) {
return widget is StatefulWidget
? 1
: widget is StatelessWidget
? 2
: 0;
}
}2 Element
Element 就是一个Widget 的实例,在树中详细的位置。
An instantiation of a Widget at a particular location in the tree
3 RenderObject
渲染树上的一个对象。负责具体布局和绘制这些事情。
4 结合图说一下其三者的关系
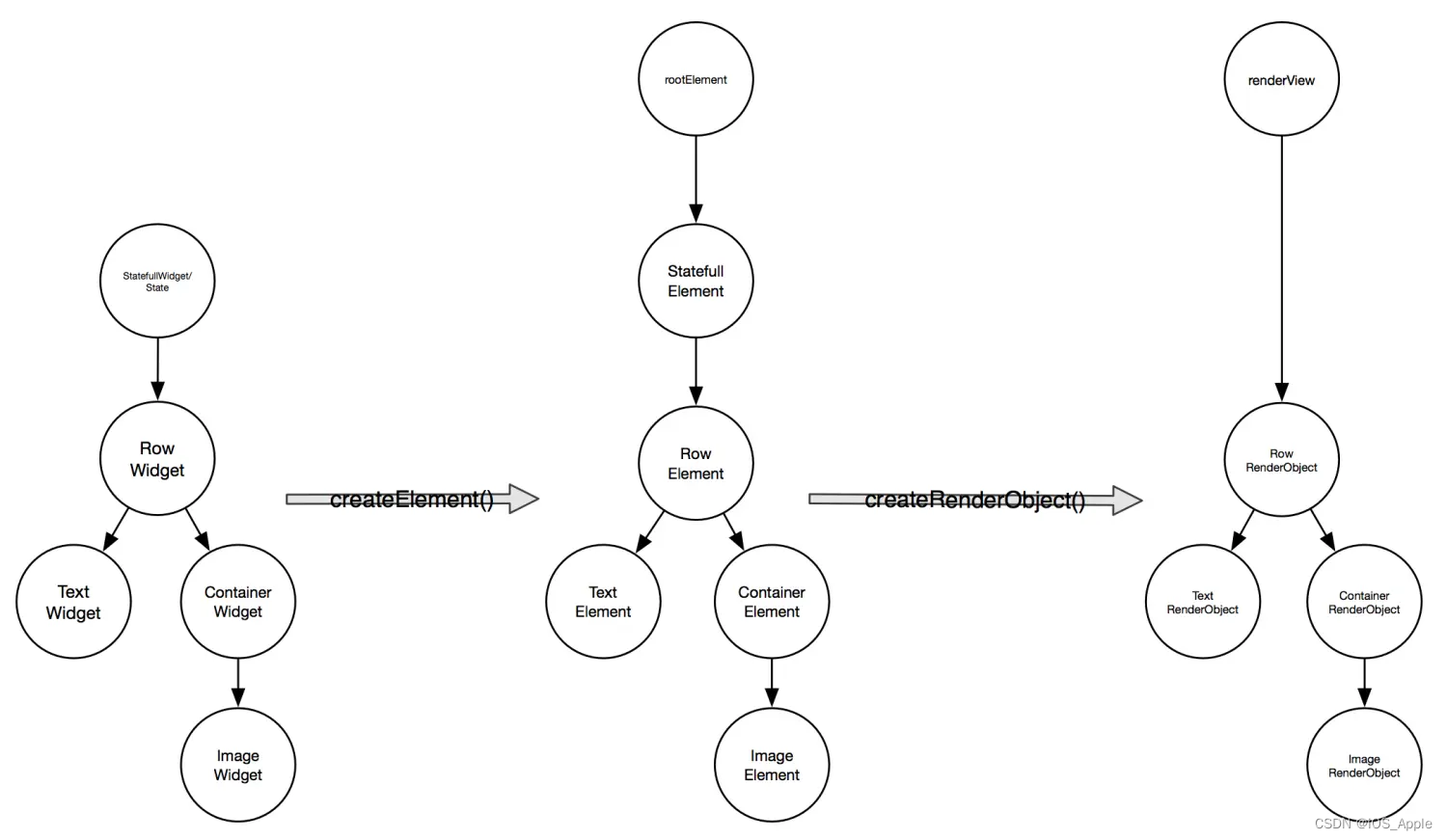
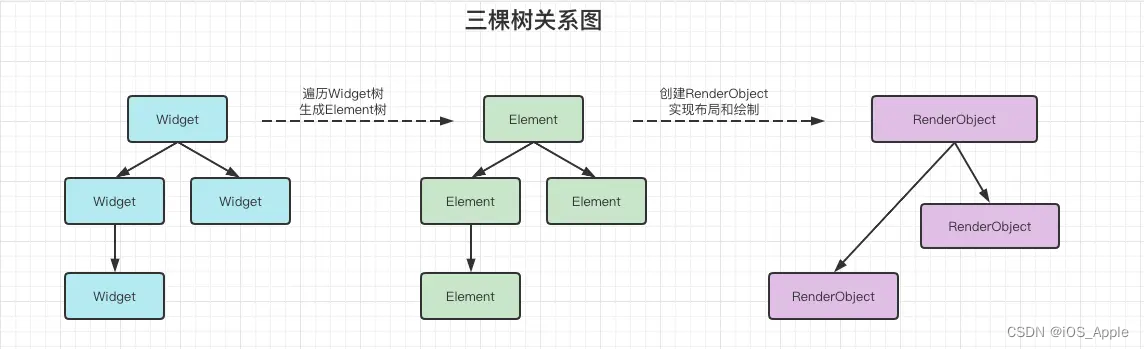
从创建到渲染的流程 :
根据Widget 生成Element,然后创建响应的RenderObject并且关联到Element.renderObject 属性。最后再通过RenderObject 来完成布局和绘制。
依赖关系:
Element 树根据Widget 树生成,而渲染树又依赖于widget 树。
5 一些小问题?
5.1 widget 和 element 是一一对应的吗 ? 为什么 ?
答:是一一对应的。
因为 abstract class Widget ,本身是一个抽象类,这个抽象类中有一个抽象方法叫做createElement(),子类必须实现这个抽象方法,所以是一一对应的。
5.2 widget 和 renderObject 是一一对应的吗 ? 为什么 ?
答:不是的
因为只有这个widget 继承自RenderObjectWidget 的时候,才会有对应的renderObject
像类似 Padding , Row,SizedBox,Center 这种组件继承自RenderObjectWidget的组件会有一一对应的关系
//class Padding extends SingleChildRenderObjectWidget
// Padding();
// class Flex extends MultiChildRenderObjectWidget
// Row()5.3 BuildContext 是什么 ?
答:是Element,不管是StatefulWidget 还是StatelessWidget 都会重写父类的build 方法,
build 方法传入的一个参数叫做BuildContext, 我们拿StatelessWidget来说,其本身创建一个StatelessElement,而在这个Element内部重写StatelessElement父类的build方法,而在这个build方法内部会调用_widget.build 方法,并且把this传递进去。那么这个this 就是element 。
/// An [Element] that uses a [StatelessWidget] as its configuration.
class StatelessElement extends ComponentElement {
/// Creates an element that uses the given widget as its configuration.
StatelessElement(StatelessWidget super.widget);
@override
Widget build() => (widget as StatelessWidget).build(this);
@override
void update(StatelessWidget newWidget) {
super.update(newWidget);
assert(widget == newWidget);
_dirty = true;
rebuild();
}
}
5.4 Widget 频繁更改创建是否会影响性能?复用和更新机制是什么样的?
不会影响性能,因为只是一些配置信息,没有有布局渲染到页面上去。中间层Element 会通过widget 的runtimeType 和 Key 来对比是否进行更新操作。
5.5 Build 方法会在什么时候调用 ?
Element 创建完毕之后会调用mount 方法,对于非渲染的ComponentElement 来说,mount主要执行的是Widget 中的build 方法。在StatelessElement 中直接使用的是 widget.build(this),
而在StatefullWidget 方法中,通过的是state.build(this)。在StatefulElement 这个类中,
初始化列表的给state 进行了赋值操作。通过widget调用createState方法之后,把state赋值给自己的_state 属性。
StatefulElement(StatefulWidget widget)
: _state = widget.createState(),
5.6 createState 方法什么时候调用?
答:创建Element 的时候。
Flutter 会在遍历 Widget 树时调用 Widget 里面的 createElement 方法去生成对应节点的 Element 对象,同时执行 StatefulWidget 里面的 createState 方法创建 state,并且赋值给 Element 里的 _state 属性,当前 widget 也同时赋值给了 state 里的_widget,state 里面有个 widget 的get 方法可以获取到 _widget 对象。






















 841
841











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








